
翻訳者 | Bugatti
レビュアー | Sun Shujuan
物理的なスペースを節約したり、バックアップを作成したりするために、ドキュメントをデジタル化したい場合があります。いずれにせよ、紙の文書の写真を準形式に変換するプログラムを作成することは、まさに Python が得意とすることです。
適切なライブラリを組み合わせて使用すると、ドキュメントをデジタル化するための小さなアプリケーションを構築できます。プログラムは、物理文書の画像を入力として受け取り、それにいくつかの画像処理手法を適用して、入力のスキャンされたバージョンを出力します。
まず、Python の基本を理解し、NumPy Python ライブラリの使用方法を知る必要があります。 。
任意の Python IDE を開き、2 つの Python ファイルを作成します。一方に main.py という名前を付け、もう一方にtransform.py という名前を付けます。次に、ターミナル上で次のコマンドを実行して、必要なライブラリをインストールします。
pip install OpenCV-Python imutils scikit-image NumPy
OpenCV-Python を使用して画像入力を取得し、画像処理を行い、Imutils を使用して入力画像と出力画像のサイズを変更し、scikit-image を使用して画像のしきい値を設定します。 NumPy は配列を扱うのに役立ちます。
import cv2 import imutils from skimage.filters import threshold_local from transform import perspective_transform

# 入力画像のパスを OpenCV に渡します。遠近法変換時に必要となるため、元の画像のコピーを作成します。元の画像の高さを、サイズを変更したい高さで割ります。これによりアスペクト比が維持されます。最後に、調整された画像が出力されます。
# Passing the image path
original_img = cv2.imread('sample.jpg')
copy = original_img.copy()
# The resized height in hundreds
ratio = original_img.shape[0] / 500.0
img_resize = imutils.resize(original_img, height=500)
# Displaying output
cv2.imshow('Resized image', img_resize)
# Waiting for the user to press any key
cv2.waitKey(0)上記のコードの出力は次のとおりです:
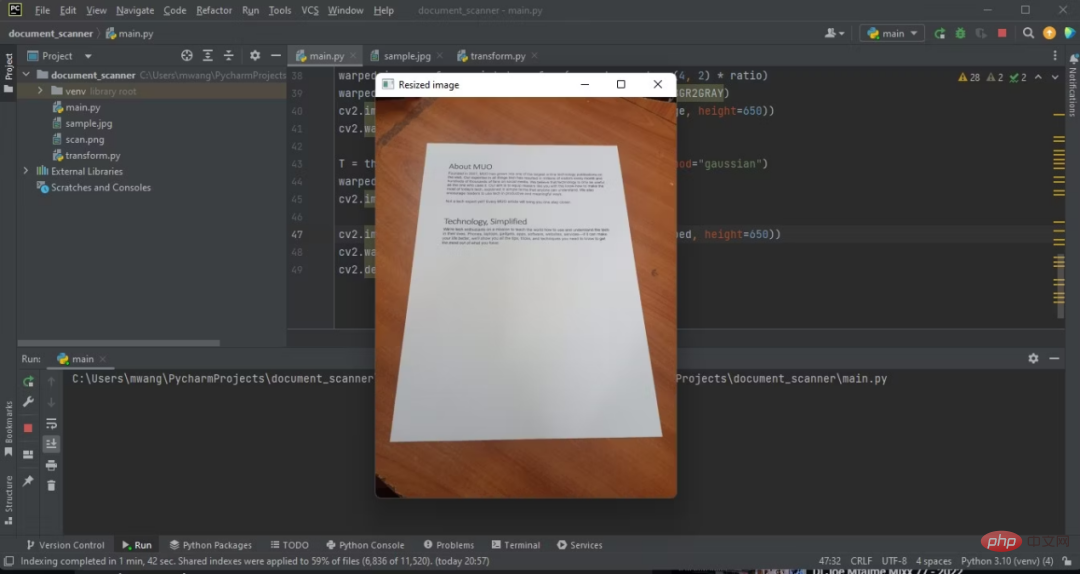
これで、元の画像の高さが 500 ピクセルに調整されました。
4. 調整した画像をグレースケール画像に変換します
調整した RGB 画像をグレースケール画像に変換します。ほとんどの画像処理ライブラリは、処理が簡単なため、グレースケール画像のみを処理します。
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(img_resize, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('Grayed Image', gray_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)元のイメージとグレースケール イメージの違いに注目してください。
#IDE 上で灰色のイメージを表示するプログラム出力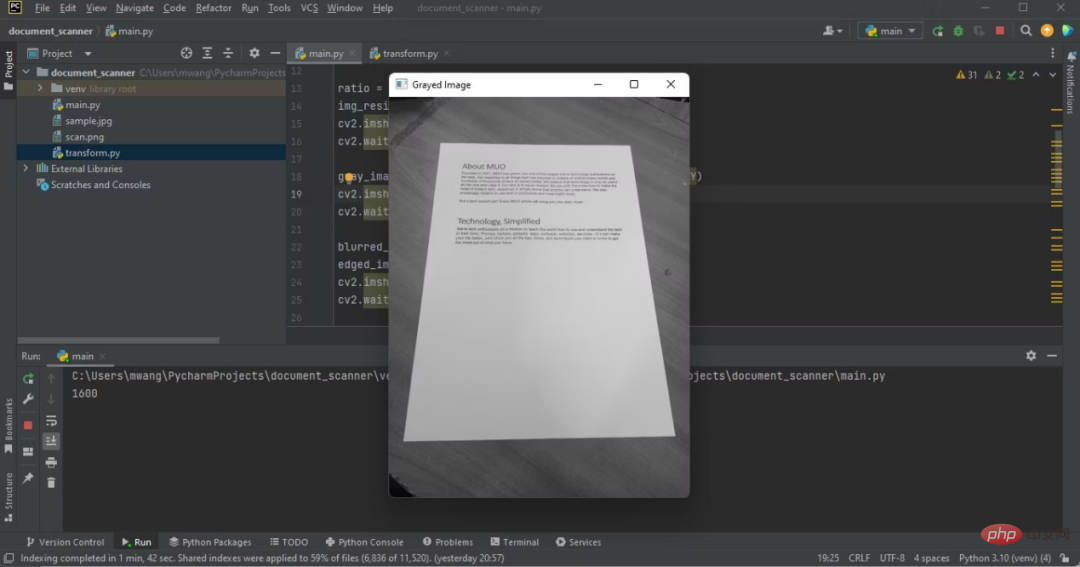
blurred_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_image, (5, 5), 0)
edged_img = cv2.Canny(blurred_image, 75, 200)
cv2.imshow('Image edges', edged_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)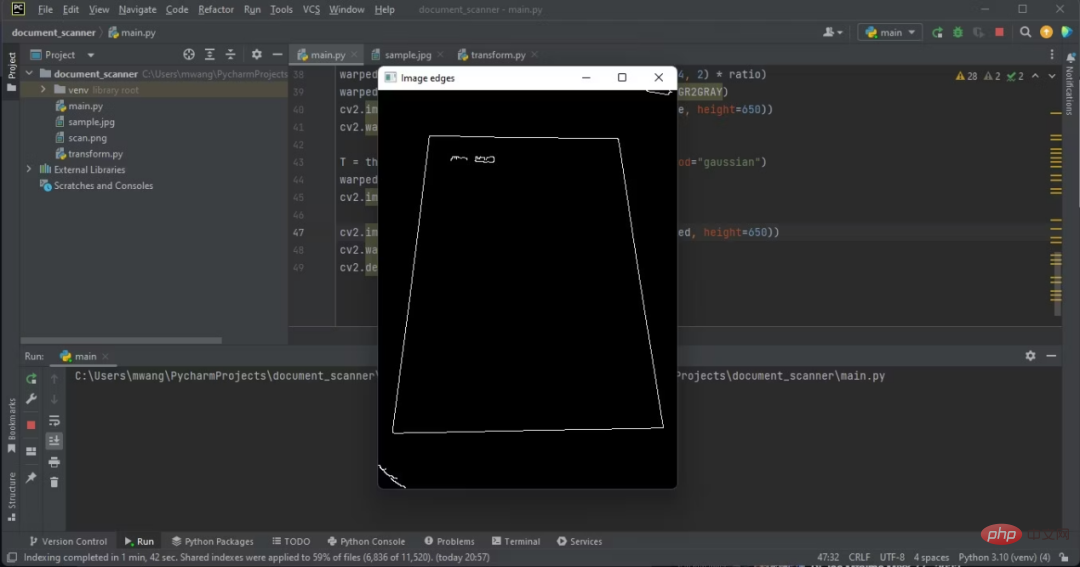 #これから作業するエッジは、ドキュメントのエッジです。
#これから作業するエッジは、ドキュメントのエッジです。
6. 最大の輪郭を見つける
cnts, _ = cv2.findContours(edged_img, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[:5] for c in cnts: peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True) approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True) if len(approx) == 4: doc = approx break
4 辺があるアウトラインには、ドキュメントが含まれる可能性があります。
7. 文書の輪郭の四隅を丸で囲みます
p = []
for d in doc:
tuple_point = tuple(d[0])
cv2.circle(img_resize, tuple_point, 3, (0, 0, 255), 4)
p.append(tuple_point)
cv2.imshow('Circled corner points', img_resize)
cv2.waitKey(0)調整された RGB 画像のいくつかの角を丸で囲みます。
#ドキュメントを検出したら、画像からドキュメントを抽出する必要があります。 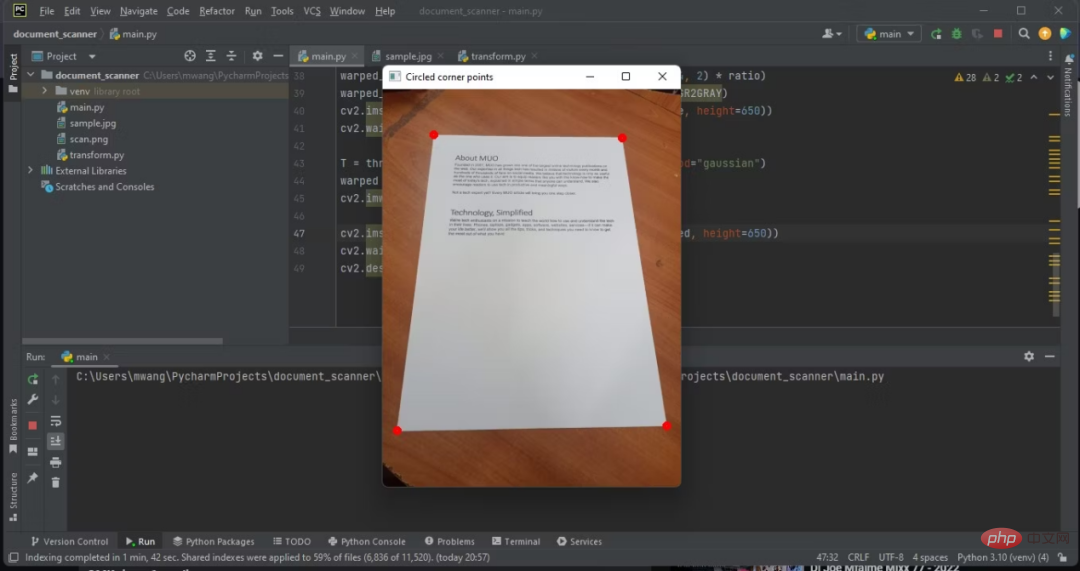
warped_image = perspective_transform(copy, doc.reshape(4, 2) * ratio)
warped_image = cv2.cvtColor(warped_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow("Warped Image", imutils.resize(warped_image, height=650))
cv2.waitKey(0)该模块将对文档角的点进行排序。它还会将文档图像转换成不同的平面,并将相机角度更改为俯拍。
打开之前创建的那个transform.py文件,导入OpenCV库和NumPy库。
import numpy as np import cv2
这个模块将含有两个函数。创建一个对文档角点的坐标进行排序的函数。第一个坐标将是左上角的坐标,第二个将是右上角的坐标,第三个将是右下角的坐标,第四个将是左下角的坐标。
def order_points(pts): # initializing the list of coordinates to be ordered rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype = "float32") s = pts.sum(axis = 1) # top-left point will have the smallest sum rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)] # bottom-right point will have the largest sum rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)] '''computing the difference between the points, the top-right point will have the smallest difference, whereas the bottom-left will have the largest difference''' diff = np.diff(pts, axis = 1) rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)] rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)] # returns ordered coordinates return rect
创建将计算新图像的角坐标,并获得俯拍的第二个函数。然后,它将计算透视变换矩阵,并返回扭曲的图像。
def perspective_transform(image, pts): # unpack the ordered coordinates individually rect = order_points(pts) (tl, tr, br, bl) = rect '''compute the width of the new image, which will be the maximum distance between bottom-right and bottom-left x-coordinates or the top-right and top-left x-coordinates''' widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2)) maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB)) '''compute the height of the new image, which will be the maximum distance between the top-left and bottom-left y-coordinates''' heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2)) heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB)) '''construct the set of destination points to obtain an overhead shot''' dst = np.array([ [0, 0], [maxWidth - 1, 0], [maxWidth - 1, maxHeight - 1], [0, maxHeight - 1]], dtype = "float32") # compute the perspective transform matrix transform_matrix = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst) # Apply the transform matrix warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, transform_matrix, (maxWidth, maxHeight)) # return the warped image return warped
现在您已创建了转换模块。perspective_transform导入方面的错误现在将消失。
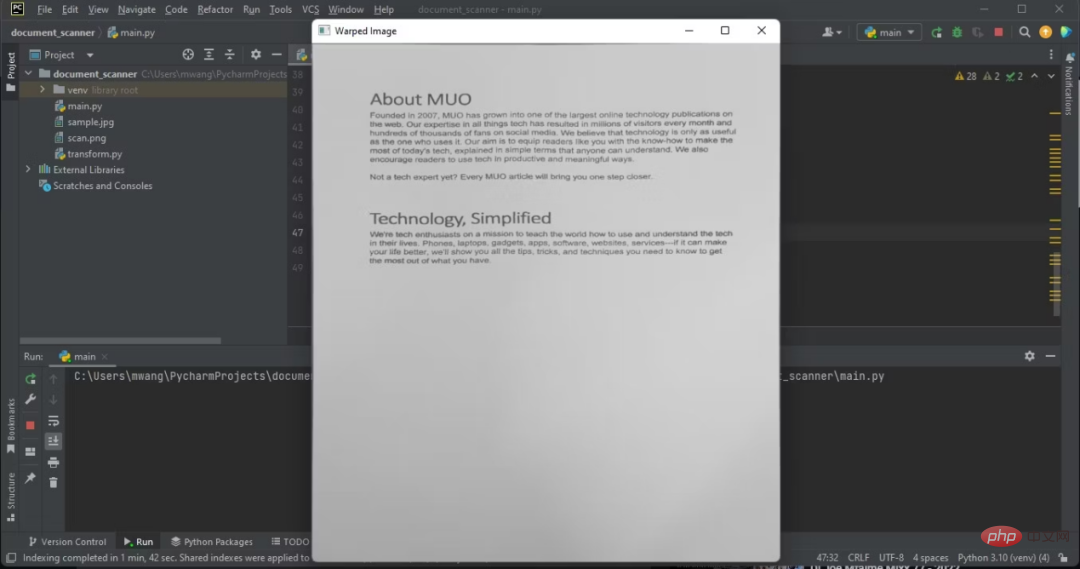
注意,显示的图像有俯拍。
在main.py文件中,对扭曲的图像运用高斯阈值。这将给扭曲的图像一个扫描后的外观。将扫描后的图像输出保存到含有程序文件的文件夹中。
T = threshold_local(warped_image, 11, offset=10, method="gaussian")
warped = (warped_image > T).astype("uint8") * 255
cv2.imwrite('./'+'scan'+'.png',warped)以PNG格式保存扫描件可以保持文档质量。
输出扫描后文档的图像:
cv2.imshow("Final Scanned image", imutils.resize(warped, height=650))
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()下图显示了程序的输出,即扫描后文档的俯拍。
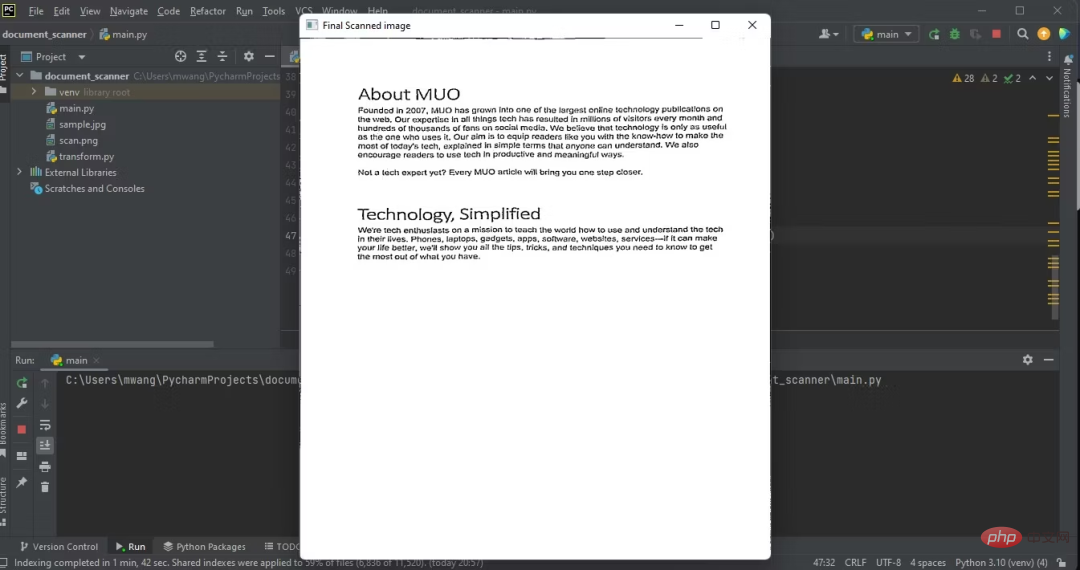
创建文档扫描器涉及计算机视觉的一些核心领域,计算机视觉是一个广泛而复杂的领域。为了在计算机视觉方面取得进步,您应该从事有趣味又有挑战性的项目。
您还应该阅读如何将计算机视觉与当前前技术结合使用方面的更多信息。这让您能了解情况,并为所处理的项目提供新的想法。
原文链接:https://www.makeuseof.com/python-create-document-scanner/
以上がPython でドキュメント スキャナーを構築するにはどうすればよいですか?の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。