JSプロトタイプとプロトタイプチェーンの詳しい解説(3)
今回は前回に引き続き、JSプロトタイプとプロトタイプチェーンについて、注意点を含めて見ていきましょう。
7. 関数オブジェクト (前の知識ポイントを確認してください)
すべての関数オブジェクトのプロトは、空の関数 (空の関数) である Function.prototype を指します
Number.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true Number.constructor == Function //true Boolean.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true Boolean.constructor == Function //true String.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true String.constructor == Function //true // 所有的构造器都来自于Function.prototype,甚至包括根构造器Object及Function自身 Object.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true Object.constructor == Function // true // 所有的构造器都来自于Function.prototype,甚至包括根构造器Object及Function自身 Function.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true Function.constructor == Function //true Array.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true Array.constructor == Function //true RegExp.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true RegExp.constructor == Function //true Error.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true Error.constructor == Function //true Date.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true Date.constructor == Function //true
ビルドされた関数がありますJavaScript の -in 合計 12 個の (組み込み) コンストラクター/オブジェクトがあります (JSON は ES5 で新たに追加されました)。アクセス可能なコンストラクターは 8 つです。 Global などの残りの部分には直接アクセスできません。引数は関数が呼び出されたときに JS エンジンによってのみ作成されます。Math と JSON はオブジェクトの形式で存在し、new を必要としません。それらのプロトは Object.prototype です。以下の通りです
Math.__proto__ === Object.prototype // true Math.construrctor == Object // true JSON.__proto__ === Object.prototype // true JSON.construrctor == Object //true
上記の関数オブジェクトにはカスタムのものも確かに含まれています。以下の通り
rreeeこれはどういう意味ですか?
** ルート コンストラクターの Object や Function 自体も含め、すべてのコンストラクターは Function.prototype から来ています。すべてのコンストラクターは Function.prototype のプロパティとメソッドを継承します。 length、call、apply、bind など**
(最初の文を理解する必要があります。次のセクションで 2 番目の文について引き続き説明します。最初に穴を掘ります:))
Function.prototype も唯一のものです。 typeof XXX.prototype は関数のプロトタイプです。他のコンストラクターのプロトタイプはオブジェクトです (理由はセクション 3 で説明されています)。以下のとおりです (再確認):
// 函数声明
function Person() {}
// 函数表达式
var Perosn = function() {}
console.log(Person.__proto__ === Function.prototype) // true
console.log(Man.__proto__ === Function.prototype) // trueああ、これは空の関数 console.log(Function.prototype) であることも上で述べましたが、見てください (注意してください。これについては次のセクションでもう一度説明します) )
わかりました。すべてのコンストラクター (組み込みおよびカスタムを含む) の __proto__ は Function.prototype です。では、Function.prototype の __proto__ は誰ですか?
JavaScript の関数も第一級市民であることを皆さんも聞いたことがあると思いますが、これをどのように示すことができますか?以下に示すように
console.log(typeof Function.prototype) // function console.log(typeof Object.prototype) // object console.log(typeof Number.prototype) // object console.log(typeof Boolean.prototype) // object console.log(typeof String.prototype) // object console.log(typeof Array.prototype) // object console.log(typeof RegExp.prototype) // object console.log(typeof Error.prototype) // object console.log(typeof Date.prototype) // object console.log(typeof Object.prototype) // object
これは、すべてのコンストラクターも通常の JS オブジェクトであり、コンストラクターに属性を追加/削除できることを示しています。同時に、Object.prototype のすべてのメソッド (toString、valueOf、hasOwnProperty など) も継承します。 (最初の文も理解しておく必要があります。次のセクションで 2 番目の文について引き続き説明します。穴を掘る必要はありません。それでも同じ穴です;))
Object.prototype のプロトは誰ですか最後に?
Object.prototype.__proto__ === null // true
は先頭に到達しており、null です。 (今すぐ読んで、第 5 章を振り返ってください。理解できましたか?)
8. プロトタイプ
ECMAScript コアによって定義されたすべてのプロパティの中で、最も興味深いものはプロトタイプ プロパティです。 ECMAScript の参照型の場合、プロトタイプは、すべてのインスタンス メソッドが格納される実際の場所です。つまり、toString() や valueOf() などのメソッドは実際にはプロトタイプ名で保存されますが、それぞれのオブジェクトのインスタンスを通じてアクセスされます。
——『JavaScript 高度なプログラミング』第 3 版 P116
JS には次のような組み込みメソッドがあることがわかっています。
オブジェクトは、constructor/toString()/valueOf() やその他のメソッドを使用できます。配列では、map ()/filter()/reducer() などのメソッドを使用できます。
Numbers では、parseInt()/parseFloat() などのメソッドを使用できます。 ? ?
関数を作成するとき:
var person = new Object()
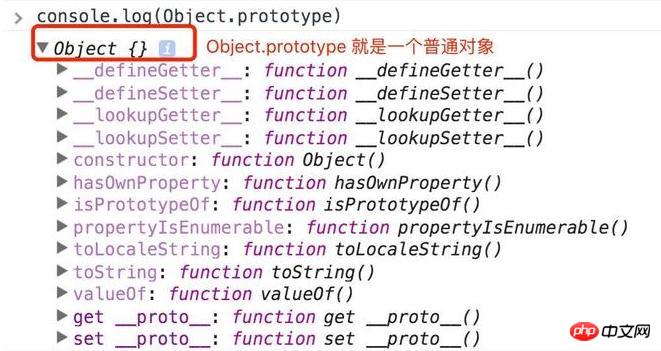 Object のすべてのメソッドを継承します。プロトタイプの
Object のすべてのメソッドを継承します。プロトタイプの
オブジェクトには上記のプロパティとメソッドがあります。
それで、 Person.constructor または Person.hasOwnProperty を使用できます。
配列を作成するとき:
var num = new Array()
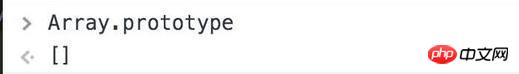 Array。
Array。
を使用して、プロトティ内のプロパティを除くすべてのプロパティ名 (列挙不可能なプロパティを含む) を取得し、配列を返すことができます:
var arrayAllKeys = Array.prototype; // [] 空数组// 只得到 arrayAllKeys 这个对象里所有的属性名(不会去找 arrayAllKeys.prototype 中的属性)console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(arrayAllKeys));
/* 输出:
["length", "constructor", "toString", "toLocaleString", "join", "pop", "push",
"concat", "reverse", "shift", "unshift", "slice", "splice", "sort", "filter", "forEach",
"some", "every", "map", "indexOf", "lastIndexOf", "reduce", "reduceRight",
"entries", "keys", "copyWithin", "find", "findIndex", "fill"]
*/
这样你就明白了随便声明一个数组,它为啥能用那么多方法了。
细心的你肯定发现了Object.getOwnPropertyNames(arrayAllKeys) 输出的数组里并没有 constructor/hasOwnPrototype等对象的方法(你肯定没发现)。
但是随便定义的数组也能用这些方法
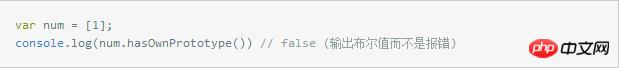
var num = [1];console.log(num.hasOwnPrototype()) // false (输出布尔值而不是报错)
Why ???
因为Array.prototype 虽然没这些方法,但是它有原型对象(__proto__):
// 上面我们说了 Object.prototype 就是一个普通对象。 Array.prototype.__proto__ == Object.prototype
所以 Array.prototype 继承了对象的所有方法,当你用num.hasOwnPrototype()时,JS 会先查一下它的构造函数 (Array) 的原型对象 Array.prototype 有没有有hasOwnPrototype()方法,没查到的话继续查一下 Array.prototype 的原型对象 Array.prototype.__proto__有没有这个方法。
当我们创建一个函数时:
var f = new Function("x","return x*x;");
//当然你也可以这么创建 f = function(x){ return x*x }
console.log(f.arguments) // arguments 方法从哪里来的?
console.log(f.call(window)) // call 方法从哪里来的?
console.log(Function.prototype) // function() {} (一个空的函数)
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(Function.prototype));
/* 输出
["length", "name", "arguments", "caller", "constructor", "bind", "toString", "call", "apply"]
*/我们再复习第八小节这句话:
所有函数对象proto都指向 Function.prototype,它是一个空函数(Empty function)
嗯,我们验证了它就是空函数。不过不要忽略前半句。我们枚举出了它的所有的方法,所以所有的函数对象都能用,比如:

九. 复习一下
第八小节我们总结了:
所有函数对象的 __proto__ 都指向 Function.prototype,它是一个空函数(Empty function)
但是你可别忘了在第三小节我们总结的:
所有对象的 __proto__ 都指向其构造器的 prototype
我们下面再复习下这句话。
先看看 JS 内置构造器:
var obj = {name: 'jack'}
var arr = [1,2,3]
var reg = /hello/g
var date = new Date
var err = new Error('exception')
console.log(obj.__proto__ === Object.prototype) // true
console.log(arr.__proto__ === Array.prototype) // true
console.log(reg.__proto__ === RegExp.prototype) // true
console.log(date.__proto__ === Date.prototype) // true
console.log(err.__proto__ === Error.prototype) // true再看看自定义的构造器,这里定义了一个 Person:
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
var p = new Person('jack')
console.log(p.__proto__ === Person.prototype) // truep 是 Person 的实例对象,p 的内部原型总是指向其构造器 Person 的原型对象 prototype。
每个对象都有一个 constructor 属性,可以获取它的构造器,因此以下打印结果也是恒等的:
function Person(name) {
this.name = name
}
var p = new Person('jack')
console.log(p.__proto__ === p.constructor.prototype) // true上面的Person没有给其原型添加属性或方法,这里给其原型添加一个getName方法:
function Person(name) {
this.name = name
}
// 修改原型
Person.prototype.getName = function() {}
var p = new Person('jack')
console.log(p.__proto__ === Person.prototype) // true
console.log(p.__proto__ === p.constructor.prototype) // true可以看到p.__proto__与Person.prototype,p.constructor.prototype都是恒等的,即都指向同一个对象。
如果换一种方式设置原型,结果就有些不同了:
function Person(name) {
this.name = name
}
// 重写原型Person.prototype = {
getName: function() {}
}
var p = new Person('jack')
console.log(p.__proto__ === Person.prototype) // true
console.log(p.__proto__ === p.constructor.prototype) // false这里直接重写了 Person.prototype(注意:上一个示例是修改原型)。输出结果可以看出p.__proto__仍然指向的是Person.prototype,而不是p.constructor.prototype。
这也很好理解,给Person.prototype赋值的是一个对象直接量{getName: function(){}},使用对象直接量方式定义的对象其构造器(constructor)指向的是根构造器Object,Object.prototype是一个空对象{},{}自然与{getName: function(){}}不等。如下:
var p = {}
console.log(Object.prototype) // 为一个空的对象{}
console.log(p.constructor === Object) // 对象直接量方式定义的对象其constructor为Objectconsole.log(p.constructor.prototype === Object.prototype) // 为true,
不解释(๑ˇ3ˇ๑)十. 原型链(再复习一下:)
下面这个例子你应该能明白了!
function Person(){
}var person1 = new Person();
console.log(person1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // true
console.log(Person.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype) //true
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__) //null
Person.__proto__ == Function.prototype; //true
console.log(Function.prototype)// function(){} (空函数)
var num = new Array()console.log(num.__proto__ == Array.prototype) // true
console.log( Array.prototype.__proto__ == Object.prototype) // true
console.log(Array.prototype) // [] (空数组)
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__) //null
console.log(Array.__proto__ == Function.prototype)// true疑点解惑:
Object.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true
Object 是函数对象,是通过new Function()创建的,所以Object.__proto__指向Function.prototype。(参照第八小节:「所有函数对象的__proto__都指向Function.prototype」)
Function.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true
Function 也是对象函数,也是通过new Function()创建,所以Function.__proto__指向Function.prototype。
自己是由自己创建的,好像不符合逻辑,但仔细想想,现实世界也有些类似,你是怎么来的,你妈生的,你妈怎么来的,你姥姥生的,……类人猿进化来的,那类人猿从哪来,一直追溯下去……,就是无,(NULL生万物)
正如《道德经》里所说“无,名天地之始”。
Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype //true
其实这一点我也有点困惑,不过也可以试着解释一下。
Function.prototype是个函数对象,理论上他的__proto__应该指向 Function.prototype,就是他自己,自己指向自己,没有意义。
JS一直强调万物皆对象,函数对象也是对象,给他认个祖宗,指向Object.prototype。Object.prototype.__proto__ === null,保证原型链能够正常结束。
十一 总结
原型和原型链是JS实现继承的一种模型。
原型链的形成是真正是靠__proto__ 而非prototype
要深入理解这句话,我们再举个例子,看看前面你真的理解了吗?
var animal = function(){}; var dog = function(){};
animal.price = 2000;
dog.prototype = animal; var tidy = new dog(); console.log(dog.price) //undefined
console.log(tidy.price) // 2000这里解释一下:
var dog = function(){};
dog.prototype.price = 2000; var tidy = new dog(); console.log(tidy.price); // 2000
console.log(dog.price); //undefined
var dog = function(){}; var tidy = new dog();
tidy.price = 2000; console.log(dog.price); //undefined这个明白吧?想一想我们上面说过这句话:
实例(tidy)和 原型对象(dog.prototype)存在一个连接。不过,要明确的真正重要的一点就是,这个连接存在于实例(tidy)与构造函数的原型对象(dog.prototype)之间,而不是存在于实例(tidy)与构造函数(dog)之间。
聪明的你肯定想通了吧 :)
以上がJSプロトタイプとプロトタイプチェーンの詳しい解説(3)の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7488
7488
 15
15
 1377
1377
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 19
19
 39
39
 Win11での管理者権限の取得について詳しく解説
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Win11での管理者権限の取得について詳しく解説
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows オペレーティング システムは世界で最も人気のあるオペレーティング システムの 1 つであり、その新バージョン Win11 が大きな注目を集めています。 Win11 システムでは、管理者権限の取得は重要な操作であり、管理者権限を取得すると、ユーザーはシステム上でより多くの操作や設定を実行できるようになります。この記事では、Win11システムで管理者権限を取得する方法と、権限を効果的に管理する方法を詳しく紹介します。 Win11 システムでは、管理者権限はローカル管理者とドメイン管理者の 2 種類に分かれています。ローカル管理者はローカル コンピュータに対する完全な管理権限を持っています
 Oracle SQLの除算演算の詳細説明
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Oracle SQLの除算演算の詳細説明
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
OracleSQL の除算演算の詳細な説明 OracleSQL では、除算演算は一般的かつ重要な数学演算であり、2 つの数値を除算した結果を計算するために使用されます。除算はデータベース問合せでよく使用されるため、OracleSQL での除算演算とその使用法を理解することは、データベース開発者にとって重要なスキルの 1 つです。この記事では、OracleSQL の除算演算に関する関連知識を詳細に説明し、読者の参考となる具体的なコード例を示します。 1. OracleSQL での除算演算
 PHPモジュロ演算子の役割と使い方を詳しく解説
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
PHPモジュロ演算子の役割と使い方を詳しく解説
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
PHP のモジュロ演算子 (%) は、2 つの数値を除算した余りを取得するために使用されます。この記事では、モジュロ演算子の役割と使用法について詳しく説明し、読者の理解を深めるために具体的なコード例を示します。 1. モジュロ演算子の役割 数学では、整数を別の整数で割ると、商と余りが得られます。たとえば、10 を 3 で割ると、商は 3 になり、余りは 1 になります。モジュロ演算子は、この剰余を取得するために使用されます。 2. モジュロ演算子の使用法 PHP では、% 記号を使用してモジュロを表します。
 Linuxシステムコールsystem()関数の詳細説明
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Linuxシステムコールsystem()関数の詳細説明
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Linux システム コール system() 関数の詳細説明 システム コールは、Linux オペレーティング システムの非常に重要な部分であり、システム カーネルと対話する方法を提供します。その中でも、system()関数はよく使われるシステムコール関数の一つです。この記事では、system() 関数の使用法を詳しく紹介し、対応するコード例を示します。システム コールの基本概念 システム コールは、ユーザー プログラムがオペレーティング システム カーネルと対話する方法です。ユーザープログラムはシステムコール関数を呼び出してオペレーティングシステムを要求します。
 Linuxのcurlコマンドの詳しい説明
Feb 21, 2024 pm 10:33 PM
Linuxのcurlコマンドの詳しい説明
Feb 21, 2024 pm 10:33 PM
Linuxのcurlコマンドの詳細な説明 要約:curlは、サーバーとのデータ通信に使用される強力なコマンドラインツールです。この記事では、curl コマンドの基本的な使用法を紹介し、読者がコマンドをよりよく理解して適用できるように実際のコード例を示します。 1.カールとは何ですか? curl は、さまざまなネットワーク要求を送受信するために使用されるコマンド ライン ツールです。 HTTP、FTP、TELNETなどの複数のプロトコルをサポートし、ファイルアップロード、ファイルダウンロード、データ送信、プロキシなどの豊富な機能を提供します。
 簡単な JavaScript チュートリアル: HTTP ステータス コードを取得する方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
簡単な JavaScript チュートリアル: HTTP ステータス コードを取得する方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript チュートリアル: HTTP ステータス コードを取得する方法、特定のコード例が必要です 序文: Web 開発では、サーバーとのデータ対話が頻繁に発生します。サーバーと通信するとき、多くの場合、返された HTTP ステータス コードを取得して操作が成功したかどうかを判断し、さまざまなステータス コードに基づいて対応する処理を実行する必要があります。この記事では、JavaScript を使用して HTTP ステータス コードを取得する方法を説明し、いくつかの実用的なコード例を示します。 XMLHttpRequestの使用
 C言語学習ルートを詳細に分析
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:38 AM
C言語学習ルートを詳細に分析
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:38 AM
ソフトウェア開発の分野で広く使用されているプログラミング言語として、C 言語は多くの初心者プログラマーにとって最初の選択肢です。 C言語を学ぶと、プログラミングの基礎知識を定着させるだけでなく、問題解決能力や思考力も向上します。この記事では、初心者が学習プロセスをより適切に計画できるようにするための C 言語学習ロードマップを詳しく紹介します。 1. 基本的な文法を学ぶ C 言語の学習を始める前に、まず C 言語の基本的な文法規則を理解する必要があります。これには、変数とデータ型、演算子、制御ステートメント (if ステートメント、
 Promise.resolve() について詳しく見る
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Promise.resolve() について詳しく見る
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Promise.resolve() の詳細な説明には、特定のコード例が必要です。Promise は、非同期操作を処理するための JavaScript のメカニズムです。実際の開発では、順番に実行する必要があるいくつかの非同期タスクを処理する必要があることがよくあり、満たされた Promise オブジェクトを返すために Promise.resolve() メソッドが使用されます。 Promise.resolve() は Promise クラスの静的メソッドであり、




