
この記事の著者: Xiaozhuzz ブログアドレス: http://www.php.cn/ 転載の際は出典を明記してください
パフォーマンス ソケット クライアントの端末コード。以前は、Socket クラスを使用して、従来の非同期プログラミング モデル (BeginSend、BeginReceive など) に基づいたコードを作成し、ブログで多くの知識を読みました。Linux と Windows には、poll と epoll が実装されています。
Microsoft MSDN も IOCP を実装するために SocketAsyncEventArgs クラスが提供されています。アドレス: http://www.php.cn/
NET Framework の APM は Begin/End モードとも呼ばれます。これは、非同期操作を開始するために Begin メソッドが呼び出され、その後 IAsyncResult オブジェクトが返されるためです。オプションで、非同期操作の完了時に呼び出される Begin メソッドのパラメーターとしてプロキシを指定できます。あるいは、スレッドは IAsyncResult.AsyncWaitHandle で待機することもできます。コールバックが呼び出されるか、待機信号が発行されると、End メソッドが呼び出され、非同期操作の結果を取得します。このパターンは柔軟性があり、比較的簡単に使用でき、.NET Framework では非常に一般的です。
ただし、非同期ソケット操作を大量に行う場合は、代償を払う必要があることに注意する必要があります。操作ごとに IAsyncResult オブジェクトを作成する必要があり、このオブジェクトは再利用できません。これは、オブジェクト割り当てとガベージ コレクションを頻繁に使用するため、パフォーマンスに影響します。この問題を解決するために、新しいバージョンでは、ソケットを使用して非同期 I/O を実行する別のメソッド パターンが提供されます。この新しいモデルでは、ソケット操作ごとに操作コンテキスト オブジェクトを割り当てる必要はありません。
コードのダウンロード: http://www.php.cn/ ここのコードは
に最適化されています。上記のMicrosoftが提供するサンプルはあまり完全ではないと思います。特定のプロセスはありません。クライアントメッセージを受信した後、同じ内容がクライアントに提供されます。完全に機能する IOCP サーバーを実装するのに 1 日を費やしたため、その効果は次のとおりです。コード
1 つ目は ICOPServer.cs クラスです。これは IOCP サーバーのコア クラスです。現在、このクラスはインターネット上で比較的完全なコードです。
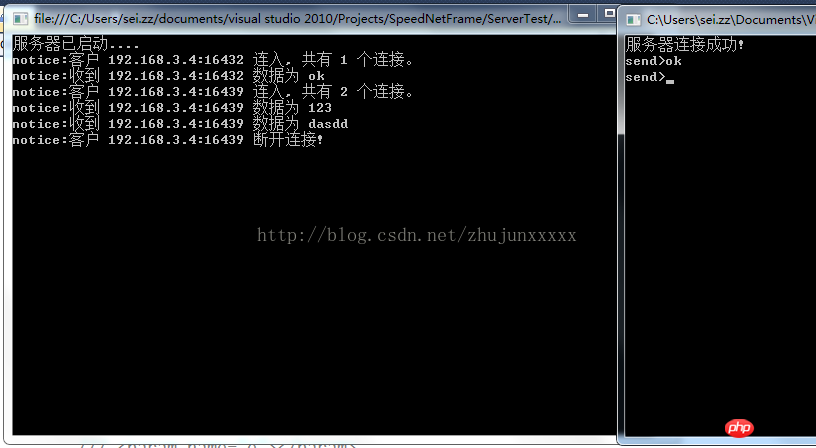
サーバー側
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Net;
using System.Threading;
namespace ServerTest
{
/// <summary>
/// IOCP SOCKET服务器
/// </summary>
public class IOCPServer : IDisposable
{
const int opsToPreAlloc = 2;
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// 服务器程序允许的最大客户端连接数
/// </summary>
private int _maxClient;
/// <summary>
/// 监听Socket,用于接受客户端的连接请求
/// </summary>
private Socket _serverSock;
/// <summary>
/// 当前的连接的客户端数
/// </summary>
private int _clientCount;
/// <summary>
/// 用于每个I/O Socket操作的缓冲区大小
/// </summary>
private int _bufferSize = 1024;
/// <summary>
/// 信号量
/// </summary>
Semaphore _maxAcceptedClients;
/// <summary>
/// 缓冲区管理
/// </summary>
BufferManager _bufferManager;
/// <summary>
/// 对象池
/// </summary>
SocketAsyncEventArgsPool _objectPool;
private bool disposed = false;
#endregion
#region Properties
/// <summary>
/// 服务器是否正在运行
/// </summary>
public bool IsRunning { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// 监听的IP地址
/// </summary>
public IPAddress Address { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// 监听的端口
/// </summary>
public int Port { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// 通信使用的编码
/// </summary>
public Encoding Encoding { get; set; }
#endregion
#region Ctors
/// <summary>
/// 异步IOCP SOCKET服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="listenPort">监听的端口</param>
/// <param name="maxClient">最大的客户端数量</param>
public IOCPServer(int listenPort,int maxClient)
: this(IPAddress.Any, listenPort, maxClient)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 异步Socket TCP服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="localEP">监听的终结点</param>
/// <param name="maxClient">最大客户端数量</param>
public IOCPServer(IPEndPoint localEP, int maxClient)
: this(localEP.Address, localEP.Port,maxClient)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 异步Socket TCP服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="localIPAddress">监听的IP地址</param>
/// <param name="listenPort">监听的端口</param>
/// <param name="maxClient">最大客户端数量</param>
public IOCPServer(IPAddress localIPAddress, int listenPort, int maxClient)
{
this.Address = localIPAddress;
this.Port = listenPort;
this.Encoding = Encoding.Default;
_maxClient = maxClient;
_serverSock = new Socket(localIPAddress.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
_bufferManager = new BufferManager(_bufferSize * _maxClient * opsToPreAlloc,_bufferSize);
_objectPool = new SocketAsyncEventArgsPool(_maxClient);
_maxAcceptedClients = new Semaphore(_maxClient, _maxClient);
}
#endregion
#region 初始化
/// <summary>
/// 初始化函数
/// </summary>
public void Init()
{
// Allocates one large byte buffer which all I/O operations use a piece of. This gaurds
// against memory fragmentation
_bufferManager.InitBuffer();
// preallocate pool of SocketAsyncEventArgs objects
SocketAsyncEventArgs readWriteEventArg;
for (int i = 0; i < _maxClient; i++)
{
//Pre-allocate a set of reusable SocketAsyncEventArgs
readWriteEventArg = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
readWriteEventArg.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnIOCompleted);
readWriteEventArg.UserToken = null;
// assign a byte buffer from the buffer pool to the SocketAsyncEventArg object
_bufferManager.SetBuffer(readWriteEventArg);
// add SocketAsyncEventArg to the pool
_objectPool.Push(readWriteEventArg);
}
}
#endregion
#region Start
/// <summary>
/// 启动
/// </summary>
public void Start()
{
if (!IsRunning)
{
Init();
IsRunning = true;
IPEndPoint localEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(Address, Port);
// 创建监听socket
_serverSock = new Socket(localEndPoint.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
//_serverSock.ReceiveBufferSize = _bufferSize;
//_serverSock.SendBufferSize = _bufferSize;
if (localEndPoint.AddressFamily == AddressFamily.InterNetworkV6)
{
// 配置监听socket为 dual-mode (IPv4 & IPv6)
// 27 is equivalent to IPV6_V6ONLY socket option in the winsock snippet below,
_serverSock.SetSocketOption(SocketOptionLevel.IPv6, (SocketOptionName)27, false);
_serverSock.Bind(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.IPv6Any, localEndPoint.Port));
}
else
{
_serverSock.Bind(localEndPoint);
}
// 开始监听
_serverSock.Listen(this._maxClient);
// 在监听Socket上投递一个接受请求。
StartAccept(null);
}
}
#endregion
#region Stop
/// <summary>
/// 停止服务
/// </summary>
public void Stop()
{
if (IsRunning)
{
IsRunning = false;
_serverSock.Close();
//TODO 关闭对所有客户端的连接
}
}
#endregion
#region Accept
/// <summary>
/// 从客户端开始接受一个连接操作
/// </summary>
private void StartAccept(SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar)
{
if (asyniar == null)
{
asyniar = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
asyniar.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnAcceptCompleted);
}
else
{
//socket must be cleared since the context object is being reused
asyniar.AcceptSocket = null;
}
_maxAcceptedClients.WaitOne();
if (!_serverSock.AcceptAsync(asyniar))
{
ProcessAccept(asyniar);
//如果I/O挂起等待异步则触发AcceptAsyn_Asyn_Completed事件
//此时I/O操作同步完成,不会触发Asyn_Completed事件,所以指定BeginAccept()方法
}
}
/// <summary>
/// accept 操作完成时回调函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Object who raised the event.</param>
/// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed accept operation.</param>
private void OnAcceptCompleted(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
ProcessAccept(e);
}
/// <summary>
/// 监听Socket接受处理
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed accept operation.</param>
private void ProcessAccept(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
Socket s = e.AcceptSocket;//和客户端关联的socket
if (s.Connected)
{
try
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref _clientCount);//原子操作加1
SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar = _objectPool.Pop();
asyniar.UserToken = s;
Log4Debug(String.Format("客户 {0} 连入, 共有 {1} 个连接。", s.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), _clientCount));
if (!s.ReceiveAsync(asyniar))//投递接收请求
{
ProcessReceive(asyniar);
}
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
Log4Debug(String.Format("接收客户 {0} 数据出错, 异常信息: {1} 。", s.RemoteEndPoint, ex.ToString()));
//TODO 异常处理
}
//投递下一个接受请求
StartAccept(e);
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 发送数据
/// <summary>
/// 异步的发送数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e"></param>
/// <param name="data"></param>
public void Send(SocketAsyncEventArgs e, byte[] data)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
Socket s = e.AcceptSocket;//和客户端关联的socket
if (s.Connected)
{
Array.Copy(data, 0, e.Buffer, 0, data.Length);//设置发送数据
//e.SetBuffer(data, 0, data.Length); //设置发送数据
if (!s.SendAsync(e))//投递发送请求,这个函数有可能同步发送出去,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件
{
// 同步发送时处理发送完成事件
ProcessSend(e);
}
else
{
CloseClientSocket(e);
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 同步的使用socket发送数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="socket"></param>
/// <param name="buffer"></param>
/// <param name="offset"></param>
/// <param name="size"></param>
/// <param name="timeout"></param>
public void Send(Socket socket, byte[] buffer, int offset, int size, int timeout)
{
socket.SendTimeout = 0;
int startTickCount = Environment.TickCount;
int sent = 0; // how many bytes is already sent
do
{
if (Environment.TickCount > startTickCount + timeout)
{
//throw new Exception("Timeout.");
}
try
{
sent += socket.Send(buffer, offset + sent, size - sent, SocketFlags.None);
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
if (ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.WouldBlock ||
ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.IOPending ||
ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.NoBufferSpaceAvailable)
{
// socket buffer is probably full, wait and try again
Thread.Sleep(30);
}
else
{
throw ex; // any serious error occurr
}
}
} while (sent < size);
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送完成时处理函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">与发送完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void ProcessSend(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken;
//TODO
}
else
{
CloseClientSocket(e);
}
}
#endregion
#region 接收数据
/// <summary>
///接收完成时处理函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">与接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void ProcessReceive(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)//if (e.BytesTransferred > 0 && e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
// 检查远程主机是否关闭连接
if (e.BytesTransferred > 0)
{
Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken;
//判断所有需接收的数据是否已经完成
if (s.Available == 0)
{
//从侦听者获取接收到的消息。
//String received = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(e.Buffer, e.Offset, e.BytesTransferred);
//echo the data received back to the client
//e.SetBuffer(e.Offset, e.BytesTransferred);
byte[] data = new byte[e.BytesTransferred];
Array.Copy(e.Buffer, e.Offset, data, 0, data.Length);//从e.Buffer块中复制数据出来,保证它可重用
string info=Encoding.Default.GetString(data);
Log4Debug(String.Format("收到 {0} 数据为 {1}",s.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(),info));
//TODO 处理数据
//增加服务器接收的总字节数。
}
if (!s.ReceiveAsync(e))//为接收下一段数据,投递接收请求,这个函数有可能同步完成,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件
{
//同步接收时处理接收完成事件
ProcessReceive(e);
}
}
}
else
{
CloseClientSocket(e);
}
}
#endregion
#region 回调函数
/// <summary>
/// 当Socket上的发送或接收请求被完成时,调用此函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">激发事件的对象</param>
/// <param name="e">与发送或接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void OnIOCompleted(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
// Determine which type of operation just completed and call the associated handler.
switch (e.LastOperation)
{
case SocketAsyncOperation.Accept:
ProcessAccept(e);
break;
case SocketAsyncOperation.Receive:
ProcessReceive(e);
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentException("The last operation completed on the socket was not a receive or send");
}
}
#endregion
#region Close
/// <summary>
/// 关闭socket连接
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed send/receive operation.</param>
private void CloseClientSocket(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
Log4Debug(String.Format("客户 {0} 断开连接!",((Socket)e.UserToken).RemoteEndPoint.ToString()));
Socket s = e.UserToken as Socket;
CloseClientSocket(s, e);
}
/// <summary>
/// 关闭socket连接
/// </summary>
/// <param name="s"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void CloseClientSocket(Socket s, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
try
{
s.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Send);
}
catch (Exception)
{
// Throw if client has closed, so it is not necessary to catch.
}
finally
{
s.Close();
}
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _clientCount);
_maxAcceptedClients.Release();
_objectPool.Push(e);//SocketAsyncEventArg 对象被释放,压入可重用队列。
}
#endregion
#region Dispose
/// <summary>
/// Performs application-defined tasks associated with freeing,
/// releasing, or resetting unmanaged resources.
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
/// <summary>
/// Releases unmanaged and - optionally - managed resources
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing"><c>true</c> to release
/// both managed and unmanaged resources; <c>false</c>
/// to release only unmanaged resources.</param>
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!this.disposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
try
{
Stop();
if (_serverSock != null)
{
_serverSock = null;
}
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
//TODO 事件
}
}
disposed = true;
}
}
#endregion
public void Log4Debug(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine("notice:"+msg);
}
}
}
クライアント
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IOCPServer server = new IOCPServer(8088, 1024);
server.Start();
Console.WriteLine("服务器已启动....");
System.Console.ReadLine();
}client.cs
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IPAddress remote=IPAddress.Parse("192.168.3.4");
client c = new client(8088,remote);
c.connect();
Console.WriteLine("服务器连接成功!");
while (true)
{
Console.Write("send>");
string msg=Console.ReadLine();
if (msg == "exit")
break;
c.send(msg);
}
c.disconnect();
Console.ReadLine();
}SocketAsyncEventArgs クラスを使用して確立されたソケット クライアントです。 MSDN によれば、このクラスは Web サーバー アプリケーション専用に設計されていますが、クライアント コードでの APM の使用には制限はありません。 IOCPClient クラスのサンプル コードを以下に示します。
public class client
{
public TcpClient _client;
public int port;
public IPAddress remote;
public client(int port,IPAddress remote)
{
this.port = port;
this.remote = remote;
}
public void connect()
{
this._client=new TcpClient();
_client.Connect(remote, port);
}
public void disconnect()
{
_client.Close();
}
public void send(string msg)
{
byte[] data=Encoding.Default.GetBytes(msg);
_client.GetStream().Write(data, 0, data.Length);
}
}このクラスはテストしていませんが、理論的には問題ありません。 上記は C#、SocketAsyncEventArgs、サーバーの内容です。さらに関連する内容については、PHP 中国語 Web サイト (www.php.cn) に注目してください。