Pythonで気象データをクローリングして視覚的に分析する方法とは?
1. データ取得
Web サイトへのリンクをリクエスト
まず、中国気象ネットワークを確認してください。ここで、地元の気象 Web サイトにアクセスしてください。さまざまな地域をクロールしたい場合は、最後の 101280701 エリア番号を変更するだけです。前面の天気は 7 日間の Web ページを表し、weather1d は当日を表し、weather15d は次の 14 日間を表します。ここでは主に 7 日間および 14 日間の中国気象ネットワークを参照します。 request.get() メソッドを使用して Web ページをリクエストします。アクセスが成功すると、Web ページのすべての文字列テキストが取得されます。これがリクエストのプロセスです。
def getHTMLtext(url):
"""请求获得网页内容"""
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout = 30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
print("成功访问")
return r.text
except:
print("访问错误")
return" "有用な情報の抽出
BeautifulSoup ライブラリは、取得した文字列からデータを抽出するために使用されます。まず、Web ページをチェックして、データを取得する必要があるタグを見つけます:
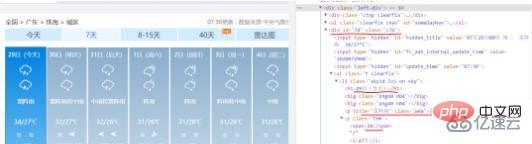
7 日間のデータ情報は id="7d" の div タグ内にあり、日付、天気、気温、風速などの情報は ul タグ内にあることがわかります。と li タグがあるため、BeautifulSoup を使用できます。取得した Web ページのテキストで div タグ id="7d" を検索し、それに含まれるすべての ul タグと li タグを見つけて、タグ内の対応するデータ値を抽出して保存します。それらを対応するリストに追加します。
ここで注意すべき点は、日付に最高気温がない場合があり、データがない状況を判断して処理する必要があることです。さらに、温度の後ろにある摂氏記号、日付数値の抽出、風速テキストの抽出など、一部のデータ保存形式を事前に処理する必要があり、文字検索や文字列のスライス処理が必要になります。
def get_content(html):
"""处理得到有用信息保存数据文件"""
final = []# 初始化一个列表保存数据
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")# 创建BeautifulSoup对象
body = bs.body
data = body.find('div', {'id': '7d'})# 找到div标签且id = 7d以下は当日のデータをクロールします
data2 = body.find_all('div',{'class':'left-div'})
text = data2[2].find('script').string
text = text[text.index('=')+1 :-2] # 移除改var data=将其变为json数据
jd = json.loads(text)
dayone = jd['od']['od2'] # 找到当天的数据
final_day = [] # 存放当天的数据
count = 0
for i in dayone:
temp = []
if count <=23:
temp.append(i['od21']) # 添加时间
temp.append(i['od22']) # 添加当前时刻温度
temp.append(i['od24']) # 添加当前时刻风力方向
temp.append(i['od25']) # 添加当前时刻风级
temp.append(i['od26']) # 添加当前时刻降水量
temp.append(i['od27']) # 添加当前时刻相对湿度
temp.append(i['od28']) # 添加当前时刻控制质量
#print(temp)
final_day.append(temp)
count = count +1以下は7日間のデータをクロールします
ul = data.find('ul')# 找到所有的ul标签 li = ul.find_all('li')# 找到左右的li标签 i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数 for day in li:# 遍历找到的每一个li if i < 7 and i > 0: temp = []# 临时存放每天的数据 date = day.find('h2').string # 得到日期 date = date[0:date.index('日')] # 取出日期号 temp.append(date) inf = day.find_all('p')# 找出li下面的p标签,提取第一个p标签的值,即天气 temp.append(inf[0].string) tem_low = inf[1].find('i').string # 找到最低气温 if inf[1].find('span') is None: # 天气预报可能没有最高气温 tem_high = None else: tem_high = inf[1].find('span').string# 找到最高气温 temp.append(tem_low[:-1]) if tem_high[-1] == '℃': temp.append(tem_high[:-1]) else: temp.append(tem_high) wind = inf[2].find_all('span')# 找到风向 for j in wind: temp.append(j['title']) wind_scale = inf[2].find('i').string # 找到风级 index1 = wind_scale.index('级') temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1])) final.append(temp) i = i + 1 return final_day,final
同様に/weather15dに対して同じ処理を行います:15日間情報, ここを確認したところ、彼の 15 日間の Web ページには 8 ~ 14 日だけが含まれていることがわかりました。前の 1 ~ 7 日間は /weather にありました。ここでは、2 つの Web ページにそれぞれアクセスし、クロールされたデータをマージして最終的なデータを取得しました14 日間のデータ。 - 手前は今後14日間のデータクローリング処理です その日の24時間気象情報データは検索したところjsonデータであることが分かり jsonを通じてその日のデータを取得できます.loads() メソッドを使用して、その日の天気情報を抽出します。

csv ファイルを保存します
先ほどクロールしたデータをリストに追加し、ここで csv ライブラリを導入し、f_csv.writerow(header) と f_csv を使用します。 writerows(data) メソッドは、テーブルヘッダーと各行のデータをそれぞれ書き込みます。ここでは、1 日と次の 14 日のデータを別々に保存し、それぞれweather1.csvとweather14.csvとして保存します。彼らが保存した表:
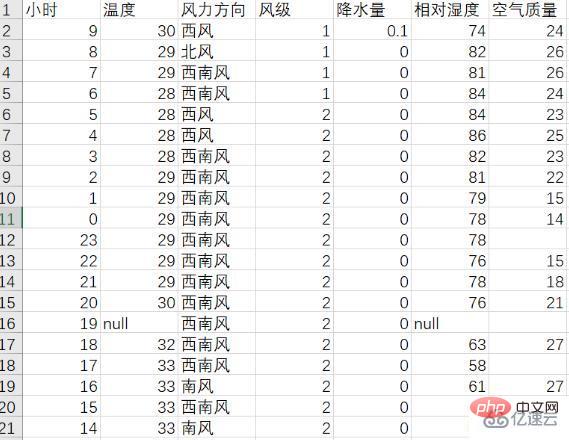
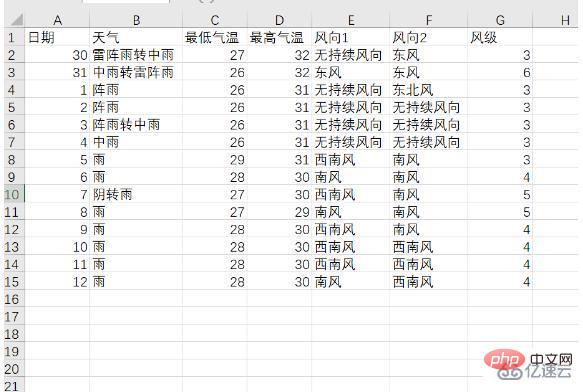
2. 視覚的分析
その日の気温変化曲線
matplotlib() メソッドで plt.plot を使用して 1 日 24 時間の温度変化曲線を描画し、plt.text() メソッドを使用して最高気温と最低気温を示し、平均気温の線を描画します。は温度変化曲線です: (コードについては付録を参照)
素晴らしい!プライベートな仕事を引き受けるのに不可欠な N オープンソース プロジェクト!急いで集めてください
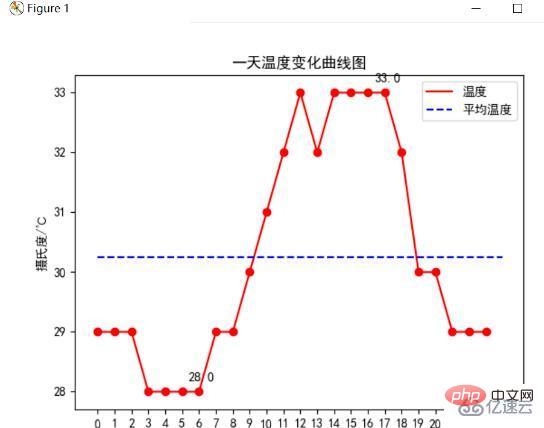
分析の結果、この日の最高気温は33℃、最低気温は28℃、平均気温は約20.4℃であることが分かりました。時間分析により、昼と夜の温度差は5℃あり、早朝は気温が低く、正午から午後にかけて気温が高いことがわかります。
今日の相対湿度変化曲線グラフ
matplotlib の plt.plot() メソッドを使用して、1 日 24 時間の湿度変化曲線を描き、平均相対湿度線を描きます。次の図は、湿度変化の曲線グラフを示しています: (コードについては付録を参照)
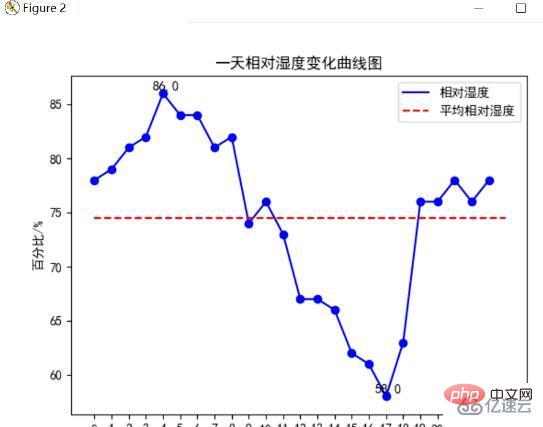
分析により、この日の最高相対湿度は 86%、最低相対湿度であることがわかります。気温は 58℃、平均相対湿度は約 75% です。時間分析によると、早朝は湿度が比較的高く、午後から夕暮れまでは湿度が低いことがわかります。
温度と湿度の相関関係分析図
上の 2 つの図の分析を通じて、温度と湿度の間には関係があることがわかります。この関係をより明確かつ直感的に感じるためには、 plt.scatter() メソッドは、横軸に温度、縦軸に湿度を設定します。各瞬間の点がグラフ内で強調表示され、相関係数が計算されます。次の図は結果です:
######分析により、1 日の温度と湿度には強い相関関係があることがわかりました。それらは負の相関関係にあり、時間と負の相関があることを意味します。さらに分析すると、温度が低いほど、空気中の水分が多くなります。 、湿度 当然のことながら、気温が高くなると水分が蒸発し、空気が乾燥して湿度が低くなりますが、これは通常の気象現象と一致します。
大気質指数棒グラフ
大気質指数 AQI は、大気質の状態を定量的に表す指標で、値が大きいほど大気汚染が深刻で、人体への被害が大きいことを示します。健康。 。大気質指数は一般に6段階に分かれており、レベルが高いほど汚染が深刻であることを示しており、以下はplt.bar法を用いて1日24時間の大気質のヒストグラムを6段階に分けてグラフ化したものです。 , 対応するヒストグラム 色も明るい色から暗い色に変化し、汚染が徐々に増加していることも示し、汚染状況をより直感的に示します。最高および最低の大気質指数もマークされ、平均大気質指数は次のように描画されます。点線. 下の図はその描画結果です. :
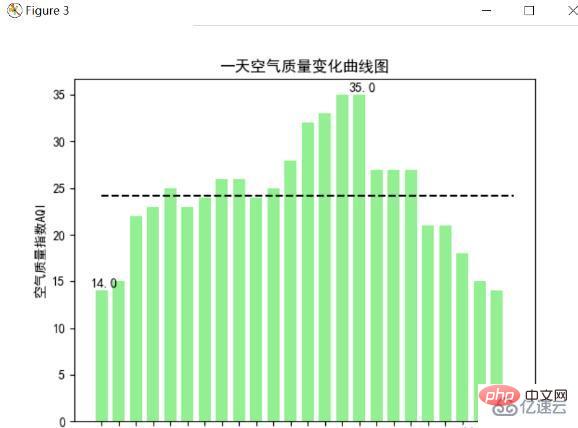
上の図は南部の珠海の管理品質チャートです.大気質指数の最大値も健全な範囲にあり、珠海の空気が非常に良好であることを示しています。分析によると、この日の大気質指数は最高が 35 に達し、最低はわずか 14、平均は約 25 です。また、基本的に空気が最も良いのは早朝(4時から9時)で、大気汚染が最も深刻になるのは午後であることが時間によっても分かるので、通常は外に出て新鮮な空気を吸うことができます。汚染が最小限に抑えられる早朝。
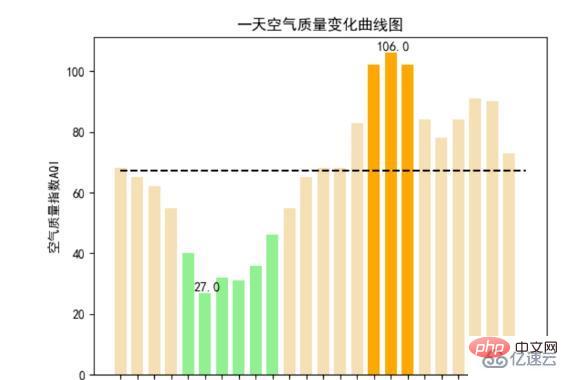
下の大気質地図は北部の都市のものですが、ここの環境が珠海よりもはるかに劣っていることがわかります。
風向風向レーダーチャート
一日の風力と風向の統計。風力と風向は極座標を使用するとより適切に表示されます。極座標はその日の風力と風向図を表示します。円は 8 つの部分に分割され、各部分は風向を表し、半径は平均風力を表します。風レベルが増加するにつれて、
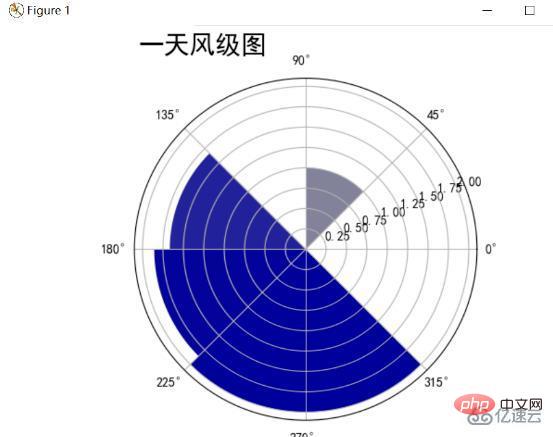
この日は南西の風が最も強く、平均風速は200mに達したと分析されています。 1.75。北東の風も1.0レベルと少量で、その他のブランク方向には風はありませんでした。
今後 14 日間の最高気温と最低気温の変化曲線図
今後 14 日間の最高気温と最低気温の変化を統計し、その変化曲線図を点線で描画します。平均気温線、最終結果は次のとおりです:
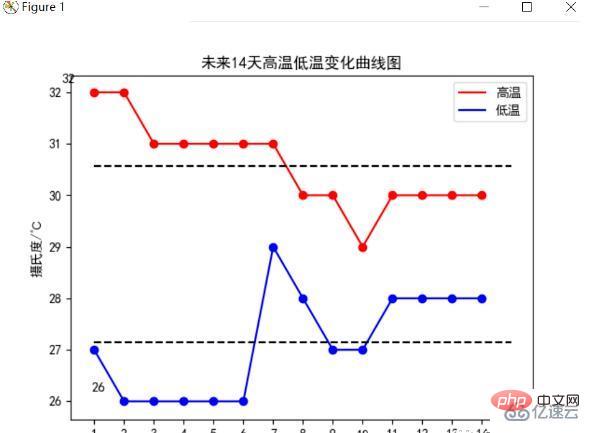
分析により、今後 14 日間の平均最高気温は 30.5℃ であることがわかります。気温はまだ比較的低いです。気温は高くなりますが、今後 8 日間は寒くなるので、それを行う必要があります。冷却の準備をしておくと良いでしょう。最低気温は安定傾向にあり、8 日目には下がり始めます。最高気温に加えて、気温が上がると全体の気温が下がり、平均最低気温は27℃程度になります。
今後 14 日間の風向と風位レーダー チャート
今後 14 日間の風向と平均風力を統計します。以前と同様に極座標を使用し、円を 8 等分します。 8 つの方向を表す部分で、色が濃いほど風レベルが高くなります。最終結果は次のとおりです:
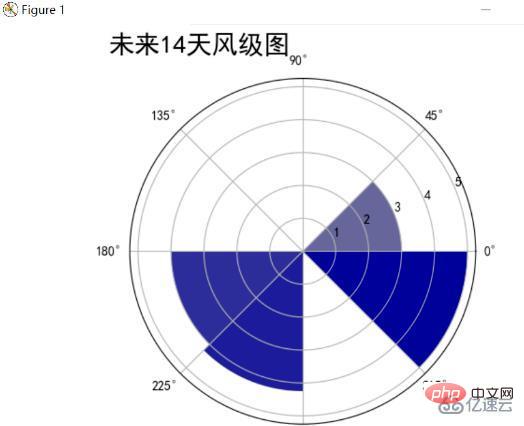
分析により、主な風向と風レベルを見つけることができます。次の 14 日間の南東と南西の風レベルは、最高レベルがレベル 5 に達し、最も低い平均西風レベルはレベル 3 でした。
今後 14 日間の気候分布円グラフ
今後 14 日間の気候を数え、各気候の合計日数を求め、最後に各気候の円グラフを描画します。結果は次のとおりです。
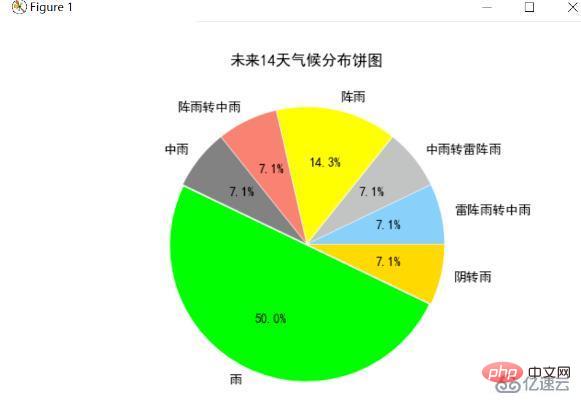
分析の結果、今後 14 日間の気候は基本的に「雨」、「曇りから雨」、「にわか雨」となることがわかります。雨の日が多くなります 前回の気温分布と合わせると、8日、9日と気温が下がっていることが分かりますが、この日は雨が降ったため気温が下がったと推測できます。
3. 結論
1. まず、クロールされた温度と湿度のデータを分析すると、気温は朝の低温から昼の高温、そして夕方の低温まで変化します。湿度と温度の傾向は逆である 相関係数により、温度と湿度には強い負の相関関係があることが判明 データを検討した結果、温度が上昇すると水蒸気の蒸発が激しくなり、室内の水分が減少することがわかった空気が減り、湿度が下がります。もちろん、湿度は気圧と雨の両方の影響を受け、雨が降ると湿度は大幅に上昇します。
2.经查阅资料空气质量不仅跟工厂、汽车等排放的烟气、废气等有关,更为重要的是与气象因素有关。由于昼夜温差明显变化,当地面温度高于高空温度时,空气上升,污染物易被带到高空扩散;当地面温度低于一定高度的温度时,天空形成逆温层,它像一个大盖子一样压在地面上空,使地表空气中各种污染物不易扩散。一般在晚间和清晨影响较大,而当太阳出来后,地面迅速升温,逆温层就会逐渐消散,于是污染空气也就扩散了。
3.风是由气压在水平方向分布的不均匀导致的。风受大气环流、地形、水域等不同因素的综合影响,表现形式多种多样,如季风、地方性的海陆风、山谷风等,一天的风向也有不同的变化,根据未来14天的风向雷达图可以发现未来所有风向基本都有涉及,并且没有特别的某个风向,原因可能是近期没有降水和气文变化不大,导致风向也没有太大的变化规律。
4.天气是指某一个地区距离地表较近的大气层在短时间内的具体状态。跟某瞬时内大气中各种气象要素分布的综合表现。根据未来14天的天气和温度变化可以大致推断出某个时间的气候,天气和温度之间也是有联系的。
4、代码框架
代码主要分为weather.py:对中国天气网进行爬取天气数据并保存csv文件;data1_analysis.py:对当天的天气信息进行可视化处理;data14_analysis.py:对未来14天的天气信息进行可视化处理。下面是代码的结构图:
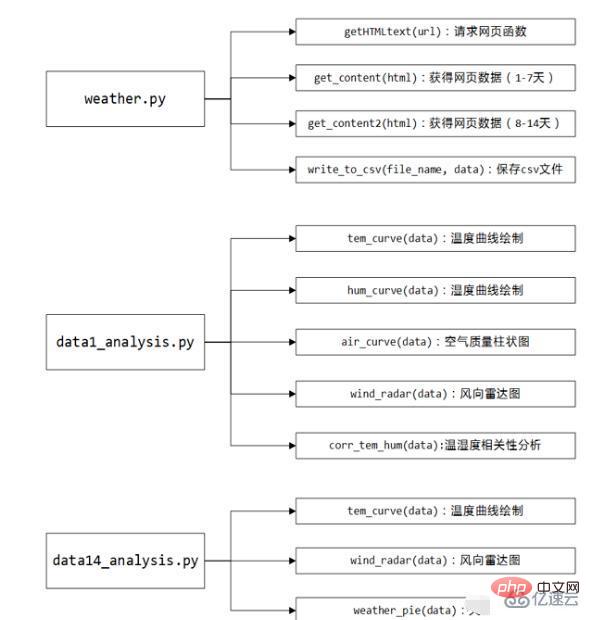
附源代码
weather.py
# weather.py
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import json
def getHTMLtext(url):
"""请求获得网页内容"""
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout = 30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
print("成功访问")
return r.text
except:
print("访问错误")
return" "
def get_content(html):
"""处理得到有用信息保存数据文件"""
final = []# 初始化一个列表保存数据
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")# 创建BeautifulSoup对象
body = bs.body
data = body.find('div', {'id': '7d'})# 找到div标签且id = 7d
# 下面爬取当天的数据
data2 = body.find_all('div',{'class':'left-div'})
text = data2[2].find('script').string
text = text[text.index('=')+1 :-2] # 移除改var data=将其变为json数据
jd = json.loads(text)
dayone = jd['od']['od2'] # 找到当天的数据
final_day = [] # 存放当天的数据
count = 0
for i in dayone:
temp = []
if count <=23:
temp.append(i['od21']) # 添加时间
temp.append(i['od22']) # 添加当前时刻温度
temp.append(i['od24']) # 添加当前时刻风力方向
temp.append(i['od25']) # 添加当前时刻风级
temp.append(i['od26']) # 添加当前时刻降水量
temp.append(i['od27']) # 添加当前时刻相对湿度
temp.append(i['od28']) # 添加当前时刻控制质量
#print(temp)
final_day.append(temp)
count = count +1
# 下面爬取7天的数据
ul = data.find('ul')# 找到所有的ul标签
li = ul.find_all('li')# 找到左右的li标签
i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数
for day in li:# 遍历找到的每一个li
if i < 7 and i > 0:
temp = []# 临时存放每天的数据
date = day.find('h2').string # 得到日期
date = date[0:date.index('日')] # 取出日期号
temp.append(date)
inf = day.find_all('p')# 找出li下面的p标签,提取第一个p标签的值,即天气
temp.append(inf[0].string)
tem_low = inf[1].find('i').string # 找到最低气温
if inf[1].find('span') is None: # 天气预报可能没有最高气温
tem_high = None
else:
tem_high = inf[1].find('span').string# 找到最高气温
temp.append(tem_low[:-1])
if tem_high[-1] == '℃':
temp.append(tem_high[:-1])
else:
temp.append(tem_high)
wind = inf[2].find_all('span')# 找到风向
for j in wind:
temp.append(j['title'])
wind_scale = inf[2].find('i').string # 找到风级
index1 = wind_scale.index('级')
temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1]))
final.append(temp)
i = i + 1
return final_day,final
#print(final)
def get_content2(html):
"""处理得到有用信息保存数据文件"""
final = []# 初始化一个列表保存数据
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")# 创建BeautifulSoup对象
body = bs.body
data = body.find('div', {'id': '15d'})# 找到div标签且id = 15d
ul = data.find('ul')# 找到所有的ul标签
li = ul.find_all('li')# 找到左右的li标签
final = []
i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数
for day in li: # 遍历找到的每一个li
if i < 8:
temp = [] # 临时存放每天的数据
date = day.find('span',{'class':'time'}).string# 得到日期
date = date[date.index('(')+1:-2]# 取出日期号
temp.append(date)
weather = day.find('span',{'class':'wea'}).string# 找到天气
temp.append(weather)
tem = day.find('span',{'class':'tem'}).text# 找到温度
temp.append(tem[tem.index('/')+1:-1]) # 找到最低气温
temp.append(tem[:tem.index('/')-1])# 找到最高气温
wind = day.find('span',{'class':'wind'}).string# 找到风向
if '转' in wind: # 如果有风向变化
temp.append(wind[:wind.index('转')])
temp.append(wind[wind.index('转')+1:])
else: # 如果没有风向变化,前后风向一致
temp.append(wind)
temp.append(wind)
wind_scale = day.find('span',{'class':'wind1'}).string# 找到风级
index1 = wind_scale.index('级')
temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1]))
final.append(temp)
return final
def write_to_csv(file_name, data, day=14):
"""保存为csv文件"""
with open(file_name, 'a', errors='ignore', newline='') as f:
if day == 14:
header = ['日期','天气','最低气温','最高气温','风向1','风向2','风级']
else:
header = ['小时','温度','风力方向','风级','降水量','相对湿度','空气质量']
f_csv = csv.writer(f)
f_csv.writerow(header)
f_csv.writerows(data)
def main():
"""主函数"""
print("Weather test")
# 珠海
url1 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101280701.shtml'# 7天天气中国天气网
url2 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather15d/101280701.shtml' # 8-15天天气中国天气网
html1 = getHTMLtext(url1)
data1, data1_7 = get_content(html1)# 获得1-7天和当天的数据
html2 = getHTMLtext(url2)
data8_14 = get_content2(html2) # 获得8-14天数据
data14 = data1_7 + data8_14
#print(data)
write_to_csv('weather14.csv',data14,14) # 保存为csv文件
write_to_csv('weather1.csv',data1,1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()data1_analysis.py:
# data1_analysis.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import math
def tem_curve(data):
"""温度曲线绘制"""
hour = list(data['小时'])
tem = list(data['温度'])
for i in range(0,24):
if math.isnan(tem[i]) == True:
tem[i] = tem[i-1]
tem_ave = sum(tem)/24 # 求平均温度
tem_max = max(tem)
tem_max_hour = hour[tem.index(tem_max)] # 求最高温度
tem_min = min(tem)
tem_min_hour = hour[tem.index(tem_min)] # 求最低温度
x = []
y = []
for i in range(0, 24):
x.append(i)
y.append(tem[hour.index(i)])
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(x,y,color='red',label='温度') # 画出温度曲线
plt.scatter(x,y,color='red') # 点出每个时刻的温度点
plt.plot([0, 24], [tem_ave, tem_ave], c='blue', linestyle='--',label='平均温度')# 画出平均温度虚线
plt.text(tem_max_hour+0.15, tem_max+0.15, str(tem_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高温度
plt.text(tem_min_hour+0.15, tem_min+0.15, str(tem_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低温度
plt.xticks(x)
plt.legend()
plt.title('一天温度变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('时间/h')
plt.ylabel('摄氏度/℃')
plt.show()
def hum_curve(data):
"""相对湿度曲线绘制"""
hour = list(data['小时'])
hum = list(data['相对湿度'])
for i in range(0,24):
if math.isnan(hum[i]) == True:
hum[i] = hum[i-1]
hum_ave = sum(hum)/24 # 求平均相对湿度
hum_max = max(hum)
hum_max_hour = hour[hum.index(hum_max)] # 求最高相对湿度
hum_min = min(hum)
hum_min_hour = hour[hum.index(hum_min)] # 求最低相对湿度
x = []
y = []
for i in range(0, 24):
x.append(i)
y.append(hum[hour.index(i)])
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(x,y,color='blue',label='相对湿度') # 画出相对湿度曲线
plt.scatter(x,y,color='blue') # 点出每个时刻的相对湿度
plt.plot([0, 24], [hum_ave, hum_ave], c='red', linestyle='--',label='平均相对湿度')# 画出平均相对湿度虚线
plt.text(hum_max_hour+0.15, hum_max+0.15, str(hum_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高相对湿度
plt.text(hum_min_hour+0.15, hum_min+0.15, str(hum_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低相对湿度
plt.xticks(x)
plt.legend()
plt.title('一天相对湿度变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('时间/h')
plt.ylabel('百分比/%')
plt.show()
def air_curve(data):
"""空气质量曲线绘制"""
hour = list(data['小时'])
air = list(data['空气质量'])
print(type(air[0]))
for i in range(0,24):
if math.isnan(air[i]) == True:
air[i] = air[i-1]
air_ave = sum(air)/24 # 求平均空气质量
air_max = max(air)
air_max_hour = hour[air.index(air_max)] # 求最高空气质量
air_min = min(air)
air_min_hour = hour[air.index(air_min)] # 求最低空气质量
x = []
y = []
for i in range(0, 24):
x.append(i)
y.append(air[hour.index(i)])
plt.figure(3)
for i in range(0,24):
if y[i] <= 50:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='lightgreen',width=0.7)# 1等级
elif y[i] <= 100:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='wheat',width=0.7) # 2等级
elif y[i] <= 150:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='orange',width=0.7) # 3等级
elif y[i] <= 200:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='orangered',width=0.7)# 4等级
elif y[i] 300:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='maroon',width=0.7) # 6等级
plt.plot([0, 24], [air_ave, air_ave], c='black', linestyle='--')# 画出平均空气质量虚线
plt.text(air_max_hour+0.15, air_max+0.15, str(air_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高空气质量
plt.text(air_min_hour+0.15, air_min+0.15, str(air_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低空气质量
plt.xticks(x)
plt.title('一天空气质量变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('时间/h')
plt.ylabel('空气质量指数AQI')
plt.show()
def wind_radar(data):
"""风向雷达图"""
wind = list(data['风力方向'])
wind_speed = list(data['风级'])
for i in range(0,24):
if wind[i] == "北风":
wind[i] = 90
elif wind[i] == "南风":
wind[i] = 270
elif wind[i] == "西风":
wind[i] = 180
elif wind[i] == "东风":
wind[i] = 360
elif wind[i] == "东北风":
wind[i] = 45
elif wind[i] == "西北风":
wind[i] = 135
elif wind[i] == "西南风":
wind[i] = 225
elif wind[i] == "东南风":
wind[i] = 315
degs = np.arange(45,361,45)
temp = []
for deg in degs:
speed = []
# 获取 wind_deg 在指定范围的风速平均值数据
for i in range(0,24):
if wind[i] == deg:
speed.append(wind_speed[i])
if len(speed) == 0:
temp.append(0)
else:
temp.append(sum(speed)/len(speed))
print(temp)
N = 8
theta = np.arange(0.+np.pi/8,2*np.pi+np.pi/8,2*np.pi/8)
# 数据极径
radii = np.array(temp)
# 绘制极区图坐标系
plt.axes(polar=True)
# 定义每个扇区的RGB值(R,G,B),x越大,对应的颜色越接近蓝色
colors = [(1-x/max(temp), 1-x/max(temp),0.6) for x in radii]
plt.bar(theta,radii,width=(2*np.pi/N),bottom=0.0,color=colors)
plt.title('一天风级图',x=0.2,fontsize=20)
plt.show()
def calc_corr(a, b):
"""计算相关系数"""
a_avg = sum(a)/len(a)
b_avg = sum(b)/len(b)
cov_ab = sum([(x - a_avg)*(y - b_avg) for x,y in zip(a, b)])
sq = math.sqrt(sum([(x - a_avg)**2 for x in a])*sum([(x - b_avg)**2 for x in b]))
corr_factor = cov_ab/sq
return corr_factor
def corr_tem_hum(data):
"""温湿度相关性分析"""
tem = data['温度']
hum = data['相对湿度']
plt.scatter(tem,hum,color='blue')
plt.title("温湿度相关性分析图")
plt.xlabel("温度/℃")
plt.ylabel("相对湿度/%")
plt.text(20,40,"相关系数为:"+str(calc_corr(tem,hum)),fontdict={'size':'10','color':'red'})
plt.show()
print("相关系数为:"+str(calc_corr(tem,hum)))
def main():
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 解决中文显示问题
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False# 解决负号显示问题
data1 = pd.read_csv('weather1.csv',encoding='gb2312')
print(data1)
tem_curve(data1)
hum_curve(data1)
air_curve(data1)
wind_radar(data1)
corr_tem_hum(data1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
data14_analysis.py:
# data14_analysis.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import math
def tem_curve(data):
"""温度曲线绘制"""
date = list(data['日期'])
tem_low = list(data['最低气温'])
tem_high = list(data['最高气温'])
for i in range(0,14):
if math.isnan(tem_low[i]) == True:
tem_low[i] = tem_low[i-1]
if math.isnan(tem_high[i]) == True:
tem_high[i] = tem_high[i-1]
tem_high_ave = sum(tem_high)/14 # 求平均高温
tem_low_ave = sum(tem_low)/14 # 求平均低温
tem_max = max(tem_high)
tem_max_date = tem_high.index(tem_max) # 求最高温度
tem_min = min(tem_low)
tem_min_date = tem_low.index(tem_min) # 求最低温度
x = range(1,15)
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(x,tem_high,color='red',label='高温')# 画出高温度曲线
plt.scatter(x,tem_high,color='red') # 点出每个时刻的温度点
plt.plot(x,tem_low,color='blue',label='低温')# 画出低温度曲线
plt.scatter(x,tem_low,color='blue') # 点出每个时刻的温度点
plt.plot([1, 15], [tem_high_ave, tem_high_ave], c='black', linestyle='--')# 画出平均温度虚线
plt.plot([1, 15], [tem_low_ave, tem_low_ave], c='black', linestyle='--')# 画出平均温度虚线
plt.legend()
plt.text(tem_max_date+0.15, tem_max+0.15, str(tem_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高温度
plt.text(tem_min_date+0.15, tem_min+0.15, str(tem_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低温度
plt.xticks(x)
plt.title('未来14天高温低温变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('未来天数/天')
plt.ylabel('摄氏度/℃')
plt.show()
def change_wind(wind):
"""改变风向"""
for i in range(0,14):
if wind[i] == "北风":
wind[i] = 90
elif wind[i] == "南风":
wind[i] = 270
elif wind[i] == "西风":
wind[i] = 180
elif wind[i] == "东风":
wind[i] = 360
elif wind[i] == "东北风":
wind[i] = 45
elif wind[i] == "西北风":
wind[i] = 135
elif wind[i] == "西南风":
wind[i] = 225
elif wind[i] == "东南风":
wind[i] = 315
return wind
def wind_radar(data):
"""风向雷达图"""
wind1 = list(data['风向1'])
wind2 = list(data['风向2'])
wind_speed = list(data['风级'])
wind1 = change_wind(wind1)
wind2 = change_wind(wind2)
degs = np.arange(45,361,45)
temp = []
for deg in degs:
speed = []
# 获取 wind_deg 在指定范围的风速平均值数据
for i in range(0,14):
if wind1[i] == deg:
speed.append(wind_speed[i])
if wind2[i] == deg:
speed.append(wind_speed[i])
if len(speed) == 0:
temp.append(0)
else:
temp.append(sum(speed)/len(speed))
print(temp)
N = 8
theta = np.arange(0.+np.pi/8,2*np.pi+np.pi/8,2*np.pi/8)
# 数据极径
radii = np.array(temp)
# 绘制极区图坐标系
plt.axes(polar=True)
# 定义每个扇区的RGB值(R,G,B),x越大,对应的颜色越接近蓝色
colors = [(1-x/max(temp), 1-x/max(temp),0.6) for x in radii]
plt.bar(theta,radii,width=(2*np.pi/N),bottom=0.0,color=colors)
plt.title('未来14天风级图',x=0.2,fontsize=20)
plt.show()
def weather_pie(data):
"""绘制天气饼图"""
weather = list(data['天气'])
dic_wea = { }
for i in range(0,14):
if weather[i] in dic_wea.keys():
dic_wea[weather[i]] += 1
else:
dic_wea[weather[i]] = 1
print(dic_wea)
explode=[0.01]*len(dic_wea.keys())
color = ['lightskyblue','silver','yellow','salmon','grey','lime','gold','red','green','pink']
plt.pie(dic_wea.values(),explode=explode,labels=dic_wea.keys(),autopct='%1.1f%%',colors=color)
plt.title('未来14天气候分布饼图')
plt.show()
def main():
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 解决中文显示问题
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False# 解决负号显示问题
data14 = pd.read_csv('weather14.csv',encoding='gb2312')
print(data14)
tem_curve(data14)
wind_radar(data14)
weather_pie(data14)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()以上がPythonで気象データをクローリングして視覚的に分析する方法とは?の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7643
7643
 15
15
 1392
1392
 52
52
 91
91
 11
11
 33
33
 151
151
 PHPおよびPython:さまざまなパラダイムが説明されています
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHPおよびPython:さまざまなパラダイムが説明されています
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHPは主に手順プログラミングですが、オブジェクト指向プログラミング(OOP)もサポートしています。 Pythonは、OOP、機能、手続き上のプログラミングなど、さまざまなパラダイムをサポートしています。 PHPはWeb開発に適しており、Pythonはデータ分析や機械学習などのさまざまなアプリケーションに適しています。
 PHPとPythonの選択:ガイド
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHPとPythonの選択:ガイド
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHPはWeb開発と迅速なプロトタイピングに適しており、Pythonはデータサイエンスと機械学習に適しています。 1.PHPは、単純な構文と迅速な開発に適した動的なWeb開発に使用されます。 2。Pythonには簡潔な構文があり、複数のフィールドに適しており、強力なライブラリエコシステムがあります。
 Windows 8でコードを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Windows 8でコードを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VSコードはWindows 8で実行できますが、エクスペリエンスは大きくない場合があります。まず、システムが最新のパッチに更新されていることを確認してから、システムアーキテクチャに一致するVSコードインストールパッケージをダウンロードして、プロンプトとしてインストールします。インストール後、一部の拡張機能はWindows 8と互換性があり、代替拡張機能を探すか、仮想マシンで新しいWindowsシステムを使用する必要があることに注意してください。必要な拡張機能をインストールして、適切に動作するかどうかを確認します。 Windows 8ではVSコードは実行可能ですが、開発エクスペリエンスとセキュリティを向上させるために、新しいWindowsシステムにアップグレードすることをお勧めします。
 VSCODE拡張機能は悪意がありますか?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VSCODE拡張機能は悪意がありますか?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VSコード拡張機能は、悪意のあるコードの隠れ、脆弱性の活用、合法的な拡張機能としての自慰行為など、悪意のあるリスクを引き起こします。悪意のある拡張機能を識別する方法には、パブリッシャーのチェック、コメントの読み取り、コードのチェック、およびインストールに注意してください。セキュリティ対策には、セキュリティ認識、良好な習慣、定期的な更新、ウイルス対策ソフトウェアも含まれます。
 Visual StudioコードはPythonで使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Visual StudioコードはPythonで使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VSコードはPythonの書き込みに使用でき、Pythonアプリケーションを開発するための理想的なツールになる多くの機能を提供できます。ユーザーは以下を可能にします。Python拡張機能をインストールして、コードの完了、構文の強調表示、デバッグなどの関数を取得できます。デバッガーを使用して、コードを段階的に追跡し、エラーを見つけて修正します。バージョンコントロールのためにGitを統合します。コードフォーマットツールを使用して、コードの一貫性を維持します。糸くずツールを使用して、事前に潜在的な問題を発見します。
 ターミナルVSCODEでプログラムを実行する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
ターミナルVSCODEでプログラムを実行する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
VSコードでは、次の手順を通じて端末でプログラムを実行できます。コードを準備し、統合端子を開き、コードディレクトリが端末作業ディレクトリと一致していることを確認します。プログラミング言語(pythonのpython your_file_name.pyなど)に従って実行コマンドを選択して、それが正常に実行されるかどうかを確認し、エラーを解決します。デバッガーを使用して、デバッグ効率を向上させます。
 Python vs. JavaScript:学習曲線と使いやすさ
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:学習曲線と使いやすさ
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Pythonは、スムーズな学習曲線と簡潔な構文を備えた初心者により適しています。 JavaScriptは、急な学習曲線と柔軟な構文を備えたフロントエンド開発に適しています。 1。Python構文は直感的で、データサイエンスやバックエンド開発に適しています。 2。JavaScriptは柔軟で、フロントエンドおよびサーバー側のプログラミングで広く使用されています。
 vscodeはMacに使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
vscodeはMacに使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VSコードはMacで利用できます。強力な拡張機能、GIT統合、ターミナル、デバッガーがあり、豊富なセットアップオプションも提供しています。ただし、特に大規模なプロジェクトまたは非常に専門的な開発の場合、コードと機能的な制限がある場合があります。




