Python を使用してリモート サーバーへの自動 SSH ログインを作成する例を共有します。
多くの場合、UI インターフェイスを備えたツール領域を使用してサーバーに接続するのではなく、コンピューターのターミナルから Linux サーバーに直接 ssh 接続したいと考えます。ただし、ターミナルで ssh を使用する場合、毎回アカウントとパスワードを入力する必要があり、これも面倒なので、Linux/Mac OS 上で動作する ssh 経由でリモート サーバーに自動的にログインする小さなツールを簡単に作成できます。
これが GIF アニメーションの例です まず:
概要
最初に必要な関数を整理しましょう:
1. 添加/删除连接服务器需要的IP,端口,密码2. 自动输入密码登录远程服务器
はい、そのような単純な関数を実行します
コードを書き始めます
コードは比較的長いですので、Github と Code Cloud にも置きました。アドレスは記事の最後にあります:
1. モジュール ディレクトリ osnssh (オープン ソース noob ssh) を作成して、以下にさらに 2 つのディレクトリを作成します (1 つはメイン用)。 bin という名前のプログラムを作成し、ログインデータ (IP、ポート、パスワード) を保存するものを data と呼びます。
-osnssh
-bin
-data1. 設定プログラム: IP、ポート、パスワードを追加/削除します。py ファイルを作成します。bin/setting.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python#-*-coding:utf-8-*-import re, base64, os, sys
path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))'''
选项配置管理
__author__ = 'allen woo'
'''def add_host_main():while 1:if add_host():break
print("\n\nAgain:")def add_host():'''
添加主机信息
:return:
'''
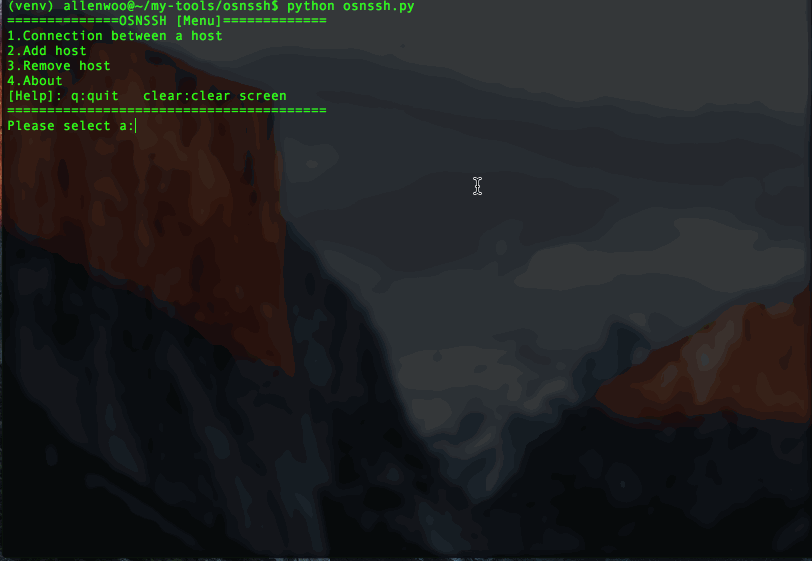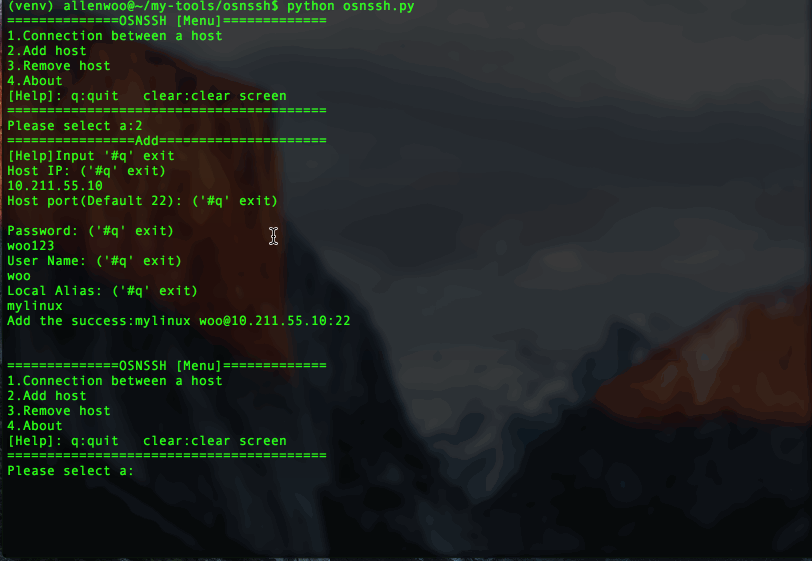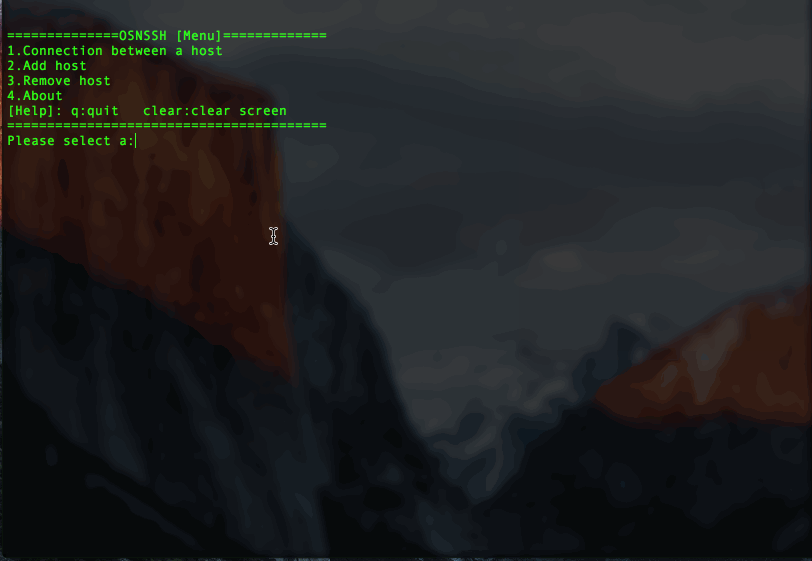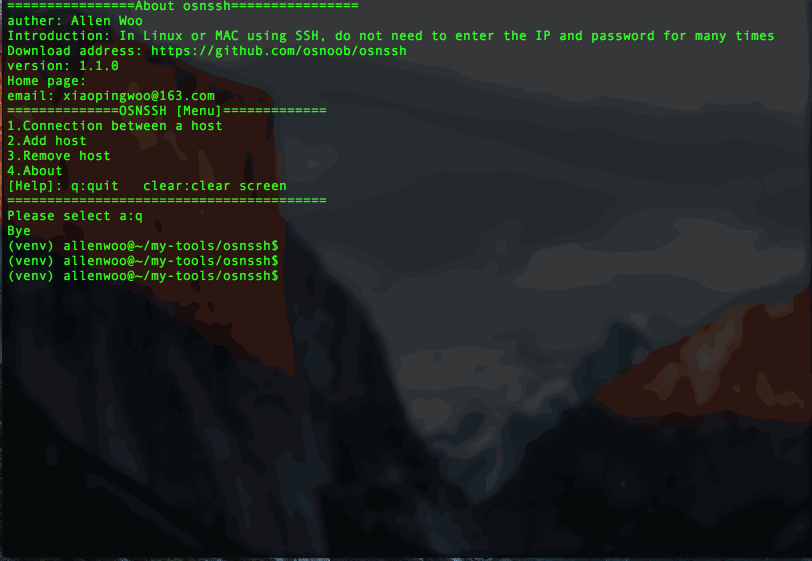
print("================Add=====================")
print("[Help]Input '#q' exit")# 输入IP
host_ip = str_format("Host IP:", "^(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|1[0-9][0-9]|[1-9]?[0-9])\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|1[0-9][0-9]|[1-9]?[0-9])\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|1[0-9][0-9]|[1-9]?[0-9])\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|1[0-9][0-9]|[1-9]?[0-9])$")if host_ip == "#q":return 1# 输入端口
host_port = str_format("Host port(Default 22):", "[0-9]+")if host_port == "#q":return 1# 输入密码
password = str_format("Password:", ".*")if password == "#q":return 1# 密码加密
password = base64.encodestring(password)# 输入用户名
name = str_format("User Name:", "^[^ ]+$")if name == "#q":return 1elif not name:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]:User name cannot be emptyg")return 0# The alias# 输入别名
alias = str_format("Local Alias:", "^[^ ]+$")if alias == "#q":return 1elif not alias:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]:Alias cannot be emptyg")return 0# 打开数据保存文件
of = open("{}/data/information.d".format(path))
hosts = of.readlines()# 遍历文件数据,查找是否有存在的Ip,端口,还有别名for l in hosts:
l = l.strip("\n")if not l:continue
l_list = l.split(" ")if host_ip == l_list[1] and host_port == l_list[2]:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]{}:{} existing".format(host_ip, host_port))return 0if alias == l_list[4]:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]Alias '{}' existing".format(alias))return 0
of.close()# save# 保存数据到数据文件
of = open("{}/data/information.d".format(path), "a")
of.write("\n{} {} {} {} {}".format(name.strip("\n"), host_ip.strip("\n"), host_port, password.strip("\n"), alias.strip("\n")))
of.close()
print("Add the success:{} {}@{}:{}".format(alias.strip("\n"), name.strip("\n"), host_ip.strip("\n"), host_port, password.strip("\n")))return 1def remove_host():'''
删除主机信息
:return:
'''while 1:# 打开数据文件
of = open("{}/data/information.d".format(path))
hosts = of.readlines()
of.close
l = len(hosts)if l <= 0:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]There is no host")return
print("================Remove================")
print("+{}+".format("-"*40))
print("| Alias UserName@IP:PORT")
hosts_temp = []
n = 0# 遍历输出所以信息(除了密码)供选择for i in range(0, l):if not hosts[i].strip():continue
v_list = hosts[i].strip().split(" ")
print("+{}+".format("-"*40))
print("| {} | {} {}@{}:{}".format(n+1, v_list[4], v_list[0], v_list[1], v_list[2]))
n += 1
hosts_temp.append(hosts[i])
hosts = hosts_temp[:]
print("+{}+".format("-"*40))
c = raw_input("[Remove]Choose the Number or Alias('#q' to exit):")
is_alias = False
is_y = Falsetry:
c = int(c)if c > l or c < 1:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]:There is no")continuedel hosts[c-1]
is_y = Trueexcept:
is_alias = Trueif is_alias:if c.strip() == "#q":
os.system("clear")break
n = 0for l in hosts:if c.strip() == l.split(" ")[4].strip():del hosts[n]
is_y = True
n += 1if not is_y:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]:There is no")continueelse: # save# 再次确认是否删除
c = raw_input("Remove?[y/n]:")if c.strip().upper() == "Y":
of = open("{}/data/information.d".format(path), "w")for l in hosts:
of.write(l)
print("Remove the success!")
of.close()def str_format(lable, rule):'''
用于验证输入的数据格式
:param lable:
:param rule:
:return:
'''while 1:
print("{} ('#q' exit)".format(lable))
temp = raw_input().strip()
m = re.match(r"{}".format(rule), temp)if m:breakelif "port" in lable:
temp = 22breakelif temp.strip() == "#q":
os.system("clear")break
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]:Invalid format")return temp2. 私に関する情報を出力するための別の関数を settings.py に追加します。
def about():'''
输出关于这个程序的信息
:return:
'''
of = open("{}/bin/about.dat".format(path))
rf = of.read()try:
info = eval(rf)
os.system("clear")
print("================About osnssh================")for k,v in info.items():
print("{}: {}".format(k, v))except:
print("For failure.")return次に、bin ディレクトリの下に about.dat ファイルを作成し、次のような情報を書き込みます。
{"auther":"Allen Woo","Introduction":"In Linux or MAC using SSH, do not need to enter the IP and password for many times","Home page":"","Download address":"https://github.com/osnoob/osnssh","version":"1.1.0","email":"xiaopingwoo@163.com"
}これでセットアップ プログラムは次のようになります:
2. リモート サーバー プログラムに自動的にログインします。 bin 内の auto_ssh.py という名前の py ファイル:
注: ここでは、最初に pexpect、ユーザー端末インタラクション、パスワードを自動的に入力するためのインタラクション情報のキャプチャというパッケージをインストールする必要があります。
pexpect をインストールします:
pip install pexpect
それからコードを書き始めます:
#!/usr/bin/env python#-*-coding:utf-8-*-import os, sys, base64import pexpect
path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))def choose():# 打开我们的数据文件
of = open("{}/data/information.d".format(path))
hosts = of.readlines()
hosts_temp = []for h in hosts:if h.strip():
hosts_temp.append(h)
hosts = hosts_temp[:]
l = len(hosts)if l <= 0:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]Please add the host server")returnwhile 1:
print("=================SSH===================")
print("+{}+".format("-"*40))
print("| Alias UserName@IP:PORT")for i in range(0, l):
v_list = hosts[i].strip().split(" ")
print("+{}+".format("-"*40))
print("| {} | {} {}@{}:{}".format(i+1, v_list[4], v_list[0], v_list[1], v_list[2]))
print("+{}+".format("-"*40))
c = raw_input("[SSH]Choose the number or alias('#q' exit):")
is_alias = False
is_y = Falsetry:
c = int(c)if c > l or c < 1:
os.system("clear")
print("[Warning]:There is no")continue
l_list = hosts[c-1].split(" ")
name = l_list[0]
host = l_list[1]
port = l_list[2]
password = l_list[3]
is_y = Trueexcept:
is_alias = Trueif is_alias:if c.strip() == "#q":
os.system("clear")returnfor h in hosts:if c.strip() == h.split(" ")[4].strip():
l_list = h.split(" ")
name = l_list[0]
host = l_list[1]
port = l_list[2]
password = l_list[3]
is_y = Trueif not is_y:continue# ssh# 将加密保存的密码解密
password = base64.decodestring(password)
print("In the connection...")# 准备远程连接,拼接ip:port
print("{}@{}".format(name, host))if port == "22":
connection("ssh {}@{}".format(name, host), password)else:
connection("ssh {}@{}:{}".format(name, host, port), password)def connection(cmd, pwd):'''
连接远程服务器
:param cmd:
:param pwd:
:return:
'''
child = pexpect.spawn(cmd)
i = child.expect([".*password.*", ".*continue.*?", pexpect.EOF, pexpect.TIMEOUT])if( i == 0 ):# 如果交互中出现.*password.*,就是叫我们输入密码# 我们就把密码自动填入下去
child.sendline("{}\n".format(pwd))
child.interact()elif( i == 1):# 如果交互提示是否继续,一般第一次连接时会出现# 这个时候我们发送"yes",然后再自动输入密码
child.sendline("yes\n")
child.sendline("{}\n".format(pwd))#child.interact() else:# 连接失败
print("[Error]The connection fails") さて、あとはプログラムを開いた後の最初のメニューであるファイルを起動するだけです
3. osnssh ディレクトリに osnssh.py ファイルを作成します。
#!/usr/bin/env python#-*-coding:utf-8-*-import os, sys
sys.path.append("../")from bin import setting, auto_ssh
path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))'''
方便在LINUX终端使用ssh,保存使用的IP:PORT , PASSWORD
自动登录
__author__ = 'allen woo'
'''def main():while 1:
print("==============OSNSSH [Menu]=============")
print("1.Connection between a host\n2.Add host\n3.Remove host\n4.About\n[Help]: q:quit clear:clear screen")
print("="*40)
c = raw_input("Please select a:")if c == 1 or c == "1":
auto_ssh.choose()if c == 2 or c == "2":
setting.add_host_main()if c == 3 or c == "3":
setting.remove_host()if c == 4 or c == "4":
setting.about()elif c == "clear":
os.system("clear")elif c == "q" or c == "Q" or c == "quit":
print("Bye")
sys.exit()else:
print("\n")if __name__ == '__main__':try:
of = open("{}/data/information.d".format(path))except:
of = open("{}/data/information.d".format(path), "w")
of.close()
main()$python osnssh.py
626062078 への参加を歓迎します。一緒に Python を学びましょう!
以上がPython を使用してリモート サーバーへの自動 SSH ログインを作成する例を共有します。の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7669
7669
 15
15
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1206
1206
 24
24
 91
91
 11
11
 PHPおよびPython:さまざまなパラダイムが説明されています
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHPおよびPython:さまざまなパラダイムが説明されています
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHPは主に手順プログラミングですが、オブジェクト指向プログラミング(OOP)もサポートしています。 Pythonは、OOP、機能、手続き上のプログラミングなど、さまざまなパラダイムをサポートしています。 PHPはWeb開発に適しており、Pythonはデータ分析や機械学習などのさまざまなアプリケーションに適しています。
 PHPとPythonの選択:ガイド
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHPとPythonの選択:ガイド
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHPはWeb開発と迅速なプロトタイピングに適しており、Pythonはデータサイエンスと機械学習に適しています。 1.PHPは、単純な構文と迅速な開発に適した動的なWeb開発に使用されます。 2。Pythonには簡潔な構文があり、複数のフィールドに適しており、強力なライブラリエコシステムがあります。
 Visual StudioコードはPythonで使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Visual StudioコードはPythonで使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VSコードはPythonの書き込みに使用でき、Pythonアプリケーションを開発するための理想的なツールになる多くの機能を提供できます。ユーザーは以下を可能にします。Python拡張機能をインストールして、コードの完了、構文の強調表示、デバッグなどの関数を取得できます。デバッガーを使用して、コードを段階的に追跡し、エラーを見つけて修正します。バージョンコントロールのためにGitを統合します。コードフォーマットツールを使用して、コードの一貫性を維持します。糸くずツールを使用して、事前に潜在的な問題を発見します。
 Windows 8でコードを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Windows 8でコードを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VSコードはWindows 8で実行できますが、エクスペリエンスは大きくない場合があります。まず、システムが最新のパッチに更新されていることを確認してから、システムアーキテクチャに一致するVSコードインストールパッケージをダウンロードして、プロンプトとしてインストールします。インストール後、一部の拡張機能はWindows 8と互換性があり、代替拡張機能を探すか、仮想マシンで新しいWindowsシステムを使用する必要があることに注意してください。必要な拡張機能をインストールして、適切に動作するかどうかを確認します。 Windows 8ではVSコードは実行可能ですが、開発エクスペリエンスとセキュリティを向上させるために、新しいWindowsシステムにアップグレードすることをお勧めします。
 VSCODE拡張機能は悪意がありますか?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VSCODE拡張機能は悪意がありますか?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VSコード拡張機能は、悪意のあるコードの隠れ、脆弱性の活用、合法的な拡張機能としての自慰行為など、悪意のあるリスクを引き起こします。悪意のある拡張機能を識別する方法には、パブリッシャーのチェック、コメントの読み取り、コードのチェック、およびインストールに注意してください。セキュリティ対策には、セキュリティ認識、良好な習慣、定期的な更新、ウイルス対策ソフトウェアも含まれます。
 PHPとPython:彼らの歴史を深く掘り下げます
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHPとPython:彼らの歴史を深く掘り下げます
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHPは1994年に発信され、Rasmuslerdorfによって開発されました。もともとはウェブサイトの訪問者を追跡するために使用され、サーバー側のスクリプト言語に徐々に進化し、Web開発で広く使用されていました。 Pythonは、1980年代後半にGuidovan Rossumによって開発され、1991年に最初にリリースされました。コードの読みやすさとシンプルさを強調し、科学的コンピューティング、データ分析、その他の分野に適しています。
 ターミナルVSCODEでプログラムを実行する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
ターミナルVSCODEでプログラムを実行する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
VSコードでは、次の手順を通じて端末でプログラムを実行できます。コードを準備し、統合端子を開き、コードディレクトリが端末作業ディレクトリと一致していることを確認します。プログラミング言語(pythonのpython your_file_name.pyなど)に従って実行コマンドを選択して、それが正常に実行されるかどうかを確認し、エラーを解決します。デバッガーを使用して、デバッグ効率を向上させます。
 Python vs. JavaScript:学習曲線と使いやすさ
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:学習曲線と使いやすさ
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Pythonは、スムーズな学習曲線と簡潔な構文を備えた初心者により適しています。 JavaScriptは、急な学習曲線と柔軟な構文を備えたフロントエンド開発に適しています。 1。Python構文は直感的で、データサイエンスやバックエンド開発に適しています。 2。JavaScriptは柔軟で、フロントエンドおよびサーバー側のプログラミングで広く使用されています。




