
この記事では、js の一般的な継承メソッドとは何なのかを例を挙げて紹介します。 (例付き) なので、困っている友人の参考になれば幸いです。
#オブジェクト指向プログラミングの非常に重要な側面は、オブジェクトの継承です。B オブジェクトを継承することにより、A オブジェクトは B オブジェクトのすべてのプロパティとメソッドを直接所有できます。これはコードを再利用する場合に非常に役立ちます。
ほとんどのオブジェクト指向プログラミング言語は、「クラス」を通じてオブジェクトの継承を実装します。従来、JavaScript 言語の継承はクラス (ES6 ではクラス構文が導入されました) を通じてではなく、「プロトタイプ オブジェクト」を通じて実装されていました。では、JS の一般的な継承メソッドにはどのようなものがあるのでしょうか? この記事のソース コードが必要な場合は、6 つの一般的な継承方法
方法 1. プロトタイプ チェーンの継承# をクリックしてください。 ## このアプローチの鍵は次のとおりです。
サブタイプのプロトタイプは、親タイプのインスタンス オブジェクトです。 //父类型
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.play = [1, 2, 3]
this.setName = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () { }
//子类型
function Student(price) {
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = new Person() // 子类型的原型为父类型的一个实例对象
var s1 = new Student(15000)
var s2 = new Student(14000)
console.log(s1,s2)
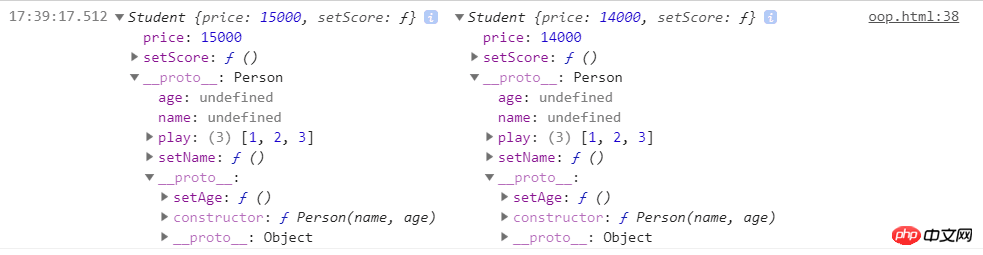 しかし、このメソッドの本質は、サブクラスのプロトタイプが親クラスのインスタンスを指すことです。したがって、 インスタンスPerson のインスタンスである __proto__ を介して Student.prototype にアクセスできるため、親クラスのプライベート メソッドにアクセスし、__proto__ を使用して親クラスのプロトタイプをポイントし、親クラス プロトタイプのメソッドを取得できます。 .
しかし、このメソッドの本質は、サブクラスのプロトタイプが親クラスのインスタンスを指すことです。したがって、 インスタンスPerson のインスタンスである __proto__ を介して Student.prototype にアクセスできるため、親クラスのプライベート メソッドにアクセスし、__proto__ を使用して親クラスのプロトタイプをポイントし、親クラス プロトタイプのメソッドを取得できます。 .
。したがって、親クラスのプライベートおよびパブリック メソッドとプロパティは、サブクラスのパブリック プロパティとして扱われます。
。基本的なデータ型を操作する場合は値を操作し、参照データ型を操作する場合はアドレスを操作することは誰もが知っています。親クラスのプライベート プロパティは、サブクラスによって継承されるときにパブリック属性として使用されるため、サブクラス 1 がこの属性を操作すると、サブクラス 2 に影響します。 s1.play.push(4)
console.log(s1.play, s2.play)
console.log(s1.__proto__ === s2.__proto__)//true
console.log(s1.__proto__.__proto__ === s2.__proto__.__proto__)//true
 s1 の再生属性が変更され、それに応じて s2 の再生属性も変更されます。
s1 の再生属性が変更され、それに応じて s2 の再生属性も変更されます。
もう 1 つ注意すべき点は、
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(price) {
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
// Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }//在这里写子类的原型方法和属性是无效的,
//因为会改变原型的指向,所以应该放到重新指定之后
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student(15000)
console.log(s1)
プロトタイプ メソッド/プロトタイプ属性を親クラスに追加しました。サブクラスからアクセスできます
##シンプルで実装が簡単
多重継承を実装できない
プロトタイプ オブジェクトのすべてのプロパティはすべてのインスタンスで共有されます
サブクラス インスタンスを作成する場合、パラメーターを親クラスのコンストラクターに渡すことはできません
サブクラスに属性とメソッドを追加する場合は、
Student.prototype = new Person()このメソッドの重要な点は次のとおりです。サブタイプ コンストラクターで一般的な call() を使用して、親型コンストラクター
<script>
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setName = function () {}
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age) // 相当于: this.Person(name, age)
/*this.name = name
this.age = age*/
this.price = price
}
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)</script>
#このメソッドは部分的な継承のみを実装します。親クラスのプロトタイプにもメソッドと属性がある場合、サブクラスは取得できません。これらのメソッドと属性。 console.log(s1.setAge())//Uncaught TypeError: s1.setAge is not a function
 特長
特長
:
プロトタイプチェーン継承で親クラスの参照属性を共有するサブクラスインスタンスの問題を解決します
:
インスタンスは親クラスのインスタンスではなく、サブクラスのインスタンスです
优点: 可以继承实例属性/方法,也可以继承原型属性/方法 不存在引用属性共享问题 可传参 函数可复用 缺点: 调用了两次父类构造函数,生成了两份实例 方式四: 组合继承优化1 这种方式通过父类原型和子类原型指向同一对象,子类可以继承到父类的公有方法当做自己的公有方法,而且不会初始化两次实例方法/属性,避免的组合继承的缺点。 优点: 不会初始化两次实例方法/属性,避免的组合继承的缺点 缺点: 没办法辨别是实例是子类还是父类创造的,子类和父类的构造函数指向是同一个。 方式五: 组合继承优化2 借助原型可以基于已有的对象来创建对象, 同样的,Student继承了所有的Person原型对象的属性和方法。目前来说,最完美的继承方法! 方式六:ES6中class 的继承 ES6中引入了class关键字,class可以通过extends关键字实现继承,还可以通过static关键字定义类的静态方法,这比 ES5 的通过修改原型链实现继承,要清晰和方便很多。 ES5 的继承,实质是先创造子类的实例对象this,然后再将父类的方法添加到this上面(Parent.apply(this))。ES6 的继承机制完全不同,实质是先将父类实例对象的属性和方法,加到this上面(所以必须先调用super方法),然后再用子类的构造函数修改this。 需要注意的是,class关键字只是原型的语法糖,JavaScript继承仍然是基于原型实现的。 语法简单易懂,操作更方便 缺点: 并不是所有的浏览器都支持class关键字 function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setAge = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this,name,age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.constructor = Student//组合继承也是需要修复构造函数指向的
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
var s2 = new Student('Jack', 22, 14000)
console.log(s1)
console.log(s1.constructor) //Student
console.log(p1.constructor) //Person
这种方式融合原型链继承和构造函数的优点,是 JavaScript 中最常用的继承模式。不过也存在缺点就是无论在什么情况下,都会调用两次构造函数:一次是在创建子类型原型的时候,另一次是在子类型构造函数的内部,子类型最终会包含父类型对象的全部实例属性,但我们不得不在调用子类构造函数时重写这些属性。
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setAge = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = Person.prototype
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
console.log(s1)
但这种方式没办法辨别是对象是子类还是父类实例化console.log(s1 instanceof Student, s1 instanceof Person)//true true
console.log(s1.constructor)//Person
var B = Object.create(A)以A对象为原型,生成了B对象。B继承了A的所有属性和方法。 function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () {}
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype)//核心代码
Student.prototype.constructor = Student//核心代码
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
console.log(s1 instanceof Student, s1 instanceof Person) // true true
console.log(s1.constructor) //Student
console.log(s1)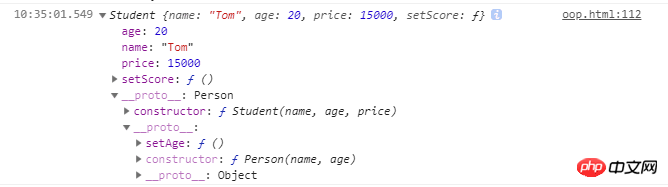
class Person {
//调用类的构造方法
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
//定义一般的方法
showName() {
console.log("调用父类的方法")
console.log(this.name, this.age);
}
}
let p1 = new Person('kobe', 39)
console.log(p1)
//定义一个子类
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, salary) {
super(name, age)//通过super调用父类的构造方法
this.salary = salary
}
showName() {//在子类自身定义方法
console.log("调用子类的方法")
console.log(this.name, this.age, this.salary);
}
}
let s1 = new Student('wade', 38, 1000000000)
console.log(s1)
s1.showName()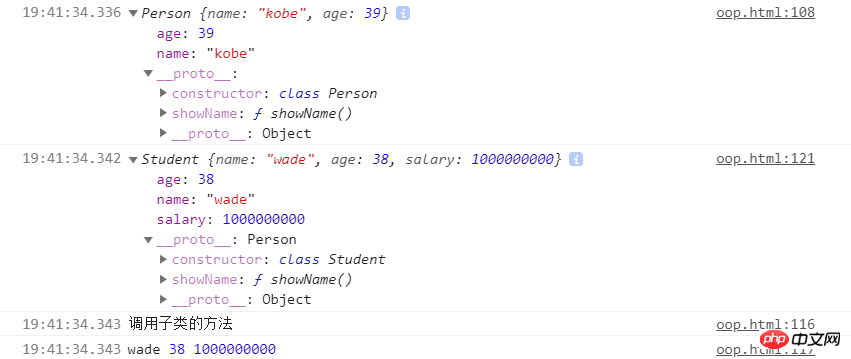
优点:
以上がjsの一般的な継承メソッドは何ですか? (例付き)の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。