Java Spring Beanのライフサイクル管理の分析例
Spring Bean のライフサイクル管理
1. Spring Bean のライフサイクル
通过以下方式来指定Bean的初始化和销毁方法, 当Bean为单例时,Bean归Spring容器管理,Spring容器关闭,就会调用Bean的销毁方法 当Bean为多例时,Bean不归Spring容器管理,Spring容器关闭,不会调用Bean的销毁方法
2. @Bean パラメータ (initMethod、destroyMethod) を通じて Bean の初期化メソッドと破棄メソッドを指定します
1. プロジェクト構造
2. 人物
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}3. Bean 登録設定クラス (単一インスタンス)
import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}4. テスト クラス
import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import com.dashu.config.BeanConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载配置类获取容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
//获取Bean
Person bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
//关闭容器
annotationConfigApplicationContext.close();
}
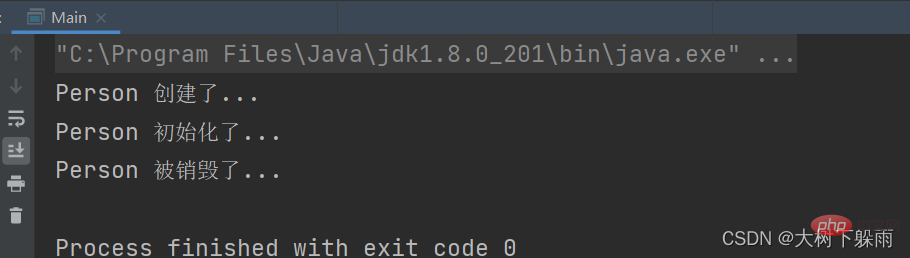
}5. テスト結果
6. Bean 登録設定クラス (複数のインスタンス)
import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
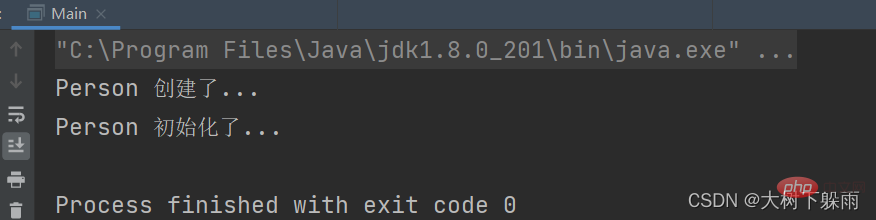
}7. テスト結果
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}ログイン後にコピー
2. Bean登録設定クラスimport org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}ログイン後にコピー
3. テスト結果import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}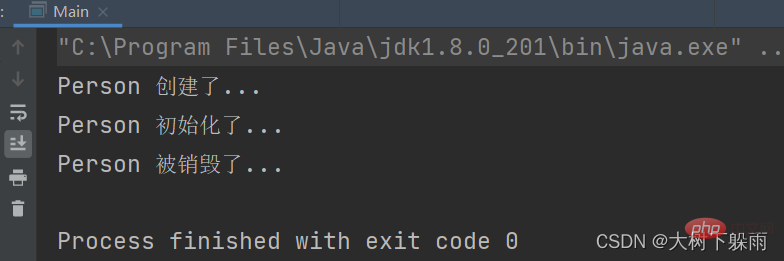 ##4. アノテーション @PostConstruct と@PreDestroy
##4. アノテーション @PostConstruct と@PreDestroy
@PostConstruct:标注在Bean的初始化方法上 @PreDestroy:标注在Bean的销毁方法上
1、Person
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}2、テスト結果
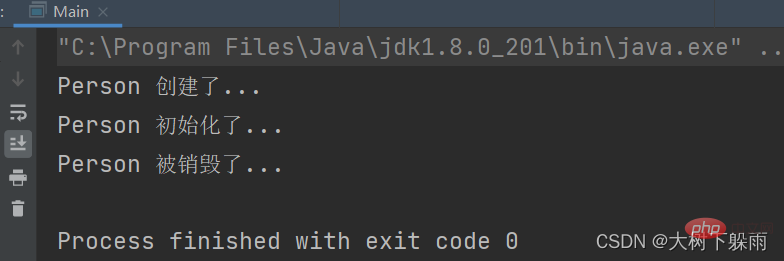 5. インターフェース BeanPostProcessor 実装クラス (ポストプロセッサー) を使用します。 )
5. インターフェース BeanPostProcessor 実装クラス (ポストプロセッサー) を使用します。 )
1. プロジェクト構造
 2. 人物
2. 人物
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
@Component
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}3. Bean登録設定クラス
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.dashu"})
public class BeanConfig {
}4 、BeanPostProcessor 実装クラス (ポストプロセッサ)
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 后置处理器:初始化前后进行处理工作
*/
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 初始化之前工作
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之前..."+beanName+"=["+bean+"]");
return bean;
}
/**
* 初始化之后工作
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之后..."+beanName+"=["+bean+"]");
return bean;
}
}5、テスト結果
以上がJava Spring Beanのライフサイクル管理の分析例の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1325
1325
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1252
1252
 24
24
 Java 8 Stream Foreachから休憩または戻ってきますか?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 Stream Foreachから休憩または戻ってきますか?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8は、Stream APIを導入し、データ収集を処理する強力で表現力のある方法を提供します。ただし、ストリームを使用する際の一般的な質問は次のとおりです。 従来のループにより、早期の中断やリターンが可能になりますが、StreamのForeachメソッドはこの方法を直接サポートしていません。この記事では、理由を説明し、ストリーム処理システムに早期終了を実装するための代替方法を調査します。 さらに読み取り:JavaストリームAPIの改善 ストリームを理解してください Foreachメソッドは、ストリーム内の各要素で1つの操作を実行する端末操作です。その設計意図はです
 PHP:Web開発の重要な言語
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:Web開発の重要な言語
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHPは、サーバー側で広く使用されているスクリプト言語で、特にWeb開発に適しています。 1.PHPは、HTMLを埋め込み、HTTP要求と応答を処理し、さまざまなデータベースをサポートできます。 2.PHPは、ダイナミックWebコンテンツ、プロセスフォームデータ、アクセスデータベースなどを生成するために使用され、強力なコミュニティサポートとオープンソースリソースを備えています。 3。PHPは解釈された言語であり、実行プロセスには語彙分析、文法分析、編集、実行が含まれます。 4.PHPは、ユーザー登録システムなどの高度なアプリケーションについてMySQLと組み合わせることができます。 5。PHPをデバッグするときは、error_reporting()やvar_dump()などの関数を使用できます。 6. PHPコードを最適化して、キャッシュメカニズムを使用し、データベースクエリを最適化し、組み込み関数を使用します。 7
 PHP対Python:違いを理解します
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP対Python:違いを理解します
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHPは、シンプルな構文と高い実行効率を備えたWeb開発に適しています。 2。Pythonは、簡潔な構文とリッチライブラリを備えたデータサイエンスと機械学習に適しています。
 PHP対その他の言語:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP対その他の言語:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHPは、特に迅速な開発や動的なコンテンツの処理に適していますが、データサイエンスとエンタープライズレベルのアプリケーションには良くありません。 Pythonと比較して、PHPはWeb開発においてより多くの利点がありますが、データサイエンスの分野ではPythonほど良くありません。 Javaと比較して、PHPはエンタープライズレベルのアプリケーションでより悪化しますが、Web開発により柔軟性があります。 JavaScriptと比較して、PHPはバックエンド開発により簡潔ですが、フロントエンド開発のJavaScriptほど良くありません。
 PHP対Python:コア機能と機能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP対Python:コア機能と機能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHPとPythonにはそれぞれ独自の利点があり、さまざまなシナリオに適しています。 1.PHPはWeb開発に適しており、組み込みのWebサーバーとRich Functionライブラリを提供します。 2。Pythonは、簡潔な構文と強力な標準ライブラリを備えたデータサイエンスと機械学習に適しています。選択するときは、プロジェクトの要件に基づいて決定する必要があります。
 PHPの影響:Web開発など
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPの影響:Web開発など
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
phphassiblasifly-impactedwebdevevermentandsbeyondit.1)itpowersmajorplatformslikewordpratsandexcelsindatabase interactions.2)php'sadaptableability allowsitale forlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikelavel.3)
 PHP:多くのウェブサイトの基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP:多くのウェブサイトの基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHPが多くのWebサイトよりも優先テクノロジースタックである理由には、その使いやすさ、強力なコミュニティサポート、広範な使用が含まれます。 1)初心者に適した学習と使用が簡単です。 2)巨大な開発者コミュニティと豊富なリソースを持っています。 3)WordPress、Drupal、その他のプラットフォームで広く使用されています。 4)Webサーバーとしっかりと統合して、開発の展開を簡素化します。
 PHP対Python:ユースケースとアプリケーション
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP対Python:ユースケースとアプリケーション
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHPはWeb開発およびコンテンツ管理システムに適しており、Pythonはデータサイエンス、機械学習、自動化スクリプトに適しています。 1.PHPは、高速でスケーラブルなWebサイトとアプリケーションの構築においてうまく機能し、WordPressなどのCMSで一般的に使用されます。 2。Pythonは、NumpyやTensorflowなどの豊富なライブラリを使用して、データサイエンスと機械学習の分野で驚くほどパフォーマンスを発揮しています。




