
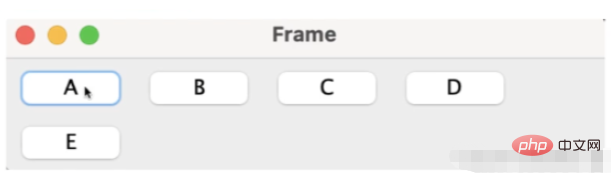
すべてのコンポーネントがフローのように 1 つずつ排出され、1 行が埋まると次の行が配置されます。コンポーネントは中央に配置されていますが、設定することもできます。
フローレイアウトの構築方法:
new FlowLayout();
new FlowLayout(intalignment);//配置を設定します(デフォルトはFlowLayout.CENTER) Centered) の場合、通常は FlowLayout.LEFT
new FlowLayout(int aligment,int horizGap,int vertGap);//配置の上下のオフセット
aligment 値を設定します。
FlowLayout.LEFT = 0
FlowLayout.CENTER = 1
FlowLayout.RIGHT = 2
setLayout 関数で設定しますレイアウト
例:jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
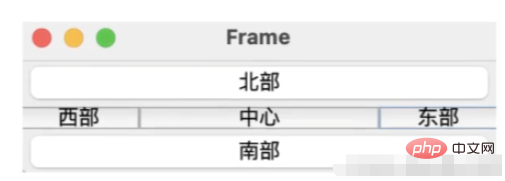
ボーダー レイアウトは、既定のレイアウト管理方法です。ボーダー レイアウトは、コンテナーを東 (BorderLayout.EAST)、西 (BorderLayout.WEST)、南 (BorderLayout.SOUTH)、北 (BorderLayout.NORTH)、中央 ( BorderLayout) .CENTER) 5 エリア
新規作成時にコンテンツを指定
JFrame コンテナにコンポーネントを追加するときに境界を指定
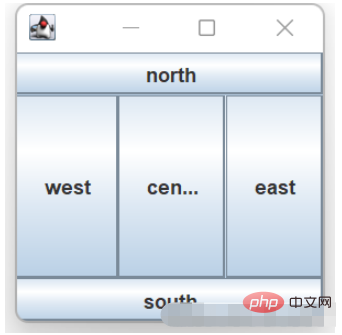
例:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class Borderlayout{
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jf = new JFrame();
jf.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JButton east = new JButton("east");
JButton west = new JButton("west");
JButton south = new JButton("south");
JButton north = new JButton("north");
JButton center = new JButton("center");
jf.add(east,BorderLayout.EAST);
jf.add(west,BorderLayout.WEST);
jf.add(south,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
jf.add(north,BorderLayout.NORTH);
jf.add(center,BorderLayout.CENTER);
jf.setSize(200,200);
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
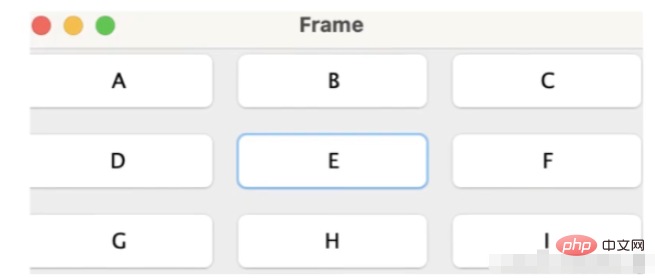
グリッド レイアウトの分割コンテナをグリッドに配置し、すべてのコンポーネントは行と列の数に従って決定されます。各コンポーネントはスペースを埋め、コンテナのサイズを変更し、それに応じてコンポーネントのサイズも変更します。
構築方法:
GridLayout(int rows,int columns) ;// 行数と列数を指定します
GridLayout(int rows,int columns,int horizGap,int vertGap);//行数と列数、水平間隔と垂直間隔を指定します
以上がJava GUI での 3 つの一般的なレイアウト方法とその使用法の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。