
前書き ハイブリッド アプリケーションの強化により、HTML5 エンジニアは、デスクトップ エクスペリエンスをモバイルに移植するだけでは満足できなくなり、モバイル ネイティブ アプリケーションの人間味あふれる操作エクスペリエンス、特にネイティブ アプリケーションの固有の利点を切望しています。 。 HTML5 は、すぐに使えるジェスチャ システムを提供しませんが、タッチ イベントの下位レベルの監視を提供します。これに基づいて、独自のジェスチャ ライブラリを作成できます。 ジェスチャー一般的に使用される HTML5 ジェスチャーは、1 点ジェスチャーと 2 点ジェスチャーの 2 つのカテゴリに分類できます。シングルポイント ジェスチャには、タップ、ダブル タップ、ロング タップ、スワイプ、移動が含まれます。 2 点ジェスチャには、ピンチ (ズーム) と回転 (回転) が含まれます。 次に、これらのジェスチャーを検出する JavaScript ライブラリを実装し、このジェスチャー ライブラリを使用してクールなインタラクティブ効果を作成します。



_getTime() {
return new Date().getTime();
}
_onTouchStart(e) {
//记录touch开始的位置
this.startX = e.touches[0].pageX;
this.startY = e.touches[0].pageY;
if(e.touches.length > 1) {
//多点监测
...
}else {
//记录touch开始的时间
this.startTime = this._getTime();
}
}
_onTouchMove(e) {
...
//记录手指移动的位置
this.moveX = e.touches[0].pageX;
this.moveY = e.touches[0].pageY;
...
}
_onTouchEnd(e) {
let timestamp = this._getTime();
if(this.moveX !== null && Math.abs(this.moveX - this.startX) > 10 ||
this.moveY !== null && Math.abs(this.moveY - this.startY) > 10) {
...
}else {
//手指移动的位移要小于10像素并且手指和屏幕的接触时间要短语500毫秒
if(timestamp - this.startTime < 500) {
this._emitEvent('onTap')
}
}
}

_onTouchStart(e) {
if(e.touches.length > 1) {
...
} else {
if(this.previousTouchPoint) {
//两次相邻的touchstart之间距离要小于10,同时时间间隔小于300ms
if( Math.abs(this.startX -this.previousTouchPoint.startX) < 10 &&
Math.abs(this.startY - this.previousTouchPoint.startY) < 10 &&
Math.abs(this.startTime - this.previousTouchTime) < 300) {
this._emitEvent('onDoubleTap');
}
}
//保存上一次touchstart的时间和位置信息
this.previousTouchTime = this.startTime;
this.previousTouchPoint = {
startX : this.startX,
startY : this.startY
};
}
}
_onTouchStart(e) {
clearTimeout(this.longPressTimeout);
if(e.touches.length > 1) {
}else {
this.longPressTimeout = setTimeout(()=>{
this._emitEvent('onLongPress');
});
}
}
_onTouchMove(e) {
...
clearTimeout(this.longPressTimeout);
...
}
_onTouchEnd(e) {
...
clearTimeout(this.longPressTimeout);
...
}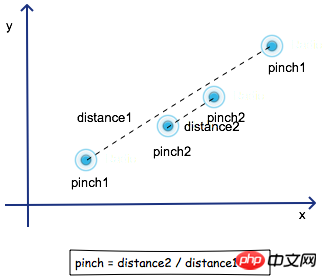
所以缩放的核心是获取两个接触点之间的直线距离。
//勾股定理
_getDistance(xLen,yLen) {
return Math.sqrt(xLen * xLen + yLen * yLen);
}这里的xLen是两个接触点x坐标差的绝对值,yLen相应的就是y坐标差的绝对值。
_onTouchStart(e) {
if(e.touches.length > 1) {
let point1 = e.touches[0];
let point2 = e.touches[1];
let xLen = Math.abs(point2.pageX - point1.pageX);
let yLen = Math.abs(point2.pageY - point1.pageY);
this.touchDistance = this._getDistance(xLen, yLen);
} else {
...
}
}在_onTouchStart函数中获取并且保存 touchstart 发生时两个接触点之间的距离。
_onTouchMove(e) {
if(e.touches.length > 1) {
let xLen = Math.abs(e.touches[0].pageX - e.touches[1].pageX);
let yLen = Math.abs(e.touches[1].pageY - e.touches[1].pageY);
let touchDistance = this._getDistance(xLen,yLen);
if(this.touchDistance) {
let pinchScale = touchDistance / this.touchDistance;
this._emitEvent('onPinch',{scale:pinchScale - this.previousPinchScale});
this.previousPinchScale = pinchScale;
}
}else {
...
}
}旋转手势需要检测两个比较重要的值,一是旋转的角度,二是旋转的方向(顺时针或逆时针)。
其中旋转角度和方向的计算需要通过向量的计算来获取,本文不再展开。
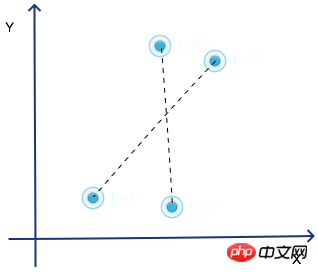
首先,需要获取向量的旋转方向和角度。
//这两个方法属于向量计算,具体原理请阅读本文最后的参考文献
_getRotateDirection(vector1,vector2) {
return vector1.x * vector2.y - vector2.x * vector1.y;
}
_getRotateAngle(vector1,vector2) {
let direction = this._getRotateDirection(vector1,vector2);
direction = direction > 0 ? -1 : 1;
let len1 = this._getDistance(vector1.x,vector1.y);
let len2 = this._getDistance(vector2.x,vector2.y);
let mr = len1 * len2;
if(mr === 0) return 0;
let dot = vector1.x * vector2.x + vector1.y * vector2.y;
let r = dot / mr;
if(r > 1) r = 1;
if(r < -1) r = -1;
return Math.acos(r) * direction * 180 / Math.PI;
}然后,我们在手指发生移动时,调用获取旋转方向和角度的方法。
_onTouchStart(e) {
...
if(e.touches.length > 1) {
this.touchVector = {
x: point2.pageX - this.startX,
y: point2.pageY - this.startY
};
}
...
}
_onTouchMove(e) {
...
if(this.touchVector) {
let vector = {
x: e.touches[1].pageX - e.touches[0].pageX,
y: e.touches[1].pageY - e.touches[0].pageY
};
let angle = this._getRotateAngle(vector,this.touchVector);
this._emitEvent('onRotate',{
angle
});
this.touchVector.x = vector.x;
this.touchVector.y = vector.y;
}
...
}好了,我们的手势系统到这里就完成了。接下来要在实战中检验这套系统是否可靠,做一个简单的图片浏览器,支持图片缩放,旋转,移动,长按。
首先,做好DOM规划,和“之前”一样,我们的事件监听机制并不直接作用在图片上,而是作用在图片的父元素上。

然后,可以开始使用上面的手势检测系统了。
render() {
return (
<Gestures onPinch={this.onPinch} onMove={this.onMove} onRotate={this.onRotate} onDoubleTap={this.onDoubleTap} onLongPress={this.onLongPress}>
<p className="wrapper" >

</p>
</Gestures>
);
}由于我们的手势系统检测的增量,因此不能直接把增量应用在对象上,而是需要把这些增量累加。以旋转为例:
onRotate(event) {
//对增量进行累加
this.angle += event.angle
this.setState({
angle:this.angle
});
}至此,我们的手势检测就完成了。
以上就是HTML5 手势检测原理和实现的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!