
この記事の内容は、React の Diff アルゴリズムとは何ですか? Diff アルゴリズムの戦略と実装には一定の参考値がありますので、困っている方は参考にしていただければ幸いです。
従来の Diff: diff アルゴリズムは、HTML DOM 構造の差分検索アルゴリズムです。ツリーアルゴリズムの検索、および 2 つのツリーの差を計算する時間計算量は O(n^3) ですが、これは明らかにコストが高すぎるため、この従来のアルゴリズムを React が採用することは不可能です。
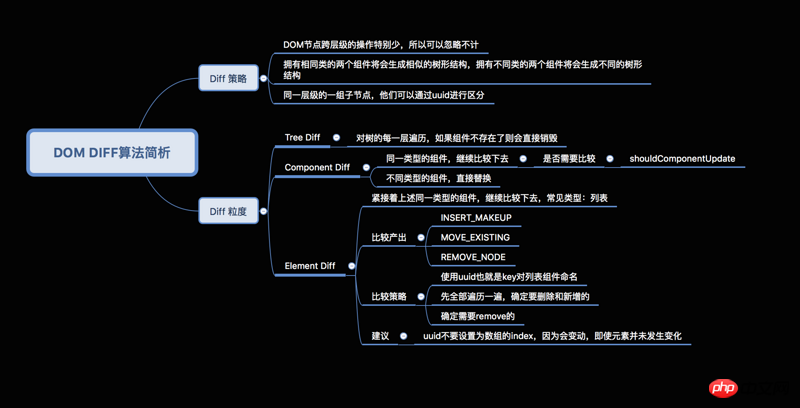
#同じクラスを持つ 2 つのコンポーネントは同様のツリー構造を生成し、異なるクラスを持つ 2 つのコンポーネントは異なるツリー構造を生成します (コンポーネント差分)
##React Diff アルゴリズム最適化戦略チャート:
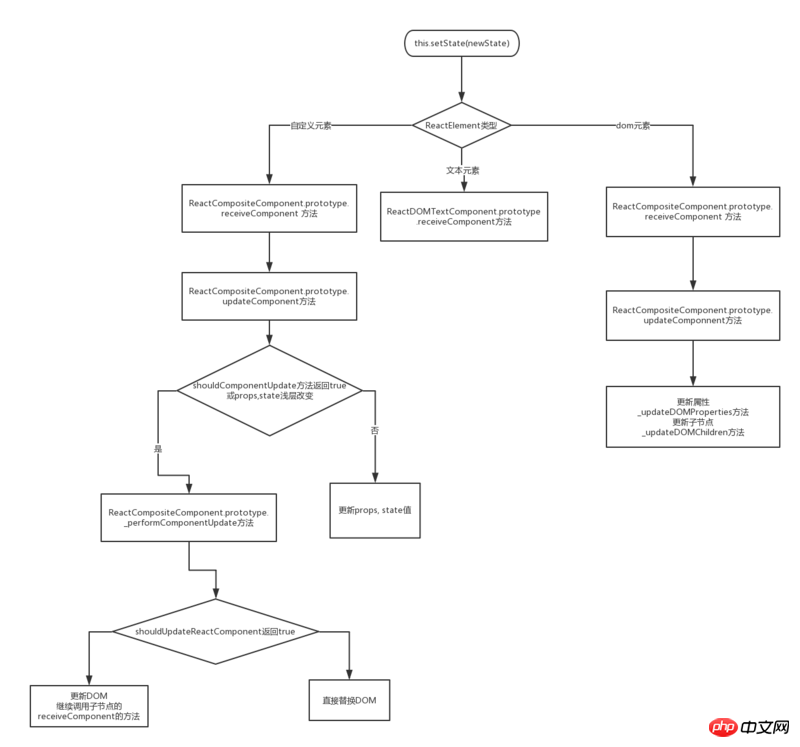
 テキスト ノードの更新は非常に簡単で、コピーを直接更新するだけです。
テキスト ノードの更新は非常に簡単で、コピーを直接更新するだけです。
ブラウザの基本要素の更新は 2 つの部分に分かれています:
実際、Diff アルゴリズムは React 更新フェーズの DOM 要素更新プロセス中にのみ呼び出されます。 ?
#1. テキスト タイプが更新され、内容が異なる場合は、複雑な Diff アルゴリズムを呼び出すことなく、直接更新および置換されます。
ReactDOMTextComponent.prototype.receiveComponent(nextText, transaction) {
//与之前保存的字符串比较
if (nextText !== this._currentElement) {
this._currentElement = nextText;
var nextStringText = '' + nextText;
if (nextStringText !== this._stringText) {
this._stringText = nextStringText;
var commentNodes = this.getHostNode();
// 替换文本元素
DOMChildrenOperations.replaceDelimitedText(
commentNodes[0],
commentNodes[1],
nextStringText
);
}
}
}class Tab extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
index: 1,
}
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
....
}
render() {
return (
<p>
</p><p>item1</p>
<p>item1</p>
)
}
}ご存知のとおり、パッケージング ボックスとして理解できます)。 React レンダリング メカニズムの図を参照してください。カスタム コンポーネントは最終的に React Diff 最適化戦略 1 と結合されます (異なるクラスの 2 つのコンポーネントは異なる構造を持っています)
3 基本要素:
ReactDOMComponent.prototype.receiveComponent = function(nextElement, transaction, context) {
var prevElement = this._currentElement;
this._currentElement = nextElement;
this.updateComponent(transaction, prevElement, nextElement, context);
}
ReactDOMComponent.prototype.updateComponent = function(transaction, prevElement, nextElement, context) {
//需要单独的更新属性
this._updateDOMProperties(lastProps, nextProps, transaction, isCustomComponentTag);
//再更新子节点
this._updateDOMChildren(
lastProps,
nextProps,
transaction,
context
);
// ......
}この中で、diff アルゴリズムは _updateDOMChildren メソッドで内部的に呼び出されます。
_updateChildren: function(nextNestedChildrenElements, transaction, context) {
var prevChildren = this._renderedChildren;
var removedNodes = {};
var mountImages = [];
// 获取新的子元素数组
var nextChildren = this._reconcilerUpdateChildren(
prevChildren,
nextNestedChildrenElements,
mountImages,
removedNodes,
transaction,
context
);
if (!nextChildren && !prevChildren) {
return;
}
var updates = null;
var name;
var nextIndex = 0;
var lastIndex = 0;
var nextMountIndex = 0;
var lastPlacedNode = null;
for (name in nextChildren) {
if (!nextChildren.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
continue;
}
var prevChild = prevChildren && prevChildren[name];
var nextChild = nextChildren[name];
if (prevChild === nextChild) {
// 同一个引用,说明是使用的同一个component,所以我们需要做移动的操作
// 移动已有的子节点
// NOTICE:这里根据nextIndex, lastIndex决定是否移动
updates = enqueue(
updates,
this.moveChild(prevChild, lastPlacedNode, nextIndex, lastIndex)
);
// 更新lastIndex
lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex);
// 更新component的.mountIndex属性
prevChild._mountIndex = nextIndex;
} else {
if (prevChild) {
// 更新lastIndex
lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex);
}
// 添加新的子节点在指定的位置上
updates = enqueue(
updates,
this._mountChildAtIndex(
nextChild,
mountImages[nextMountIndex],
lastPlacedNode,
nextIndex,
transaction,
context
)
);
nextMountIndex++;
}
// 更新nextIndex
nextIndex++;
lastPlacedNode = ReactReconciler.getHostNode(nextChild);
}
// 移除掉不存在的旧子节点,和旧子节点和新子节点不同的旧子节点
for (name in removedNodes) {
if (removedNodes.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
updates = enqueue(
updates,
this._unmountChild(prevChildren[name], removedNodes[name])
);
}
}
}、DOM 構造の安定性を維持することに注意してください。つまり、DOM 構造の動的操作をできる限り少なくすることです (特にモバイル)。オペレーション。
コンポーネントの不要な更新を減らすために shouldComponentUpdate() の使用に注意してください。
同様の構造は可能な限りコンポーネントにカプセル化する必要があります。これにより、コードの量が削減されるだけでなく、コンポーネント diff のパフォーマンス消費も削減されます。
要素の差分に基づく:
リスト構造の場合は、最後の要素を減らすようにしてください。ノード数が多すぎる場合や更新頻度が高すぎる場合、ノードをリストの先頭に移動する操作は React のレンダリング パフォーマンスにある程度影響します。
以上がReact の Diff アルゴリズムとは何ですか? Diff アルゴリズムの戦略と実装の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。