Comparable と Comparator の比較と使用
概要
1. Comparable と Comparator を使用する背景
数値データ (byte int short long float double) は、当然ながらサイズが比較可能であり、Comparable インターフェイスを実装しており、サイズを比較することもできます。カスタム クラスには多くの種類があり、並べ替えインジケーターとして使用できる共通のインジケーターがないため、この目的のために、Java は 2 つのインターフェイスを提供します。 、比較対象と比較者。
2. コレクションの並べ替え
Collections.sort() の基礎となる並べ替えは Arrays.sort() に依存しており、Arrays.sort() は並べ替えにバブル メソッドを使用します。
2 Comparable
サイズを比較する必要があるオブジェクトは、Comparable インターフェイスを実装し、比較方法を設定するために使用されるその抽象メソッドを実装できます。以下に例を示します。
1. エンティティ クラス
package com.javase.collections.comparable;public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {private String name;private int score;public Student() {super();
}public Student(String name, int score) {super();this.name = name;this.score = score;
}public String getName() {return name;
}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;
}public int getScore() {return score;
}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;
}
@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student stu) {return this.score - stu.score;// 操作对象减去参数对象,升序排列,反之降序。 }
}CompareTo() メソッドでは、「this.score-stu.score」を使用して、属性スコアが並べ替えインジケーターとして使用されます。 、最終結果は昇順に並べ、その逆に降順に並べます。
2. テストクラス
package com.javase.collections.comparable;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;import org.junit.Test;public class ComparableTest {
@Testpublic void testComparable() {
List<Student> stus = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student zhangsan = new Student("zhangsan", 100);
Student lisi = new Student("lisi", 90);
Student wanger = new Student("wanger", 95);
stus.add(zhangsan);
stus.add(lisi);
stus.add(wanger);
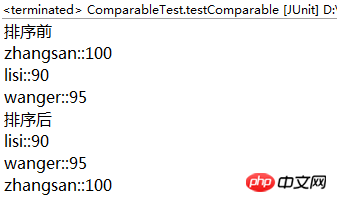
System.out.println("排序前");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
System.out.println("排序后");
Collections.sort(stus);for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
}
}出力:
クラスがComparableインターフェースを実装していない場合作成されました、そうなることを願っていますソース コードの変更 オブジェクトを並べ替えるには、Comparator インターフェイスを実装し、並べ替えメソッドを呼び出すときに並べ替え方法を指定します。以下に例を示します。
1. エンティティ クラス
package com.javase.collections.comparator;public class Student {private String name;private int score;public Student() {super();
}public Student(String name, int score) {super();this.name = name;this.score = score;
}public String getName() {return name;
}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;
}public int getScore() {return score;
}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;
}
}ログイン後にコピー
2. テスト クラス
package com.javase.collections.comparator;public class Student {private String name;private int score;public Student() {super();
}public Student(String name, int score) {super();this.name = name;this.score = score;
}public String getName() {return name;
}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;
}public int getScore() {return score;
}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;
}
}
package com.javase.collections.comparator;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.Comparator;import java.util.List;import org.junit.Test;public class ComparatorTest {
@Testpublic void test() {
List<Student> stus = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student zhangsan = new Student("zhangsan", 100);
Student lisi = new Student("lisi", 90);
Student wanger = new Student("wanger", 95);
stus.add(zhangsan);
stus.add(lisi);
stus.add(wanger);
System.out.println("排序前");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
Collections.sort(stus, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Overridepublic int compare(Student stu01, Student stu02) {// return stu01.getScore() - stu02.getScore();//升序return stu02.getScore() - stu01.getScore();// 降序 }
});
System.out.println("排序后");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
}
}ログイン後にコピー
メソッドで、属性によって並べ替えます。スコアインジケーターは「stu01.score-stu02.score」を使用し、最終結果は昇順に並べられます。また、その逆も同様です。
package com.javase.collections.comparator;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.Comparator;import java.util.List;import org.junit.Test;public class ComparatorTest {
@Testpublic void test() {
List<Student> stus = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student zhangsan = new Student("zhangsan", 100);
Student lisi = new Student("lisi", 90);
Student wanger = new Student("wanger", 95);
stus.add(zhangsan);
stus.add(lisi);
stus.add(wanger);
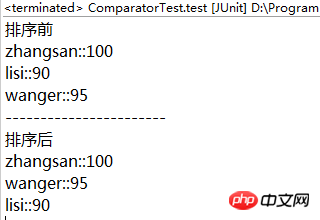
System.out.println("排序前");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
Collections.sort(stus, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Overridepublic int compare(Student stu01, Student stu02) {// return stu01.getScore() - stu02.getScore();//升序return stu02.getScore() - stu01.getScore();// 降序 }
});
System.out.println("排序后");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
}
}出力:
以上がComparable と Comparator の比較と使用の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7683
7683
 15
15
 1639
1639
 14
14
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1286
1286
 25
25
 1229
1229
 29
29
 会社のセキュリティソフトウェアはアプリケーションの実行に失敗していますか?それをトラブルシューティングと解決する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
会社のセキュリティソフトウェアはアプリケーションの実行に失敗していますか?それをトラブルシューティングと解決する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
一部のアプリケーションが適切に機能しないようにする会社のセキュリティソフトウェアのトラブルシューティングとソリューション。多くの企業は、内部ネットワークセキュリティを確保するためにセキュリティソフトウェアを展開します。 ...
 MapsTructを使用したシステムドッキングのフィールドマッピングの問題を簡素化する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
MapsTructを使用したシステムドッキングのフィールドマッピングの問題を簡素化する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
システムドッキングでのフィールドマッピング処理は、システムドッキングを実行する際に難しい問題に遭遇することがよくあります。システムのインターフェイスフィールドを効果的にマッピングする方法A ...
 エンティティクラス変数名をエレガントに取得して、データベースクエリ条件を構築する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
エンティティクラス変数名をエレガントに取得して、データベースクエリ条件を構築する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
データベース操作にMyBatis-Plusまたはその他のORMフレームワークを使用する場合、エンティティクラスの属性名に基づいてクエリ条件を構築する必要があることがよくあります。あなたが毎回手動で...
 Intellijのアイデアは、ログを出力せずにSpring Bootプロジェクトのポート番号をどのように識別しますか?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
Intellijのアイデアは、ログを出力せずにSpring Bootプロジェクトのポート番号をどのように識別しますか?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
intellijideaultimatiateバージョンを使用してスプリングを開始します...
 名前を数値に変換してソートを実装し、グループの一貫性を維持するにはどうすればよいですか?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
名前を数値に変換してソートを実装し、グループの一貫性を維持するにはどうすればよいですか?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
多くのアプリケーションシナリオでソートを実装するために名前を数値に変換するソリューションでは、ユーザーはグループ、特に1つでソートする必要がある場合があります...
 Javaオブジェクトを配列に安全に変換する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Javaオブジェクトを配列に安全に変換する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Javaオブジェクトと配列の変換:リスクの詳細な議論と鋳造タイプ変換の正しい方法多くのJava初心者は、オブジェクトのアレイへの変換に遭遇します...
 データベースクエリにTKMYBATISを使用するときに、エンティティクラスの変数名の構築クエリ条件をエレガントに取得する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
データベースクエリにTKMYBATISを使用するときに、エンティティクラスの変数名の構築クエリ条件をエレガントに取得する方法は?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
データベースクエリにTKMYBATISを使用する場合、クエリ条件を構築するためにエンティティクラスの変数名を優雅に取得する方法は一般的な問題です。この記事はピン留めします...
 Springプロジェクトは、開始時に円形の依存関係によりランダム性の問題を引き起こすのはなぜですか?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Springプロジェクトは、開始時に円形の依存関係によりランダム性の問題を引き起こすのはなぜですか?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Spring Project Startupにおける円形依存関係のランダム性を理解してください。春のプロジェクトを開発するとき、プロジェクトの起動時に循環依存関係によって引き起こされるランダム性に遭遇する可能性があります...




