ASP.NET での EntLib 例外処理の解決策
ASP.NET MVC は、非常に拡張性の高い開発フレームワークです。この記事では、その拡張機能を介してこれを EntLib と統合し、完全な例外処理ソリューションを提供します。
EntLib の例外処理アプリケーション ブロックは、構成を通じて例外処理戦略を定義できる優れた例外処理フレームワークです。 ASP.NET MVC は非常に拡張性の高い開発フレームワークです。この記事では、ASP.NET MVC をその拡張機能を通じて EntLib と統合し、完全な例外処理ソリューションを提供します。
1. 基本的な例外処理戦略
まず、私たちのソリューションで採用されている具体的な例外処理戦略について説明しましょう:
コントローラーの特定の Action メソッドの実行によってスローされた例外については、次のように処理します。指定された構成ポリシーに適用されます。ロギング、例外置換、カプセル化などの一般的な例外処理方法を採用できます。処理された例外については、例外処理ポリシーでスローする必要があると規定されている場合、例外の種類に一致するエラー ページに自動的にリダイレクトされます。 。例外タイプとエラー ビューの間の一致関係を維持します。
処理された例外について、例外処理ポリシーでスローする必要がないことが規定されている場合、現在のアクション操作に一致する
エラー処理
ModelStateのエラーメッセージを設定します。ユーザーが対応する例外処理アクションを定義していない場合でも、例外処理には「エラーページリダイレクト」メソッドが使用されます。
2. カスタムアクションによる例外の処理
上記で紹介した例外処理ページを読者に深く理解してもらうために、サンプルデモを行ってみましょう。このインスタンスは、ユーザー ログインをシミュレートするために使用されます。ユーザー名とパスワードの 2 つの属性
のみを含む次のモデルを定義します。 namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models
{
public class LoginInfo
{
[Display(Name ="User Name")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "User Name is manadatory!")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Password")]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password is manadatory!")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
} public class AccountController BaseController
{
public AccountController()
base("myPolicy")
{ }
public ActionResult SignIn()
{
return View(new LoginInfo());
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult SignIn(LoginInfo loginInfo)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = loginInfo.UserName });
}
if (loginInfo.UserName != "Foo")
{
throw new InvalidUserNameException();
}
if (loginInfo.Password != "password")
{
throw new UserNamePasswordNotMatchException();
}
ViewBag.Message = "Authentication Succeeds!";
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = loginInfo.UserName });
}
public ActionResult OnSignInError(string userName)
{
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = userName });
}
} @model Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.LoginInfo
@{
ViewBag.Title = "SignIn";
}
@Html.ValidationSummary()
@if (ViewBag.Messages != null)
{
@ViewBag.Messages
}
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.EditorForModel()
<input type="submit" value="SignIn" />
} <exceptionHandling>
<exceptionPolicies>
<add name="myPolicy">
<exceptionTypes>
<add name="InvalidUserNameException"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="None">
<exceptionHandlers>
<add name="ErrorMessageSettingHandler"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.ErrorMessageSettingHandler, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorMessage="User name does not exist!"/>
</exceptionHandlers>
</add>
<add name="UserNamePasswordNotMatchException"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="None">
<exceptionHandlers>
<add name="ErrorMessageSettingHandler"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.ErrorMessageSettingHandler, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorMessage="User name does not match password!"/>
</exceptionHandlers>
</add>
</exceptionTypes>
</add>
</exceptionPolicies>
</exceptionHandling>上記の設定では、InvalidUserNameException と UserNamePasswordNotMatchException の 2 つの例外タイプの設定ポリシーが PostHandlingAction 属性を「None」に設定します。 no 元の例外と処理された例外を再スローします。ここで、このプロパティを「ThrowNewException」に設定します。これは、処理された例外を再スローすることを意味します。 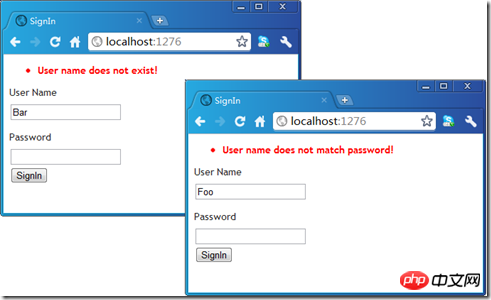
按照我们上面的异常处理策略,在这种情况下我们将采用“错误页面”的方式来进行异常处理。也HandleErrorAttribute的处理方式类似,我们支持异常类型和Error View之间的匹配关系,而这是通过类似于如下的配置来定义的。值得一提的是,这里的异常类型是经过处理后重新抛出的异常。 如上面的配置所示,我们为InvalidUserNameException和UserNamePasswordNotMatchException这两种异常类型定义了不同的Error View,分别是“InvalideUserNameError”和“UserNamePasswordNotMatchError”,详细定义如下所示: 现在我们按照上面的方式运行我们的程序,在分别输入错误的用户名和密码的情况下会自动显现相应的错误页面。 四、自定义ActionInvoker:ExceptionActionInvoker 对于上述的两种不同的异常处理方式最终是通过自定义的ActionInvoker来实现的,我们将其命名为ExceptionActionInvoker。如下面的代码片断所式,ExceptionActionInvoker直接继承自ControllerActionInvoker。属性ExceptionPolicy是一个基于指定的异常策略名称创建的ExceptionPolicyImpl 对象,用于针对EntLib进行的异常处理。而属性GetErrorView是一个用于获得作为错误页面的ViewResult对象的委托。整个异常处理的核心定义在InvokeAction方法中,该方法中指定的handleErrorActionName参数代表的是“异常处理操作名称”,整个方法就是按照上述的异常处理策略实现的。 五、自定义Controller:BaseController ExceptionActionInvoker最终在我们自定义的Controller基类BaseController中被调用的。ExceptionActionInvoker对象在构造函数中被初始化,并在重写的OnException方法中被调用。 值得一提的是:整个OnException方法中的操作都在一个ExceptionHandlingContextScope中进行的。顾名思义, 我们通过ExceptionHandlingContextScope为ExceptionHandlingContext创建了一个范围。ExceptionHandlingContext定义如下,我们可以通过它获得当前的ExceptionContext和ModelErrorCollection,而静态属性Current返回当前的ExceptionHandlingContext对象。 在BaseController的OnException方法中,当执行了ExceptionActionInvoker的InvokeAction之后,我们会将当前ExceptionHandlingContext的ModelError转移到当前的ModelState中。这就是为什么我们会通过ValidationSummary显示错误信息的原因。对于我们的例子来说,错误消息的指定是通过如下所示的ErrorMessageSettingHandler 实现的,而它仅仅将指定的错误消息添加到当前ExceptionHandlingContext的Errors属性集合中而已。 <exceptionHandling>
<exceptionPolicies>
<add name="myPolicy">
<exceptionTypes>
<add name="InvalidUserNameException" type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="ThrowNewException">
...
<add name="UserNamePasswordNotMatchException" type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="ThrowNewException">
...
</add>
</exceptionTypes>
</add>
</exceptionPolicies>
</exceptionHandling> <artech.exceptionHandling>
<add exceptionType="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorView="InvalideUserNameError"/>
<add exceptionType="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorView="UserNamePasswordNotMatchError"/>
</artech.exceptionHandling> @{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="colorRed; font-weightbold">Sorry,the user name you specify does not exist!</p>
</body>
</html>
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="colorRed; font-weightbold">Sorry, The password does not match the given user name!</p>
</body>
</html>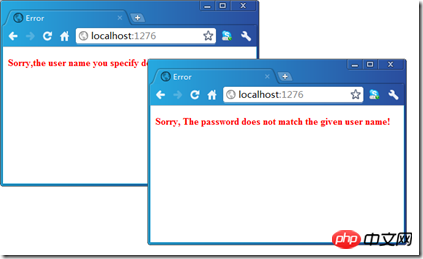
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Common.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.ExceptionHandling;
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling
{
public class ExceptionActionInvoker ControllerActionInvoker
{
protected ExceptionHandlingSettings ExceptionHandlingSettings{get; private set;}
protected virtual Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> GetErrorView { get; private set; }
public ExceptionPolicyImpl ExceptionPolicy { get; private set; }
public ExceptionActionInvoker(string exceptionPolicy,Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> getErrorView)
{
this.ExceptionPolicy = EnterpriseLibraryContainer.Current.GetInstance<ExceptionPolicyImpl>(exceptionPolicy);
this.GetErrorView = getErrorView;
this.ExceptionHandlingSettings = ExceptionHandlingSettings.GetSection();
}
public override bool InvokeAction(ControllerContext controllerContext, string handleErrorActionName)
{
ExceptionContext exceptionContext = controllerContext as ExceptionContext;
if (null == exceptionContext)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The controllerContext must be ExceptionContext!", "controllerContext");
}
try
{
exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled = true;
if (this.ExceptionPolicy.HandleException(exceptionContext.Exception))
{
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
}
else
{
if (ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors.Count == 0)
{
ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors.Add(exceptionContext.Exception.Message);
}
ControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor = this.GetControllerDescriptor(exceptionContext);
ActionDescriptor handleErrorAction = FindAction(exceptionContext, controllerDescriptor, handleErrorActionName);
if (null != handleErrorAction)
{
IDictionary<string, object> parameters = GetParameterValues(controllerContext, handleErrorAction);
exceptionContext.Result = this.InvokeActionMethod(exceptionContext, handleErrorAction, parameters);
}
else
{
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
}
}
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
exceptionContext.Exception = ex;
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
return true;
}
}
protected virtual void HandleRethrownException(ExceptionContext exceptionContext)
{
string errorViewName = this.GetErrorViewName(exceptionContext.Exception.GetType());
string controllerName = (string)exceptionContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller");
string action = (string)exceptionContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
HandleErrorInfo handleErrorInfo = new HandleErrorInfo(exceptionContext.Exception, controllerName, action);
exceptionContext.Result = this.GetErrorView(errorViewName, handleErrorInfo);
}
protected string GetErrorViewName(Type exceptionType)
{
ExceptionErrorViewElement element = ExceptionHandlingSettings.ExceptionErrorViews
.Cast<ExceptionErrorViewElement>().FirstOrDefault(el=>el.ExceptionType == exceptionType);
if(null != element)
{
return element.ErrorView;
}
if(null== element && null != exceptionType.BaseType!= null)
{
return GetErrorViewName(exceptionType.BaseType);
}
else
{
return "Error";
}
}
}
} using System;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling
{
public abstract class BaseController Controller
{
public BaseController(string exceptionPolicy)
{
Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> getErrorView = (viewName, handleErrorInfo) => this.View(viewName, handleErrorInfo);
this.ExceptionActionInvoker = new ExceptionActionInvoker(exceptionPolicy,getErrorView);
}
public BaseController(ExceptionActionInvoker actionInvoker)
{
this.ExceptionActionInvoker = actionInvoker;
}
public virtual ExceptionActionInvoker ExceptionActionInvoker { get; private set; }
protected virtual string GetHandleErrorActionName(string actionName)
{
return string.Format("On{0}Error", actionName);
}
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext)
{
using (ExceptionHandlingContextScope contextScope = new ExceptionHandlingContextScope(filterContext))
{
string actionName = RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
string handleErrorActionName = this.GetHandleErrorActionName(actionName);
this.ExceptionActionInvoker.InvokeAction(filterContext, handleErrorActionName);
foreach (var error in ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(Guid.NewGuid().ToString() ,error.ErrorMessage);
}
}
}
}
} public class ExceptionHandlingContext
{
[ThreadStatic]
private static ExceptionHandlingContext current;
public ExceptionContext ExceptionContext { get; private set; }
public ModelErrorCollection Errors { get; private set; }
public ExceptionHandlingContext(ExceptionContext exceptionContext)
{
this.ExceptionContext = exceptionContext;
this.Errors = new ModelErrorCollection();
}
public static ExceptionHandlingContext Current
{
get { return current; }
set { current = value; }
}
} [ConfigurationElementType(typeof(ErrorMessageSettingHandlerData))]
public class ErrorMessageSettingHandler IExceptionHandler
{
public string ErrorMessage { get; private set; }
public ErrorMessageSettingHandler(string errorMessage)
{
thisErrorMessage = errorMessage;
}
public Exception HandleException(Exception exception, Guid handlingInstanceId)
{
if (null == ExceptionHandlingContextCurrent)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("");
}
if (stringIsNullOrEmpty(thisErrorMessage))
{
ExceptionHandlingContextCurrentErrorsAdd(exceptionMessage);
}
else
{
ExceptionHandlingContextCurrentErrorsAdd(thisErrorMessage);
}
return exception;
}
}
【相关推荐】
2.ASP教程
以上がASP.NET での EntLib 例外処理の解決策の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7521
7521
 15
15
 1378
1378
 52
52
 81
81
 11
11
 21
21
 70
70
 C++ 関数の例外とマルチスレッド: 同時環境でのエラー処理
May 04, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
C++ 関数の例外とマルチスレッド: 同時環境でのエラー処理
May 04, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
C++ での関数例外処理は、マルチスレッド環境でスレッドの安全性とデータの整合性を確保するために特に重要です。 try-catch ステートメントを使用すると、特定の種類の例外が発生したときにそれをキャッチして処理し、プログラムのクラッシュやデータの破損を防ぐことができます。
 Java 関数の再帰呼び出しと例外処理の間にはどのような関係がありますか?
May 03, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
Java 関数の再帰呼び出しと例外処理の間にはどのような関係がありますか?
May 03, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
再帰呼び出しでの例外処理: 再帰の深さの制限: スタック オーバーフローの防止。例外処理を使用する: try-catch ステートメントを使用して例外を処理します。末尾再帰の最適化: スタックのオーバーフローを回避します。
 C++ 例外処理はカスタム エラー処理ルーチンをどのようにサポートしますか?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 12:13 PM
C++ 例外処理はカスタム エラー処理ルーチンをどのようにサポートしますか?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 12:13 PM
C++ 例外処理を使用すると、例外をスローし、try-catch ブロックを使用して例外をキャッチすることで実行時エラーを処理するカスタム エラー処理ルーチンを作成できます。 1. 例外クラスから派生したカスタム例外クラスを作成し、what() メソッドをオーバーライドします。 2. throw キーワードを使用して例外をスローし、例外のタイプを指定します。扱った。
 C++ ラムダ式で例外を処理するにはどうすればよいですか?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 03:01 PM
C++ ラムダ式で例外を処理するにはどうすればよいですか?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 03:01 PM
C++ ラムダ式の例外処理には独自のスコープがなく、デフォルトでは例外はキャッチされません。例外をキャッチするには、ラムダ式キャッチ構文を使用できます。これにより、ラムダ式がその定義スコープ内の変数をキャプチャできるようになり、try-catch ブロックで例外処理が可能になります。
 C++ テクノロジにおける例外処理: マルチスレッド環境で例外を正しく処理するにはどうすればよいですか?
May 09, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
C++ テクノロジにおける例外処理: マルチスレッド環境で例外を正しく処理するにはどうすればよいですか?
May 09, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
マルチスレッド C++ では、例外処理は適時性、スレッドの安全性、明確性という原則に従います。実際には、ミューテックスまたはアトミック変数を使用することで、例外処理コードのスレッド セーフを確保できます。さらに、例外処理コードの再入性、パフォーマンス、テストを考慮して、コードがマルチスレッド環境で安全かつ効率的に実行されることを確認してください。
 Java マルチスレッド環境での例外処理
May 01, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Java マルチスレッド環境での例外処理
May 01, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
マルチスレッド環境での例外処理の重要なポイント: 例外のキャッチ: 各スレッドは try-catch ブロックを使用して例外をキャッチします。例外の処理: エラー情報を出力するか、catch ブロックでエラー処理ロジックを実行します。スレッドを終了する: 回復が不可能な場合は、Thread.stop() を呼び出してスレッドを終了します。 UncaughtExceptionHandler: キャッチされなかった例外を処理するには、このインターフェイスを実装し、スレッドに割り当てる必要があります。実際のケース: スレッド プールでの例外処理。UncaughtExceptionHandler を使用してキャッチされなかった例外を処理します。
 PHP 例外処理: 例外追跡を通じてシステムの動作を理解する
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:57 PM
PHP 例外処理: 例外追跡を通じてシステムの動作を理解する
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:57 PM
PHP 例外処理: 例外追跡を通じてシステムの動作を理解する 例外は、PHP がエラーを処理するために使用するメカニズムであり、例外は例外ハンドラーによって処理されます。例外クラス Exception は一般的な例外を表し、Throwable クラスはすべての例外を表します。 throw キーワードを使用して例外をスローし、try...catch ステートメントを使用して例外ハンドラーを定義します。実際のケースでは、例外処理を使用して、calculate() 関数によってスローされる DivisionByZeroError をキャプチャして処理し、エラー発生時にアプリケーションが適切に失敗できるようにします。
 PHPで例外を効果的に処理する方法(試して、キャッチ、最後に、スロー)?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
PHPで例外を効果的に処理する方法(試して、キャッチ、最後に、スロー)?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
PHPでは、Try、Catch、最後にキーワードをスローすることにより、例外処理が達成されます。 1)TRYブロックは、例外をスローする可能性のあるコードを囲みます。 2)キャッチブロックは例外を処理します。 3)最後にブロックは、コードが常に実行されることを保証します。 4)スローは、例外を手動でスローするために使用されます。これらのメカニズムは、コードの堅牢性と保守性を向上させるのに役立ちます。




