
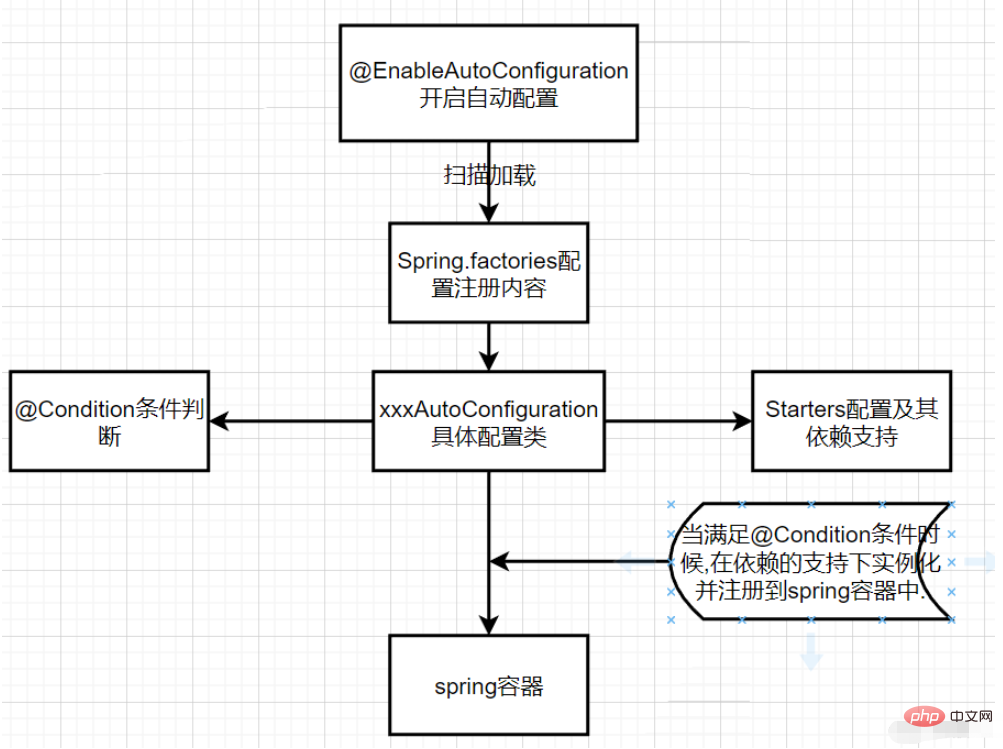
SpringBoot は、@EnableAutoConfiguration アノテーションを通じて自動構成をオンにし、jar パッケージの下の spring.factories ファイルをスキャンします。このファイルには、自動的に構成できるクラスが含まれています。 @Condition アノテーションで指定された条件が満たされると、依存関係のサポートを使用してインスタンス化され、Spring コンテナーに登録されます。
一般的に、以前に ssm プロジェクトを作成した際には、多数の座標や設定内容を設定する必要があり、プロジェクトの開発では環境を整える作業に多くの時間がかかりました。 SpringBoot はさまざまな XML 構成コンテンツを簡素化するため、SpringBoot の自動構成ではアノテーションを使用して一部の従来の構成のデフォルト構成を作成し、プロジェクトを迅速に実行できるように XML 構成コンテンツを簡素化します。
Springboot コア構成原則:
自動構成クラスは、spring-boot-autoconfigure-versionnumber.jar の下の org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure に保存されます
application.properties で debug=true を設定するとコンテナが起動します。サーバーの初期化の初期構成を確認できます。
DispatcherServletAutoConfigratioRegister フロントエンド コントローラー
EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfigurationRegister コンテナ タイプ
HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration は json または xml プロセッサを登録します
JacksonAutoConfiguration は json オブジェクト パーサーを登録します
他の関数への依存関係を追加すると、springBoot も実装しますこれらの関数の自動構成
スターター コンポーネントは、アプリケーション アイテムにロードできる Maven の依存関係です。 。対応する依存関係構成を Maven 構成に追加することによってのみ、対応するスターター コンポーネントを使用できます。たとえば、spring-boot-starter-web 依存関係を追加すると、Spring MVC および Tomcat 埋め込みコンテナを含む REST API サービスを構築することができます。
完全なスターター コンポーネントには、次の 2 つの点が含まれます。package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ServletRequest.class})
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class})
@Import({ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class})
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
......
}
@@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
//检查自动配置功能是否开启,默认开启
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
//加载自动配置的元信息
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
//获取候选配置类
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
//去掉重复的配置类
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
//获得注解中被exclude和excludeName排除的类的集合
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//检查被排除类是否可实例化、是否被自动注册配置所使用,不符合条件则抛出异常
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
//从候选配置类中去除掉被排除的类
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
//过滤
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
//将配置类和排除类通过事件传入到监听器中
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
//最终返回符合条件的自动配置类的全限定名数组
return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
"] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}com.xxx.interface= com.xxx.classname###
以上がSpringBoot自動構成の実装原理は何ですか?の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。