ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。
WeChat ミニ プログラム開発チュートリアルミニ プログラムの依存関係分析の実践を紹介します。

webpack を使用したことがある学生は、現在のプロジェクトの js ファイルの依存関係を分析するために使用できる ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。 を知っている必要があります。
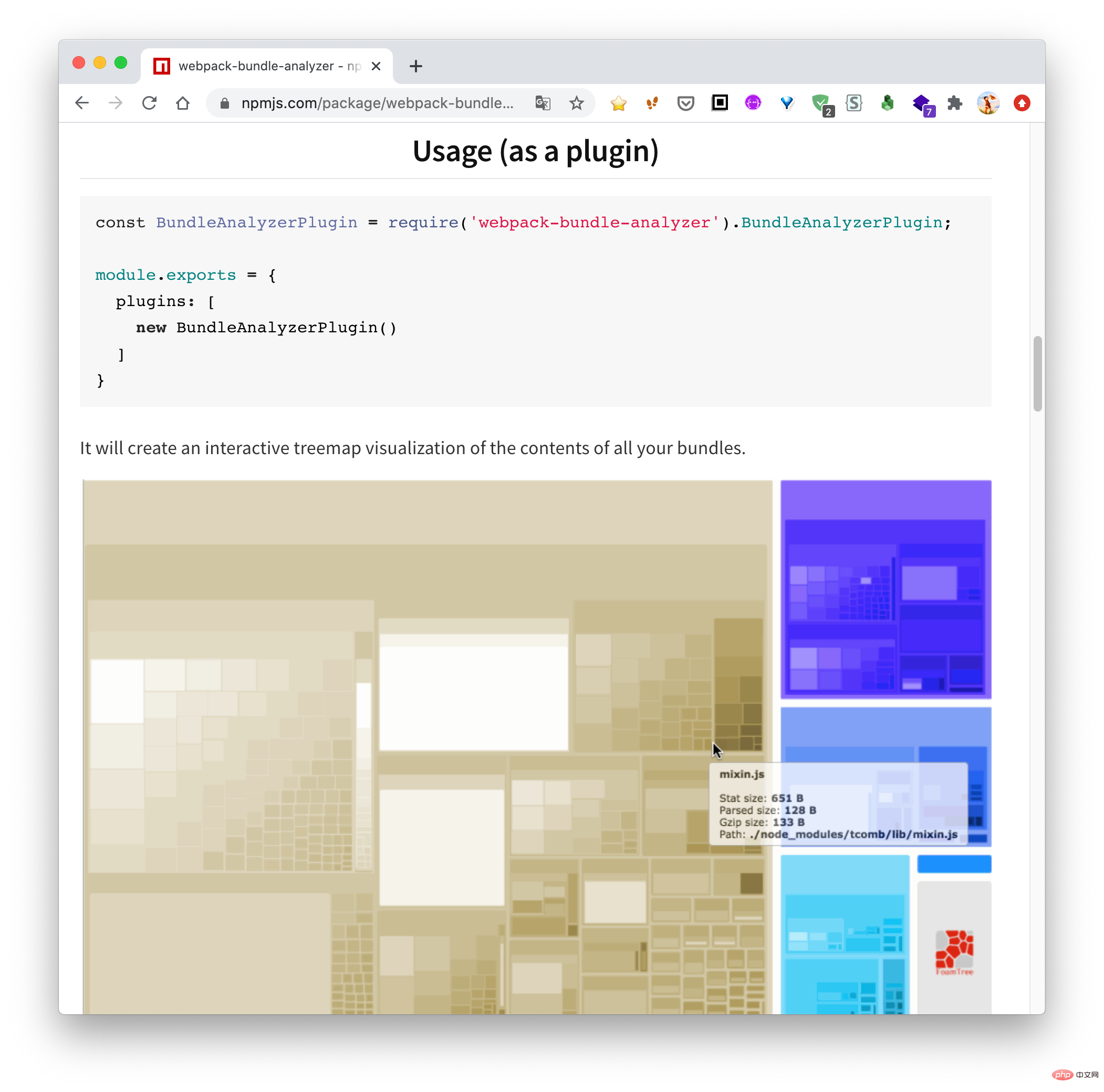
私は最近小規模プログラムのビジネスを行っており、小規模プログラムはパッケージ サイズに特に敏感であるため、現在のメインパッケージとミニプログラムのサブコントラクト間の依存関係。数日間試行錯誤した後、最終的には成功しました。その効果は次のとおりです。
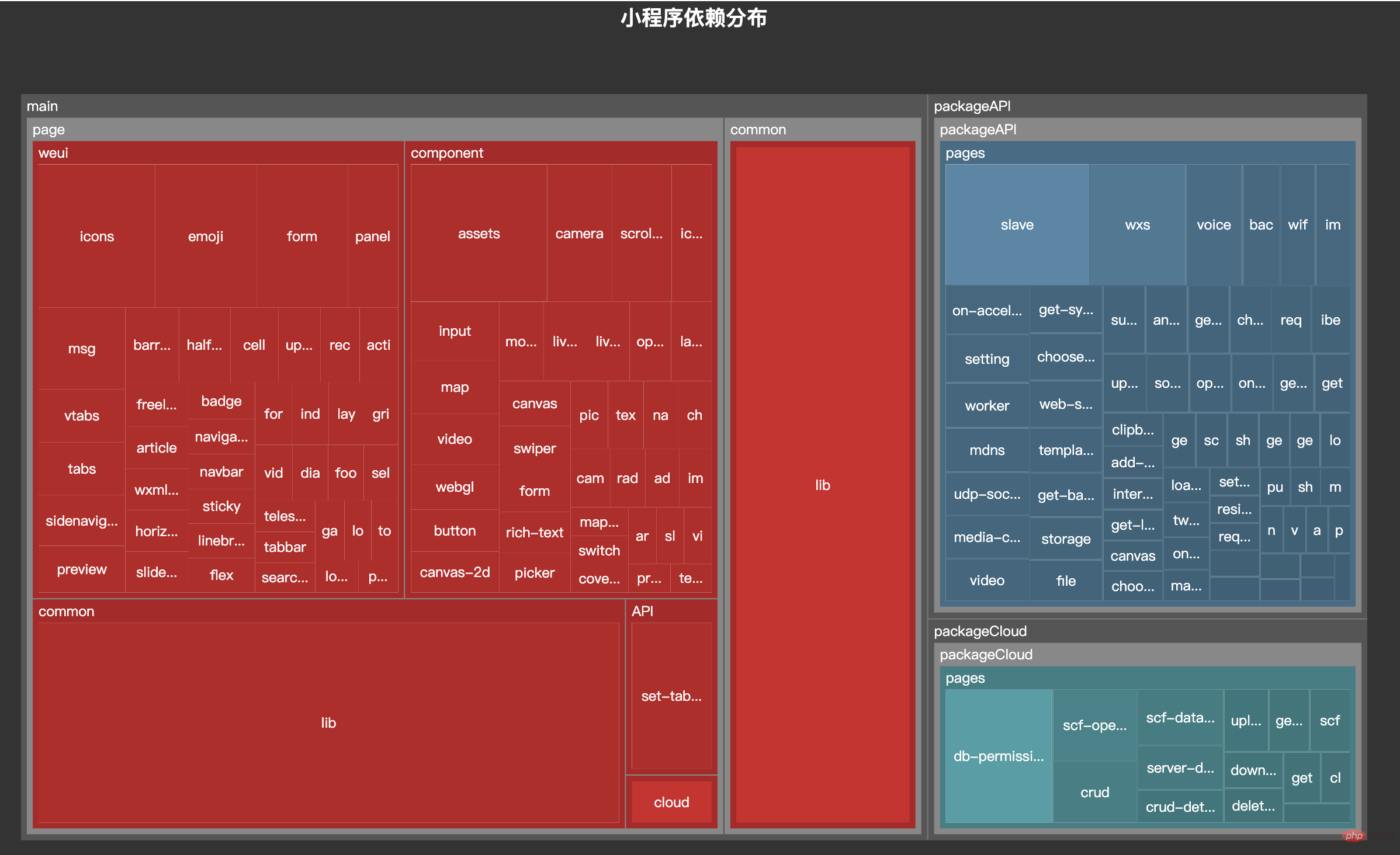
今日の記事では、このツールを実装します。
ミニ プログラムの入り口
ミニ プログラムのページは、app.json の pages パラメーターによって定義されます。これは、どのページを指定するかを指定するために使用されます。ミニプログラムを構成するページの各項目は、ページのパス(ファイル名を含む)情報に対応します。 pages の各ページについて、アプレットは対応する json、js、wxml、wxss## を探します # 4 つのファイルが処理されます。
├── app.js ├── app.json ├── app.wxss ├── pages │ │── index │ │ ├── index.wxml │ │ ├── index.js │ │ ├── index.json │ │ └── index.wxss │ └── logs │ ├── logs.wxml │ └── logs.js └── utils复制代码
{ "pages": ["pages/index/index", "pages/logs/logs"]
}复制代码depend.js を作成します。依存関係の解析に関連する作業はこのファイルに実装されます。
$ git clone git@github.com:wechat-miniprogram/miniprogram-demo.git $ cd miniprogram-demo $ touch depend.js复制代码
app.json をエントリとして使用すると、すべてのファイルを取得できます。メインパッケージページの下にあります。
const fs = require('fs-extra')const path = require('path')const root = process.cwd()class Depend { constructor() { this.context = path.join(root, 'miniprogram')
} // 获取绝对地址
getAbsolute(file) { return path.join(this.context, file)
} run() { const appPath = this.getAbsolute('app.json') const appJson = fs.readJsonSync(appPath) const { pages } = appJson // 主包的所有页面
}
}复制代码json、js、wxml、wxss: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">const Extends = ['.js', '.json', '.wxml', '.wxss']class Depend { constructor() { // 存储文件
this.files = new Set() this.context = path.join(root, 'miniprogram')
} // 修改文件后缀
replaceExt(filePath, ext = '') { const dirName = path.dirname(filePath) const extName = path.extname(filePath) const fileName = path.basename(filePath, extName) return path.join(dirName, fileName + ext)
} run() { // 省略获取 pages 过程
pages.forEach(page => { // 获取绝对地址
const absPath = this.getAbsolute(page)
Extends.forEach(ext => { // 每个页面都需要判断 js、json、wxml、wxss 是否存在
const filePath = this.replaceExt(absPath, ext) if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) { this.files.add(filePath)
}
})
})
}
}复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div>これで、ページ内のページに関連するファイルがファイルフィールドに保存されます。
ツリー構造の構築
ファイルを取得した後、依存関係を後で表示するために、各ファイルに基づいてツリー構造のファイル ツリーを構築する必要があります。
pages
ディレクトリがあり、その pages ディレクトリ内に detail、index という 2 つのページがあるとします。 、この 2 ページのフォルダーの下に 4 つの対応するファイルがあります。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">pages
├── detail
│ ├── detail.js
│ ├── detail.json
│ ├── detail.wxml
│ └── detail.wxss
└── index
├── index.js
├── index.json
├── index.wxml
└── index.wxss复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div>上記のディレクトリ構造に基づいて、次のようにファイル ツリー構造を構築します。
は現在のファイルまたはフォルダーのサイズを示すために使用され、childrenフォルダーを保存します。 ファイルの場合、children 属性はありません。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">pages = { "size": 8, "children": { "detail": { "size": 4, "children": { "detail.js": { "size": 1 }, "detail.json": { "size": 1 }, "detail.wxml": { "size": 1 }, "detail.wxss": { "size": 1 }
}
}, "index": { "size": 4, "children": { "index.js": { "size": 1 }, "index.json": { "size": 1 }, "index.wxml": { "size": 1 }, "index.wxss": { "size": 1 }
}
}
}
}复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div> まず、コンストラクターで
フィールドを構築してファイル ツリー データを保存します。次に、各ファイルを addToTree メソッドに渡してファイルを追加します。木に。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">class Depend { constructor() { this.tree = { size: 0, children: {}
} this.files = new Set() this.context = path.join(root, 'miniprogram')
}
run() { // 省略获取 pages 过程
pages.forEach(page => { const absPath = this.getAbsolute(page)
Extends.forEach(ext => { const filePath = this.replaceExt(absPath, ext) if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) { // 调用 addToTree
this.addToTree(filePath)
}
})
})
}
}复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div> 次に、
メソッドを実装します。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">class Depend { // 省略之前的部分代码
// 获取相对地址
getRelative(file) { return path.relative(this.context, file)
} // 获取文件大小,单位 KB
getSize(file) { const stats = fs.statSync(file) return stats.size / 1024
} // 将文件添加到树中
addToTree(filePath) { if (this.files.has(filePath)) { // 如果该文件已经添加过,则不再添加到文件树中
return
} const size = this.getSize(filePath) const relPath = this.getRelative(filePath) // 将文件路径转化成数组
// 'pages/index/index.js' =>
// ['pages', 'index', 'index.js']
const names = relPath.split(path.sep) const lastIdx = names.length - 1
this.tree.size += size let point = this.tree.children
names.forEach((name, idx) => { if (idx === lastIdx) {
point[name] = { size } return
} if (!point[name]) {
point[name] = {
size, children: {}
}
} else {
point[name].size += size
}
point = point[name].children
}) // 将文件添加的 files
this.files.add(filePath)
}
}复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div> 実行後、ファイルを
に出力して確認します。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"> run() { // ...
pages.forEach(page => { //...
})
fs.writeJSONSync('ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。', this.tree, { spaces: 2 })
}复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div>
 依存関係の取得
依存関係の取得
上記の手順は問題ないようですが、重要なリンクが抜けています。つまり、ファイル ツリーを構築する前に、また、出力がミニ プログラムの完全なファイル ツリーになるように、各ファイルの依存関係を取得する必要もあります。ファイルの依存関係は、
js、json、wxml、wxss の 4 つの部分に分割する必要があります。取得に依存する方法。 .js ファイルの依存関係を取得する
アプレットはモジュール化のために CommonJS をサポートします。es6 がオンになっている場合は、モジュール化のために ESM もサポートできます。
js ファイルの依存関係を取得したい場合は、まずモジュールをインポートするための js ファイルを記述する 3 つの方法を明確にする必要があります。次の 3 つの構文については、依存関係を取得するために Babel を導入できます。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">import a from './a.js'export b from './b.js'const c = require('./c.js')复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div>
を通じてコードを AST に変換し、@babel/traverse を通じて AST ノードを走査して、次の値を取得します。上記の3つのインポートメソッドを実行し、配列に配置します。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">const { parse } = require('@babel/parser')const { default: traverse } = require('@babel/traverse')class Depend { // ...
jsDeps(file) { const deps = [] const dirName = path.dirname(file) // 读取 js 文件内容
const content = fs.readFileSync(file, 'utf-8') // 将代码转化为 AST
const ast = parse(content, { sourceType: 'module', plugins: ['exportDefaultFrom']
}) // 遍历 AST
traverse(ast, { ImportDeclaration: ({ node }) => { // 获取 import from 地址
const { value } = node.source const jsFile = this.transformScript(dirName, value) if (jsFile) {
deps.push(jsFile)
}
}, ExportNamedDeclaration: ({ node }) => { // 获取 export from 地址
const { value } = node.source const jsFile = this.transformScript(dirName, value) if (jsFile) {
deps.push(jsFile)
}
}, CallExpression: ({ node }) => { if (
(node.callee.name && node.callee.name === 'require') &&
node.arguments.length >= 1
) { // 获取 require 地址
const [{ value }] = node.arguments const jsFile = this.transformScript(dirName, value) if (jsFile) {
deps.push(jsFile)
}
}
}
}) return deps
}
}复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div>依存モジュールのパスを取得した後、依存関係配列にパスをすぐに追加することはできません。これは、モジュール構文
によれば、サフィックスは省略でき、パスが必要であるためです。はファイル フォルダーです。デフォルトでは、フォルダー内の index.js がインポートされます。 <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">class Depend { // 获取某个路径的脚本文件
transformScript(url) { const ext = path.extname(url) // 如果存在后缀,表示当前已经是一个文件
if (ext === '.js' && fs.existsSync(url)) { return url
} // a/b/c => a/b/c.js
const jsFile = url + '.js'
if (fs.existsSync(jsFile)) { return jsFile
} // a/b/c => a/b/c/index.js
const jsIndexFile = path.join(url, 'index.js') if (fs.existsSync(jsIndexFile)) { return jsIndexFile
} return null
} jsDeps(file) {...}
}复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div>
を作成し、出力 deps が正しいかどうかを確認できます: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">// 文件路径:/Users/shenfq/Code/fork/miniprogram-demo/import a from './a.js'export b from '../b.js'const c = require('../../c.js')复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">ログイン後にコピー</div></div>
<p><img class="lazyload lazy" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/052/d1027296a3eafc6a3805451b6d9ef634-4.png" alt="ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。" data- style="max-width:90%" data- style="max-width:90%"></p>
<h3 id="获取-json-文件依赖">获取 .json 文件依赖</h3>
<p><code>json 文件本身是不支持模块化的,但是小程序可以通过 json 文件导入自定义组件,只需要在页面的 json 文件通过 usingComponents 进行引用声明。usingComponents 为一个对象,键为自定义组件的标签名,值为自定义组件文件路径:
{ "usingComponents": { "component-tag-name": "path/to/the/custom/component"
}
}复制代码自定义组件与小程序页面一样,也会对应四个文件,所以我们需要获取 json 中 usingComponents 内的所有依赖项,并判断每个组件对应的那四个文件是否存在,然后添加到依赖项内。
class Depend { // ...
jsonDeps(file) { const deps = [] const dirName = path.dirname(file) const { usingComponents } = fs.readJsonSync(file) if (usingComponents && typeof usingComponents === 'object') { Object.values(usingComponents).forEach((component) => {
component = path.resolve(dirName, component) // 每个组件都需要判断 js/json/wxml/wxss 文件是否存在
Extends.forEach((ext) => { const file = this.replaceExt(component, ext) if (fs.existsSync(file)) {
deps.push(file)
}
})
})
} return deps
}
}复制代码获取 .wxml 文件依赖
wxml 提供两种文件引用方式 import 和 include。
<import></import><include></include>复制代码
wxml 文件本质上还是一个 html 文件,所以可以通过 html parser 对 wxml 文件进行解析,关于 html parser 相关的原理可以看我之前写过的文章 《Vue 模板编译原理》。
const htmlparser2 = require('htmlparser2')class Depend { // ...
wxmlDeps(file) { const deps = [] const dirName = path.dirname(file) const content = fs.readFileSync(file, 'utf-8') const htmlParser = new htmlparser2.Parser({ onopentag(name, attribs = {}) { if (name !== 'import' && name !== 'require') { return
} const { src } = attribs if (src) { return
} const wxmlFile = path.resolve(dirName, src) if (fs.existsSync(wxmlFile)) {
deps.push(wxmlFile)
}
}
})
htmlParser.write(content)
htmlParser.end() return deps
}
}复制代码获取 .wxss 文件依赖
最后 wxss 文件导入样式和 css 语法一致,使用 @import 语句可以导入外联样式表。
@import "common.wxss";复制代码
可以通过 postcss 解析 wxss 文件,然后获取导入文件的地址,但是这里我们偷个懒,直接通过简单的正则匹配来做。
class Depend { // ...
wxssDeps(file) { const deps = [] const dirName = path.dirname(file) const content = fs.readFileSync(file, 'utf-8') const importRegExp = /@import\\s*['"](.+)['"];*/g
let matched while ((matched = importRegExp.exec(content)) !== null) { if (!matched[1]) { continue
} const wxssFile = path.resolve(dirName, matched[1]) if (fs.existsSync(wxmlFile)) {
deps.push(wxssFile)
}
} return deps
}
}复制代码将依赖添加到树结构中
现在我们需要修改 addToTree 方法。
class Depend { addToTree(filePath) { // 如果该文件已经添加过,则不再添加到文件树中
if (this.files.has(filePath)) { return
} const relPath = this.getRelative(filePath) const names = relPath.split(path.sep)
names.forEach((name, idx) => { // ... 添加到树中
}) this.files.add(filePath) // ===== 获取文件依赖,并添加到树中 =====
const deps = this.getDeps(filePath)
deps.forEach(dep => { this.addToTree(dep)
})
}
}复制代码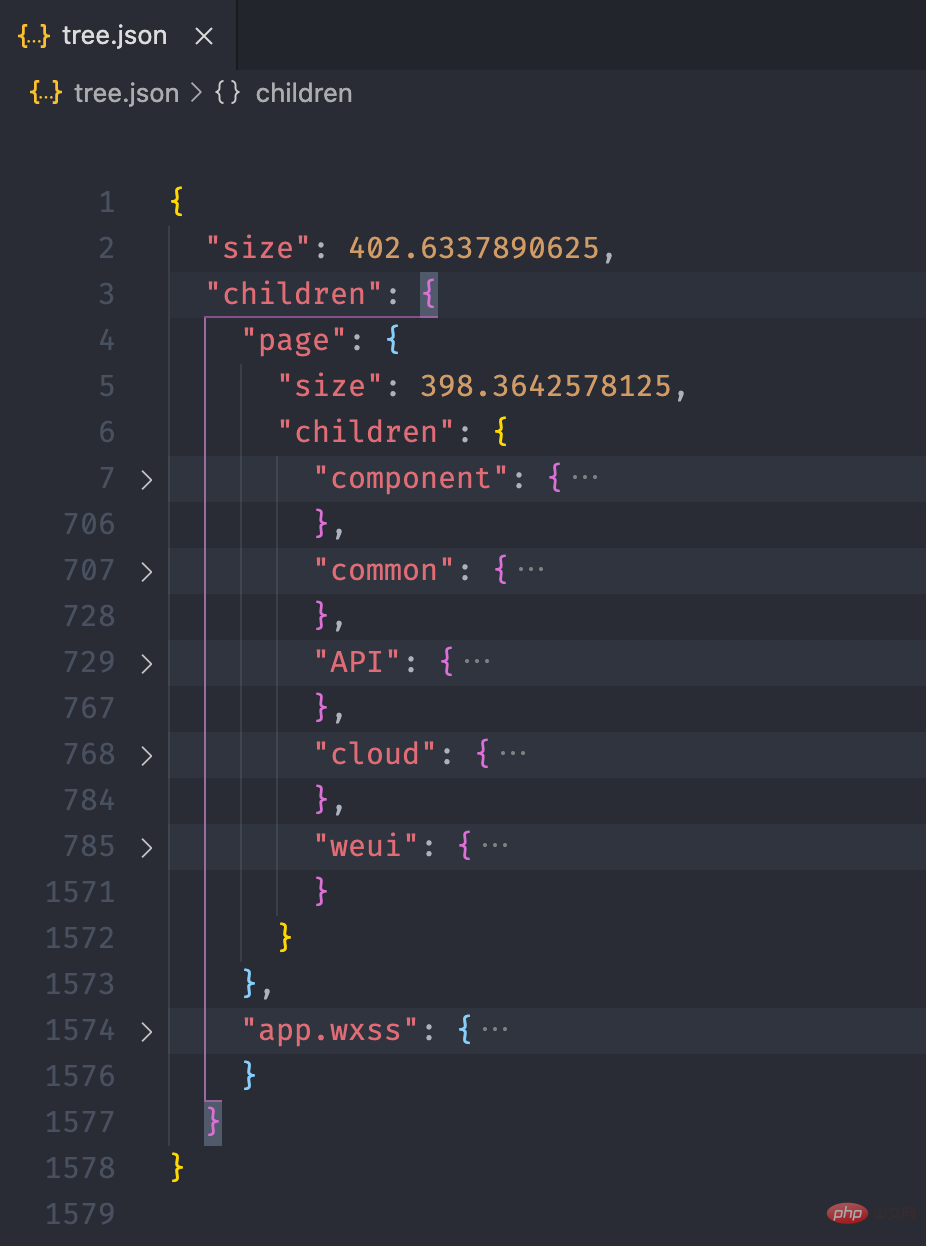
获取分包依赖
熟悉小程序的同学肯定知道,小程序提供了分包机制。使用分包后,分包内的文件会被打包成一个单独的包,在用到的时候才会加载,而其他的文件则会放在主包,小程序打开的时候就会加载。subpackages 中,每个分包的配置有以下几项:
| 字段 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| root | String | 分包根目录 |
| name | String | 分包别名,分包预下载时可以使用 |
| pages | StringArray | 分包页面路径,相对与分包根目录 |
| independent | Boolean | 分包是否是独立分包 |
所以我们在运行的时候,除了要拿到 pages 下的所有页面,还需拿到 subpackages 中所有的页面。由于之前只关心主包的内容,this.tree 下面只有一颗文件树,现在我们需要在 this.tree 下挂载多颗文件树,我们需要先为主包创建一个单独的文件树,然后为每个分包创建一个文件树。
class Depend { constructor() { this.tree = {} this.files = new Set() this.context = path.join(root, 'miniprogram')
} createTree(pkg) { this.tree[pkg] = { size: 0, children: {}
}
} addPage(page, pkg) { const absPath = this.getAbsolute(page)
Extends.forEach(ext => { const filePath = this.replaceExt(absPath, ext) if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) { this.addToTree(filePath, pkg)
}
})
} run() { const appPath = this.getAbsolute('app.json') const appJson = fs.readJsonSync(appPath) const { pages, subPackages, subpackages } = appJson
this.createTree('main') // 为主包创建文件树
pages.forEach(page => { this.addPage(page, 'main')
}) // 由于 app.json 中 subPackages、subpackages 都能生效
// 所以我们两个属性都获取,哪个存在就用哪个
const subPkgs = subPackages || subpackages // 分包存在的时候才进行遍历
subPkgs && subPkgs.forEach(({ root, pages }) => {
root = root.split('/').join(path.sep) this.createTree(root) // 为分包创建文件树
pages.forEach(page => { this.addPage(`${root}${path.sep}${page}`, pkg)
})
}) // 输出文件树
fs.writeJSONSync('ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。', this.tree, { spaces: 2 })
}
}复制代码addToTree 方法也需要进行修改,根据传入的 pkg 来判断将当前文件添加到哪个树。
class Depend { addToTree(filePath, pkg = 'main') { if (this.files.has(filePath)) { // 如果该文件已经添加过,则不再添加到文件树中
return
} let relPath = this.getRelative(filePath) if (pkg !== 'main' && relPath.indexOf(pkg) !== 0) { // 如果该文件不是以分包名开头,证明该文件不在分包内,
// 需要将文件添加到主包的文件树内
pkg = 'main'
} const tree = this.tree[pkg] // 依据 pkg 取到对应的树
const size = this.getSize(filePath) const names = relPath.split(path.sep) const lastIdx = names.length - 1
tree.size += size let point = tree.children
names.forEach((name, idx) => { // ... 添加到树中
}) this.files.add(filePath) // ===== 获取文件依赖,并添加到树中 =====
const deps = this.getDeps(filePath)
deps.forEach(dep => { this.addToTree(dep)
})
}
}复制代码这里有一点需要注意,如果 package/a 分包下的文件依赖的文件不在 package/a 文件夹下,则该文件需要放入主包的文件树内。
通过 EChart 画图
经过上面的流程后,最终我们可以得到如下的一个 json 文件:
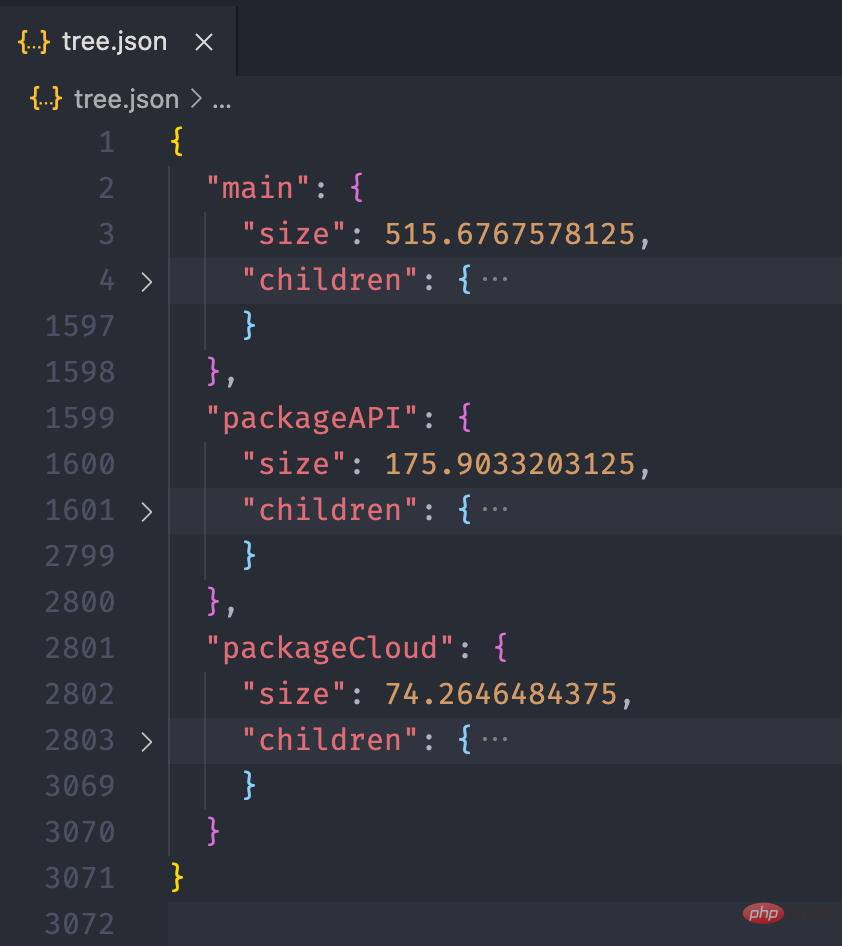
接下来,我们利用 ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。 的画图能力,将这个 json 数据以图表的形式展现出来。我们可以在 ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。 提供的实例中看到一个 Disk Usage 的案例,很符合我们的预期。
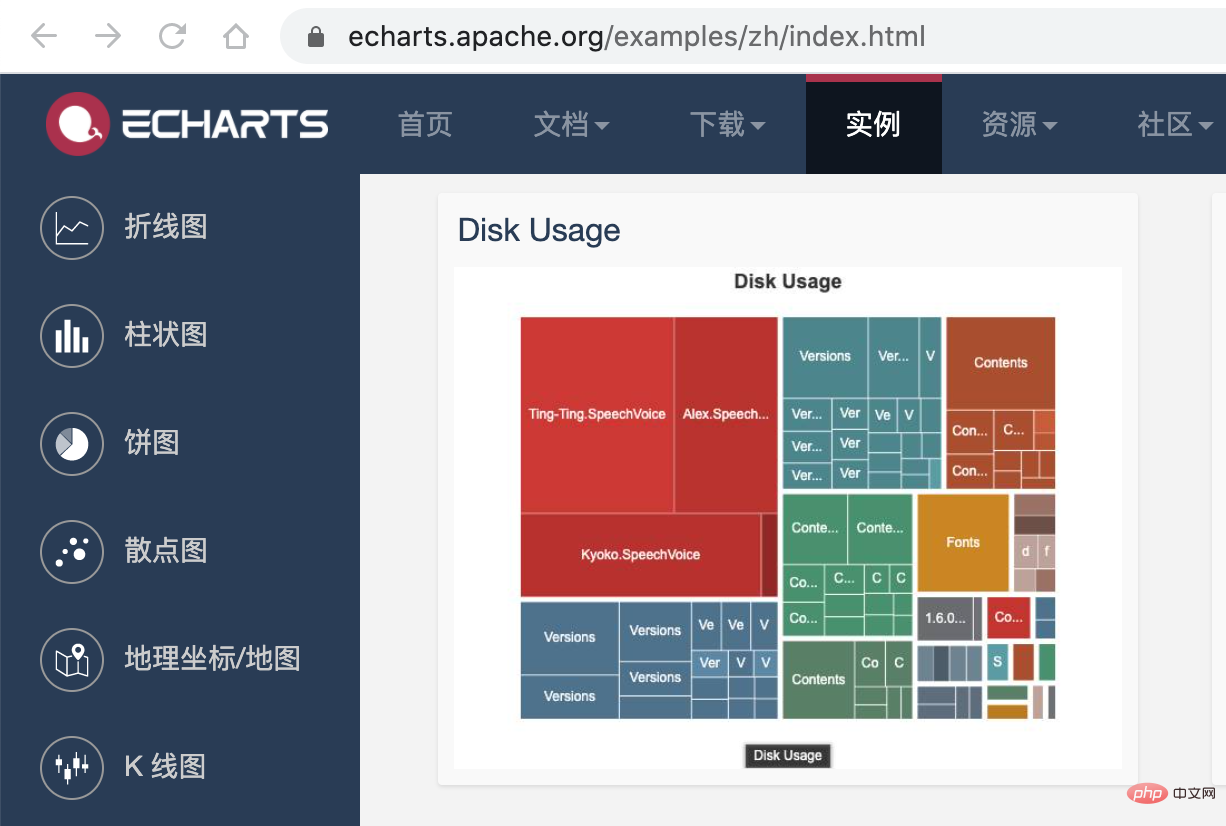
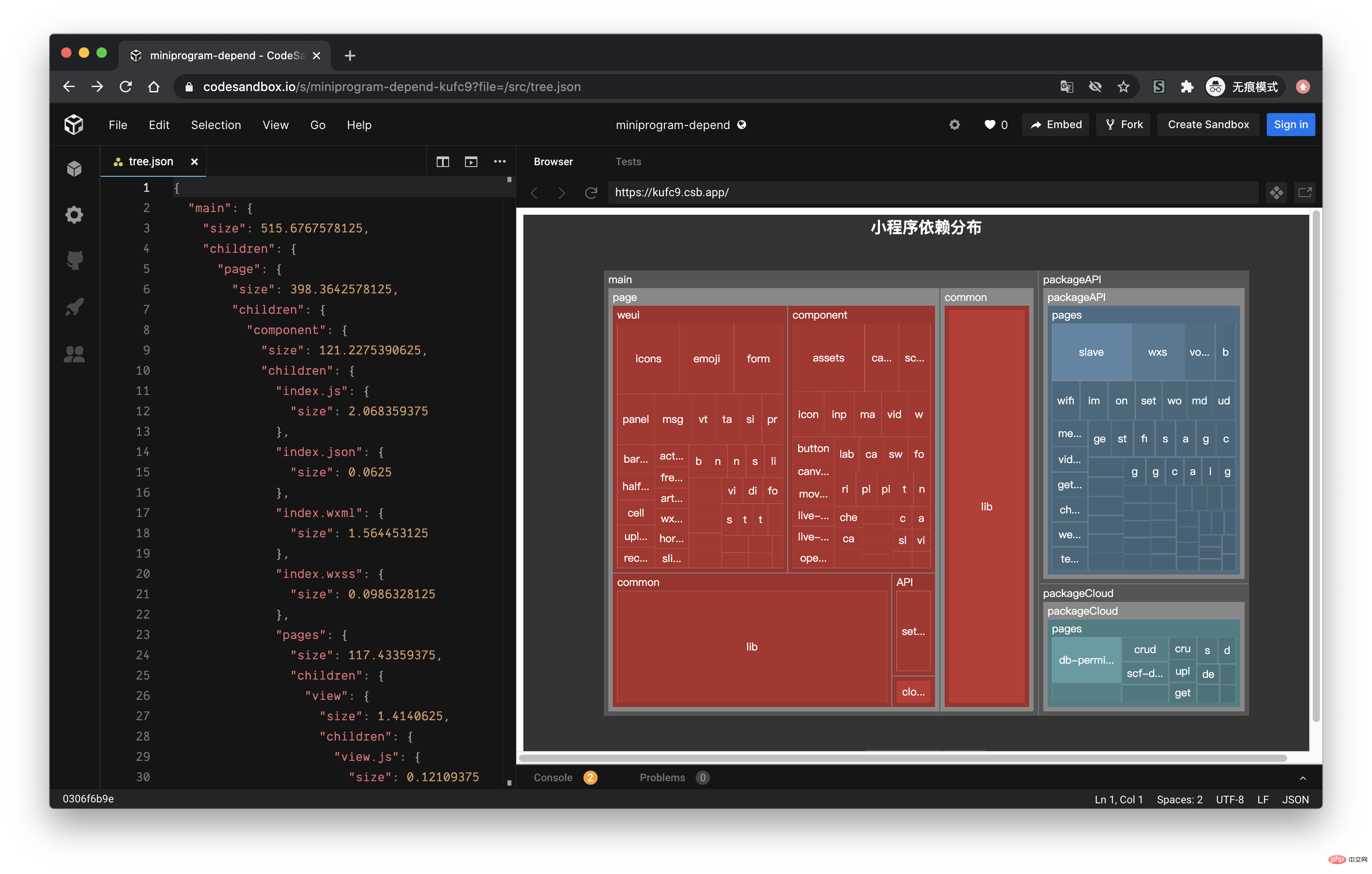
ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。 的配置这里就不再赘述,按照官网的 demo 即可,我们需要把 tree. json 的数据转化为 ミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。 需要的格式就行了,完整的代码放到 codesandbod 了,去下面的线上地址就能看到效果了。
线上地址:https://codesandbox.io/s/cold-dawn-kufc9
总结
这篇文章比较偏实践,所以贴了很多的代码,另外本文对各个文件的依赖获取提供了一个思路,虽然这里只是用文件树构造了一个这样的依赖图。
在业务开发中,小程序 IDE 每次启动都需要进行全量的编译,开发版预览的时候会等待较长的时间,我们现在有文件依赖关系后,就可以只选取目前正在开发的页面进行打包,这样就能大大提高我们的开发效率。如果有对这部分内容感兴趣的,可以另外写一篇文章介绍下如何实现。
相关免费学习推荐:微信小程序开发教程
以上がミニプログラムの依存関係解析の実践を紹介します。の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7700
7700
 15
15
 1640
1640
 14
14
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1287
1287
 25
25
 1230
1230
 29
29
 Python を使用して WeChat アプレットを開発する
Jun 17, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
Python を使用して WeChat アプレットを開発する
Jun 17, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
モバイル インターネット技術とスマートフォンの普及により、WeChat は人々の生活に欠かせないアプリケーションになりました。 WeChat ミニ プログラムを使用すると、アプリケーションをダウンロードしてインストールすることなく、ミニ プログラムを直接使用して、いくつかの簡単なニーズを解決できます。この記事では、Python を使用して WeChat アプレットを開発する方法を紹介します。 1. 準備 Python を使用して WeChat アプレットを開発する前に、関連する Python ライブラリをインストールする必要があります。ここでは、wxpy と itchat の 2 つのライブラリを使用することをお勧めします。 wxpy は WeChat マシンです
 小さなプログラムでも反応できますか?
Dec 29, 2022 am 11:06 AM
小さなプログラムでも反応できますか?
Dec 29, 2022 am 11:06 AM
ミニプログラムはreactを利用することができます 使い方: 1. 「react-reconciler」に基づいてレンダラーを実装し、DSLを生成します; 2. DSLを解析してレンダリングするためのミニプログラムコンポーネントを作成します; 3. npmをインストールし、開発者ビルドを実行しますツール内の npm; 4. パッケージを独自のページに導入し、API を使用して開発を完了します。
 WeChat ミニ プログラムにカードめくり効果を実装する
Nov 21, 2023 am 10:55 AM
WeChat ミニ プログラムにカードめくり効果を実装する
Nov 21, 2023 am 10:55 AM
WeChat ミニ プログラムでのカードめくり効果の実装 WeChat ミニ プログラムでは、カードめくり効果の実装は、ユーザー エクスペリエンスとインターフェイス インタラクションの魅力を向上させることができる一般的なアニメーション効果です。以下では、WeChat アプレットでカードめくりの特殊効果を実装する方法と、関連するコード例を詳しく紹介します。まず、ミニ プログラムのページ レイアウト ファイルに 2 つのカード要素を定義する必要があります。1 つは前面のコンテンツを表示するため、もう 1 つは背面のコンテンツを表示するためです。具体的なサンプル コードは次のとおりです: <!--index.wxml- ->&l
 アリペイ、希少文字ライブラリを収集・補完する「漢字拾い-希少文字」ミニプログラムを開始
Oct 31, 2023 pm 09:25 PM
アリペイ、希少文字ライブラリを収集・補完する「漢字拾い-希少文字」ミニプログラムを開始
Oct 31, 2023 pm 09:25 PM
10月31日の当サイトのニュースによると、今年5月27日、アント・グループは「漢字拾いプロジェクト」の立ち上げを発表し、最近新たな進展を迎えた:アリペイが「漢字拾い-珍しい文字」ミニプログラムを開始協会からコレクションを収集する レア文字は、レア文字ライブラリを補完し、アリペイでのレア文字入力方法の改善に役立つように、レア文字に異なる入力エクスペリエンスを提供します。現在、ユーザーは「漢字ピックアップ」「珍文字」などのキーワードで検索することで「珍文字」アプレットに入ることができる。ミニプログラムでは、ユーザーがシステムで認識・入力されなかった珍しい文字の画像を送信し、確認後、Alipay のエンジニアがフォントライブラリに追加エントリを作成します。当サイトでは、発音が不明瞭な珍しい単語を対象とした最新の単語分割入力方法をミニプログラムで体験できることに注目しました。ユーザー解体
 uniapp がミニ プログラムと H5 の間で迅速な変換を実現する方法
Oct 20, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
uniapp がミニ プログラムと H5 の間で迅速な変換を実現する方法
Oct 20, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
uniapp がミニ プログラムと H5 の間で迅速な変換を実現するには、具体的なコード例が必要ですが、近年、モバイル インターネットの発展とスマートフォンの普及に伴い、ミニ プログラムと H5 は不可欠なアプリケーション形式となっています。クロスプラットフォーム開発フレームワークとして、uniapp は一連のコードに基づいて小規模プログラムと H5 間の変換を迅速に実現し、開発効率を大幅に向上させます。この記事では、uniapp がミニ プログラムと H5 の間で迅速な変換を実現する方法と、具体的なコード例を紹介します。 1. uniapp uniaの紹介
 Python で簡単なチャット プログラムを作成するためのチュートリアル
May 08, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Python で簡単なチャット プログラムを作成するためのチュートリアル
May 08, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
実装アイデア: チャット ルームのさまざまな機能を処理するために、スレッドのサーバー側を確立します。x02 クライアントの確立はサーバーよりもはるかに簡単です。クライアントの機能はメッセージの送受信と、特定の文字を特定の規則に従って入力するため、クライアント側では、メッセージ受信専用とメッセージ送信専用の 2 つのスレッドを使用するだけで、さまざまな機能を使用できます。使用しないでください。
 WeChat ミニ プログラムのメンバーシップを取得する方法
May 07, 2024 am 10:24 AM
WeChat ミニ プログラムのメンバーシップを取得する方法
May 07, 2024 am 10:24 AM
1. WeChat ミニ プログラムを開き、対応するミニ プログラム ページに入ります。 2. ミニ プログラム ページでメンバー関連の入り口を見つけます。通常、メンバーの入り口は下部のナビゲーション バーまたはパーソナル センターにあります。 3. メンバーシップポータルをクリックして、メンバーシップ申請ページに入ります。 4. 入会申込ページにて、携帯電話番号、氏名等の必要事項をご入力の上、送信してください。 5. ミニ プログラムは会員申請を審査します。審査に合格すると、ユーザーは WeChat ミニ プログラムの会員になることができます。 6. 会員になると、ユーザーはポイント、クーポン、会員限定アクティビティなど、より多くの会員権を享受できます。
 ミニプログラム登録の操作方法
Sep 13, 2023 pm 04:36 PM
ミニプログラム登録の操作方法
Sep 13, 2023 pm 04:36 PM
ミニ プログラムの登録操作手順: 1. 個人 ID カード、法人営業許可証、法人 ID カードおよびその他の提出資料のコピーを準備します; 2. ミニ プログラム管理のバックグラウンドにログインします; 3. ミニ プログラム設定ページに入ります; 4. 「基本設定」を選択; 5. 出願情報を入力; 6. 出願資料をアップロード; 7. 出願申請を送信; 8. 審査結果を待ちます。出願が不合格の場合は、理由に応じて修正してください9. 出願のフォローアップ操作は可能です。




