
私は最近、仕事を探したり、上司の会社のプロジェクトの世話をしたりするために外出しなければならず、とても忙しいです。今日は会社で、忙しいスケジュールの合間を縫って、.NET での非同期呼び出し関数の実装方法をまとめました。この記事を書き始める前に、DebugLZQ がこの記事のサンプル コードをすべて書きました。 , コードで説得力を持って話すことができます。
この記事の目的は、最も簡潔なコードを使用して非同期呼び出しメソッドを明確に説明することです。それが気に入らない場合は、文句を言わないでください。邪魔しないでください~
lz さんの前回の記事は、単にそれを述べたものです。 次に、非同期を理解するという観点から、この記事は主に具体的な実装方法について書きます。非同期プログラミングを実装するには 4 つの方法から選択できます。これらの 4 種類のリクエストは、実際には 4 つの非同期呼び出しモードに対応しており、「待機」と「コールバック」の 2 つのカテゴリに分類されます。 4 つのメソッドのコードに詳細なコメントを付けましたので、ここでは詳しく説明しません。最初のメソッドである BeginEnvoke EndEnvoke メソッドは、「wait」クラスに属します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 异步调用实现方法汇总
{
/// <summary>
/// 异步调用方法总结:
/// 1.BeginEnvoke EndEnvoke
/// 当使用BeginInvoke异步调用方法时,如果方法未执行完,EndInvoke方法就会一直阻塞,直到被调用的方法执行完毕
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
Console.WriteLine("主线程");
IAsyncResult result= printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello World.", null, null);
Console.WriteLine("主线程继续执行...");
//当使用BeginInvoke异步调用方法时,如果方法未执行完,EndInvoke方法就会一直阻塞,直到被调用的方法执行完毕
printDelegate.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("异步线程开始执行:"+s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
}
注意が必要な点はコード内に記載されています。 プログラムの実行結果は次のとおりです。
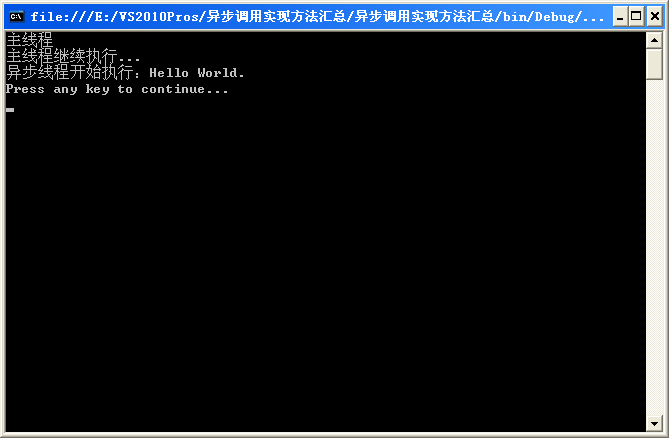 2 番目のメソッド: WaitOne。こちらも「待機中」カテゴリに属します。
2 番目のメソッド: WaitOne。こちらも「待機中」カテゴリに属します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 异步调用实现方法汇总2
{
/// <summary>
/// 异步调用方法总结:
/// 2.WaitOne
/// 可以看到,与EndInvoke类似,只是用WaitOne函数代码了EndInvoke而已。
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
Console.WriteLine("主线程");
IAsyncResult result = printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello World.", null, null);
Console.WriteLine("主线程继续执行...");
result.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(-1, false);
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("异步线程开始执行:" + s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
}
注意が必要な点はコード内に記載されています。 プログラムの実行結果は次のとおりです。
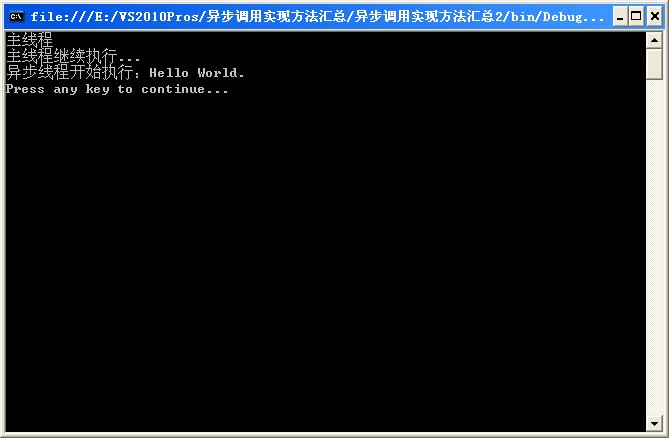 3 番目の方法: ポーリング。これも「待機」カテゴリに属します。
3 番目の方法: ポーリング。これも「待機」カテゴリに属します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 异步调用实现方法汇总3
{
/// <summary>
/// 异步调用方法总结:
/// 3.轮询
/// 之前提到的两种方法,只能等下异步方法执行完毕,
/// 在完毕之前没有任何提示信息,整个程序就像没有响应一样,用户体验不好,
/// 可以通过检查IasyncResult类型的IsCompleted属性来检查异步调用是否完成,
/// 如果没有完成,则可以适时地显示一些提示信息
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
Console.WriteLine("主线程:"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId );
IAsyncResult result = printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello world.", null, null);
Console.WriteLine("主线程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId + ",继续执行...");
while (!result.IsCompleted)
{
Console.WriteLine(".");
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
Console.WriteLine("主线程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId + " Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("当前线程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId + s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
}
注意が必要な点はコード内に記載されています。 プログラムの実行結果は次のとおりです。
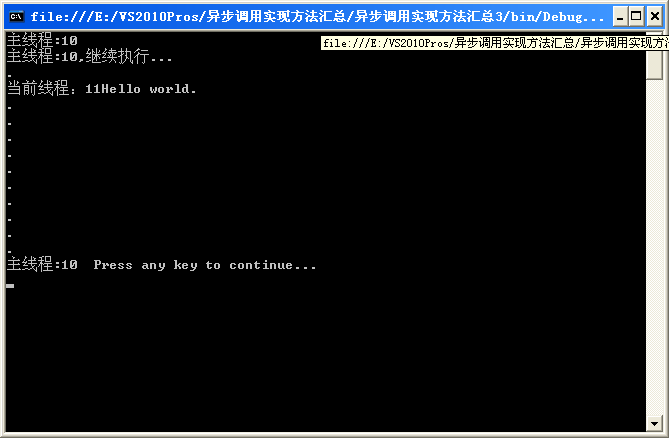 4 番目のメソッド: コールバック。間違いなく「コールバック」カテゴリに分類されます。推薦する! ! ! !
4 番目のメソッド: コールバック。間違いなく「コールバック」カテゴリに分類されます。推薦する! ! ! !
前の 3 つのメソッドは、非同期メソッドが完了するまで待機した後でのみ実行結果を取得できます。その間、メインスレッドは待機状態になります。コールバックとそれらの最大の違いは、BeginInvoke を呼び出すときにコールバック メソッドが提供されている限り、メイン スレッドは非同期スレッドが作業を完了するのを待つ必要がなく、非同期スレッドは提供されたコールバック メソッドを積極的に呼び出します。作業が完了したら、コールバック メソッドで適切な処理を実行します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 异步调用实现方法汇总4
{
/// <summary>
/// 异步调用方法总结:
/// 4.回调
/// 之前三种方法者在等待异步方法执行完毕后才能拿到执行的结果,期间主线程均处于等待状态。
/// 回调和它们最大的区别是,在调用BeginInvoke时只要提供了回调方法,那么主线程就不必要再等待异步线程工作完毕,
/// 异步线程在工作结束后会主动调用我们提供的回调方法,并在回调方法中做相应的处理,例如显示异步调用的结果。
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
Console.WriteLine("主线程.");
printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello world.", PrintComeplete, printDelegate);
Console.WriteLine("主线程继续执行...");
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("当前线程:"+s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
//回调方法要求
//1.返回类型为void
//2.只有一个参数IAsyncResult
public static void PrintComeplete(IAsyncResult result)
{
(result.AsyncState as PrintDelegate).EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("当前线程结束." + result.AsyncState.ToString());
}
}
}
注意が必要な点をコード内に記載します。 プログラムの実行結果は次のとおりです。
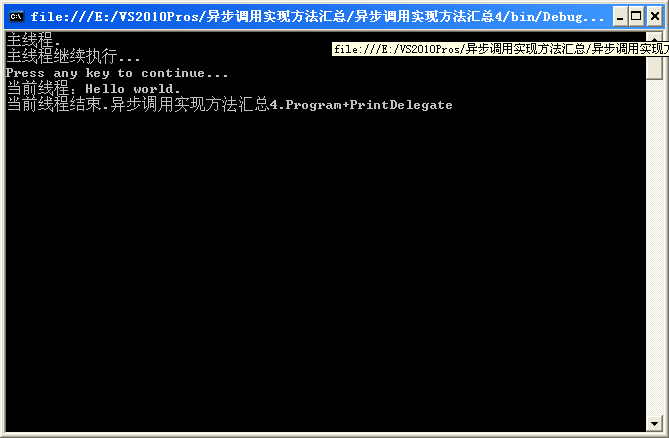 EndInvoke メソッドを通じて同期関数の戻り値を取得します。上記の同期メソッドの戻り値は void です。例を示します。
EndInvoke メソッドを通じて同期関数の戻り値を取得します。上記の同期メソッドの戻り値は void です。例を示します。
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows;
namespace TestDelegateWrapper
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void ButtonBase_OnClick(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
WrapperSyncMethodAsync("ABC");
Trace.WriteLine("Main thread continue...");
}
private delegate string SyncMethod1Delegate(string str);
private void WrapperSyncMethodAsync(string str)
{
SyncMethod1Delegate syncMethod1Delegate = SyncMethod1;
syncMethod1Delegate.BeginInvoke(str, x =>
{
var result= syncMethod1Delegate.EndInvoke(x);
// using the result to do something
Trace.WriteLine(result);
}, null);
}
private string SyncMethod1(string str)
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return str;
}
}
}
出力は次のとおりです:
Main thread continue...
ABC
上記は、非同期を実装する 4 つの方法です。関数の呼び出しは非常に明確です