Python を使用してカスタム Web フレームワークを開発する方法
カスタム Web フレームワークを開発する
Web サーバーから動的リソース要求を受信し、動的リソース要求を処理するためのサービスを Web サーバーに提供します。要求されたリソース パスのサフィックス名に基づいて決定します。
要求されたリソース パスのサフィックス名が .html の場合、それは動的リソース要求であり、Web フレームワーク プログラムに処理させます。
それ以外の場合、これは静的リソース要求であるため、Web サーバー プログラムに処理させます。
1. Web サーバーのメイン プログラムを開発します
1. クライアントの HTTP リクエストを受け入れます (最下層は TCP)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : My_Web_Server.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : 1071505897@qq.com
# @Time : 2022/7/24 21:28
from socket import *
import threading
# 开发自己的Web服务器主类
class MyHttpWebServer(object):
def __init__(self, port):
# 创建 HTTP服务的 TCP套接字
server_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# 设置端口号互用,程序退出之后不需要等待,直接释放端口
server_socket.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, True)
# 绑定 ip和 port
server_socket.bind(('', port))
# listen使套接字变为了被动连接
server_socket.listen(128)
self.server_socket = server_socket
# 处理请求函数
@staticmethod # 静态方法
def handle_browser_request(new_socket):
# 接受客户端发来的数据
recv_data = new_socket.recv(4096)
# 如果没有数据,那么请求无效,关闭套接字,直接退出
if len(recv_data) == 0:
new_socket.close()
return
# 启动服务器,并接受客户端请求
def start(self):
# 循环并多线程来接收客户端请求
while True:
# accept等待客户端连接
new_socket, ip_port = self.server_socket.accept()
print("客户端ip和端口", ip_port)
# 一个客户端的请求交给一个线程来处理
sub_thread = threading.Thread(target=MyHttpWebServer.handle_browser_request, args=(new_socket, ))
# 设置当前线程为守护线程
sub_thread.setDaemon(True)
sub_thread.start() # 启动子线程
# Web 服务器程序的入口
def main():
web_server = MyHttpWebServer(8080)
web_server.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()2. リクエストが静的リソースまたは動的リソース
# 对接收的字节数据进行转换为字符数据
request_data = recv_data.decode('utf-8')
print("浏览器请求的数据:", request_data)
request_array = request_data.split(' ', maxsplit=2)
# 得到请求路径
request_path = request_array[1]
print("请求的路径是:", request_path)
if request_path == "/":
# 如果请求路径为根目录,自动设置为:/index.html
request_path = "/index.html"
# 判断是否为:.html 结尾
if request_path.endswith(".html"):
"动态资源请求"
pass
else:
"静态资源请求"
pass3. 静的リソースをどのように扱うか?
"静态资源请求"
# 根据请求路径读取/static 目录中的文件数据,相应给客户端
response_body = None # 响应主体
response_header = None # 响应头的第一行
response_first_line = None # 响应头内容
response_type = 'test/html' # 默认响应类型
try:
# 读取 static目录中相对应的文件数据,rb模式是一种兼容模式,可以打开图片,也可以打开js
with open('static'+request_path, 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read()
if request_path.endswith('.jpg'):
response_type = 'image/webp'
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
response_header = 'Content-Length:' + str(len(response_body)) + '\r\n' + \
'Content-Type: ' + response_type + '; charset=utf-8\r\n' + \
'Date:' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()) + '\r\n' + \
'Server: Flyme awei Server\r\n'
# 浏览器读取的文件可能不存在
except Exception as e:
with open('static/404.html', 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read() # 响应的主体页面内容
# 响应头
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n'
response_header = 'Content-Length:'+str(len(response_body))+'\r\n' + \
'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n' + \
'Date:' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()) + '\r\n' + \
'Server: Flyme awei Server\r\n'
# 最后都会执行的代码
finally:
# 组成响应数据发送给(客户端)浏览器
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n').encode('utf-8') + response_body
new_socket.send(response)
# 关闭套接字
new_socket.close()
静的リソース要求の検証:
4. 動的リソースの場合対処方法
if request_path.endswith(".html"):
"动态资源请求"
# 动态资源的处理交给Web框架来处理,需要把请求参数交给Web框架,可能会有多个参数,采用字典结构
params = {
'request_path': request_path
}
# Web框架处理动态资源请求后,返回一个响应
response = MyFramework.handle_request(params)
new_socket.send(response)
new_socket.close()5. Webサーバーを閉じる
new_socket.close()
Webサーバーメインフレームワークのコード全体表示:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : My_Web_Server.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : 1071505897@qq.com
# @Time : 2022/7/24 21:28
import sys
import time
from socket import *
import threading
import MyFramework
# 开发自己的Web服务器主类
class MyHttpWebServer(object):
def __init__(self, port):
# 创建 HTTP服务的 TCP套接字
server_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# 设置端口号互用,程序退出之后不需要等待,直接释放端口
server_socket.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, True)
# 绑定 ip和 port
server_socket.bind(('', port))
# listen使套接字变为了被动连接
server_socket.listen(128)
self.server_socket = server_socket
# 处理请求函数
@staticmethod # 静态方法
def handle_browser_request(new_socket):
# 接受客户端发来的数据
recv_data = new_socket.recv(4096)
# 如果没有数据,那么请求无效,关闭套接字,直接退出
if len(recv_data) == 0:
new_socket.close()
return
# 对接收的字节数据进行转换为字符数据
request_data = recv_data.decode('utf-8')
print("浏览器请求的数据:", request_data)
request_array = request_data.split(' ', maxsplit=2)
# 得到请求路径
request_path = request_array[1]
print("请求的路径是:", request_path)
if request_path == "/":
# 如果请求路径为根目录,自动设置为:/index.html
request_path = "/index.html"
# 判断是否为:.html 结尾
if request_path.endswith(".html"):
"动态资源请求"
# 动态资源的处理交给Web框架来处理,需要把请求参数交给Web框架,可能会有多个参数,采用字典结构
params = {
'request_path': request_path
}
# Web框架处理动态资源请求后,返回一个响应
response = MyFramework.handle_request(params)
new_socket.send(response)
new_socket.close()
else:
"静态资源请求"
# 根据请求路径读取/static 目录中的文件数据,相应给客户端
response_body = None # 响应主体
response_header = None # 响应头的第一行
response_first_line = None # 响应头内容
response_type = 'test/html' # 默认响应类型
try:
# 读取 static目录中相对应的文件数据,rb模式是一种兼容模式,可以打开图片,也可以打开js
with open('static'+request_path, 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read()
if request_path.endswith('.jpg'):
response_type = 'image/webp'
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
response_header = 'Content-Length:' + str(len(response_body)) + '\r\n' + \
'Content-Type: ' + response_type + '; charset=utf-8\r\n' + \
'Date:' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()) + '\r\n' + \
'Server: Flyme awei Server\r\n'
# 浏览器读取的文件可能不存在
except Exception as e:
with open('static/404.html', 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read() # 响应的主体页面内容
# 响应头
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n'
response_header = 'Content-Length:'+str(len(response_body))+'\r\n' + \
'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n' + \
'Date:' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()) + '\r\n' + \
'Server: Flyme awei Server\r\n'
# 最后都会执行的代码
finally:
# 组成响应数据发送给(客户端)浏览器
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n').encode('utf-8') + response_body
new_socket.send(response)
# 关闭套接字
new_socket.close()
# 启动服务器,并接受客户端请求
def start(self):
# 循环并多线程来接收客户端请求
while True:
# accept等待客户端连接
new_socket, ip_port = self.server_socket.accept()
print("客户端ip和端口", ip_port)
# 一个客户端的请求交给一个线程来处理
sub_thread = threading.Thread(target=MyHttpWebServer.handle_browser_request, args=(new_socket, ))
# 设置当前线程为守护线程
sub_thread.setDaemon(True)
sub_thread.start() # 启动子线程
# Web 服务器程序的入口
def main():
web_server = MyHttpWebServer(8080)
web_server.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()2. のメインプログラムを開発します。 Web フレームワーク
1. リクエスト パスに応じて、対応するデータを動的に応答します。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : MyFramework.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : 1071505897@qq.com
# @Time : 2022/7/25 14:05
import time
# 自定义Web框架
# 处理动态资源请求的函数
def handle_request(parm):
request_path = parm['request_path']
if request_path == '/index.html': # 当前请求路径有与之对应的动态响应,当前框架只开发了 index.html的功能
response = index()
return response
else:
# 没有动态资源的数据,返回404页面
return page_not_found()
# 当前 index函数,专门处理index.html的请求
def index():
# 需求,在页面中动态显示当前系统时间
data = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
response_body = data
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
response_header = 'Content-Length:' + str(len(response_body)) + '\r\n' + \
'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n' + \
'Date:' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()) + '\r\n' + \
'Server: Flyme awei Server\r\n'
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n' + response_body).encode('utf-8')
return response
def page_not_found():
with open('static/404.html', 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read() # 响应的主体页面内容
# 响应头
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n'
response_header = 'Content-Length:' + str(len(response_body)) + '\r\n' + \
'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n' + \
'Date:' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime()) + '\r\n' + \
'Server: Flyme awei Server\r\n'
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n').encode('utf-8') + response_body
return response2. リクエスト パスに対応する応答データがない場合は、 404 ページ
3. テンプレートを使用して応答コンテンツを表示します
1. テンプレートのindex.htmlを自分で設計し、動的データを使用してそれを置き換えます。 places
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>首页 - 电影列表</title>
<link href="/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="/js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script src="/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="navbar navbar-inverse navbar-static-top ">
<div class="container">
<div class="navbar-header">
<button class="navbar-toggle" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#mymenu">
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</button>
<a href="#" class="navbar-brand">电影列表</a>
</div>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="mymenu">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li class="active"><a href="">电影信息</a></li>
<li><a href="">个人中心</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="container-fluid">
<table class="table table-hover">
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>导演</th>
<th>上映时间</th>
<th>票房</th>
<th>电影时长</th>
<th>类型</th>
<th>备注</th>
<th>删除电影</th>
</tr>
{%datas%}
</table>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>2. 置き換え方法と置き換えるデータ
response_body = response_body.replace('{%datas%}', data)
| 処理関数 | |
|---|---|
| index function | |
| user_info function |
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : My_Web_Server.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : 1071505897@qq.com
# @Time : 2022/7/24 21:28
# 定义路由表
route_list = []
# route_list = {
# ('/index.html', index),
# ('/user_info.html', user_info)
# }
# 定义一个带参数的装饰器
def route(request_path): # 参数就是URL请求
def add_route(func):
# 添加路由表
route_list.append((request_path, func))
@wraps(func)
def invoke(*args, **kwargs):
# 调用指定的处理函数,并返回结果
return func()
return invoke
return add_route
# 处理动态资源请求的函数
def handle_request(parm):
request_path = parm['request_path']
# if request_path == '/index.html': # 当前请求路径有与之对应的动态响应,当前框架只开发了 index.html的功能
# response = index()
# return response
# elif request_path == '/user_info.html': # 个人中心的功能
# return user_info()
# else:
# # 没有动态资源的数据,返回404页面
# return page_not_found()
for path, func in route_list:
if request_path == path:
return func()
else:
# 没有动态资源的数据,返回404页面
return page_not_found()@route('/user_info.html')
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : My_Web_Server.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : 1071505897@qq.com
# @Time : 2022/7/24 21:28
import socket
import sys
import threading
import time
import MyFramework
# 开发自己的Web服务器主类
class MyHttpWebServer(object):
def __init__(self, port):
# 创建HTTP服务器的套接字
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 设置端口号复用,程序退出之后不需要等待几分钟,直接释放端口
server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, True)
server_socket.bind(('', port))
server_socket.listen(128)
self.server_socket = server_socket
# 处理浏览器请求的函数
@staticmethod
def handle_browser_request(new_socket):
# 接受客户端发送过来的数据
recv_data = new_socket.recv(4096)
# 如果没有收到数据,那么请求无效,关闭套接字,直接退出
if len(recv_data) == 0:
new_socket.close()
return
# 对接受的字节数据,转换成字符
request_data = recv_data.decode('utf-8')
print("浏览器请求的数据:", request_data)
request_array = request_data.split(' ', maxsplit=2)
# 得到请求路径
request_path = request_array[1]
print('请求路径是:', request_path)
if request_path == '/': # 如果请求路径为跟目录,自动设置为/index.html
request_path = '/index.html'
# 根据请求路径来判断是否是动态资源还是静态资源
if request_path.endswith('.html'):
'''动态资源的请求'''
# 动态资源的处理交给Web框架来处理,需要把请求参数传给Web框架,可能会有多个参数,所有采用字典机构
params = {
'request_path': request_path,
}
# Web框架处理动态资源请求之后,返回一个响应
response = MyFramework.handle_request(params)
new_socket.send(response)
new_socket.close()
else:
'''静态资源的请求'''
response_body = None # 响应主体
response_header = None # 响应头
response_first_line = None # 响应头的第一行
# 其实就是:根据请求路径读取/static目录中静态的文件数据,响应给客户端
try:
# 读取static目录中对应的文件数据,rb模式:是一种兼容模式,可以打开图片,也可以打开js
with open('static' + request_path, 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read()
if request_path.endswith('.jpg'):
response_type = 'image/webp'
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
response_header = 'Server: Laoxiao_Server\r\n'
except Exception as e: # 浏览器想读取的文件可能不存在
with open('static/404.html', 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read() # 响应的主体页面内容(字节)
# 响应头 (字符数据)
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n'
response_header = 'Server: Laoxiao_Server\r\n'
finally:
# 组成响应数据,发送给客户端(浏览器)
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n').encode('utf-8') + response_body
new_socket.send(response)
new_socket.close() # 关闭套接字
# 启动服务器,并且接受客户端的请求
def start(self):
# 循环并且多线程来接受客户端的请求
while True:
new_socket, ip_port = self.server_socket.accept()
print("客户端的ip和端口", ip_port)
# 一个客户端请求交给一个线程来处理
sub_thread = threading.Thread(target=MyHttpWebServer.handle_browser_request, args=(new_socket,))
sub_thread.setDaemon(True) # 设置当前线程为守护线程
sub_thread.start() # 子线程要启动
# web服务器程序的入口
def main():
web_server = MyHttpWebServer(8080)
web_server.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : My_Web_Server.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : 1071505897@qq.com
# @Time : 2022/7/24 21:28
import time
from functools import wraps
import pymysql
# 定义路由表
route_list = []
# route_list = {
# # ('/index.html',index),
# # ('/userinfo.html',user_info)
# }
# 定义一个带参数装饰器
def route(request_path): # 参数就是URL请求
def add_route(func):
# 添加路由到路由表
route_list.append((request_path, func))
@wraps(func)
def invoke(*arg, **kwargs):
# 调用我们指定的处理函数,并且返回结果
return func()
return invoke
return add_route
# 处理动态资源请求的函数
def handle_request(params):
request_path = params['request_path']
for path, func in route_list:
if request_path == path:
return func()
else:
# 没有动态资源的数据,返回404页面
return page_not_found()
# if request_path =='/index.html': # 当前的请求路径有与之对应的动态响应,当前框架,我只开发了index.html的功能
# response = index()
# return response
#
# elif request_path =='/userinfo.html': # 个人中心的功能,user_info.html
# return user_info()
# else:
# # 没有动态资源的数据,返回404页面
# return page_not_found()
# 当前user_info函数,专门处理userinfo.html的动态请求
@route('/userinfo.html')
def user_info():
# 需求:在页面中动态显示当前系统时间
date = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
# response_body =data
with open('template/user_info.html', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
response_body = f.read()
response_body = response_body.replace('{%datas%}', date)
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
response_header = 'Server: Laoxiao_Server\r\n'
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n' + response_body).encode('utf-8')
return response
# 当前index函数,专门处理index.html的请求
@route('/index.html')
def index():
# 需求:从数据库中取得所有的电影数据,并且动态展示
# date = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
# response_body =data
# 1、从MySQL中查询数据
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='******', database='test', charset='utf8')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('select * from t_movies')
result = cursor.fetchall()
# print(result)
datas = ""
for row in result:
datas += '''<tr>
<td>%s</td>
<td>%s</td>
<td>%s</td>
<td>%s</td>
<td>%s 亿人民币</td>
<td>%s</td>
<td>%s</td>
<td>%s</td>
<td> <input type='button' value='删除'/> </td>
</tr>
''' % row
print(datas)
# 把查询的数据,转换成动态内容
with open('template/index.html', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
response_body = f.read()
response_body = response_body.replace('{%datas%}', datas)
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
response_header = 'Server: Laoxiao_Server\r\n'
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n' + response_body).encode('utf-8')
return response
# 处理没有找到对应的动态资源
def page_not_found():
with open('static/404.html', 'rb') as f:
response_body = f.read() # 响应的主体页面内容(字节)
# 响应头 (字符数据)
response_first_line = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n'
response_header = 'Server: Laoxiao_Server\r\n'
response = (response_first_line + response_header + '\r\n').encode('utf-8') + response_body
return response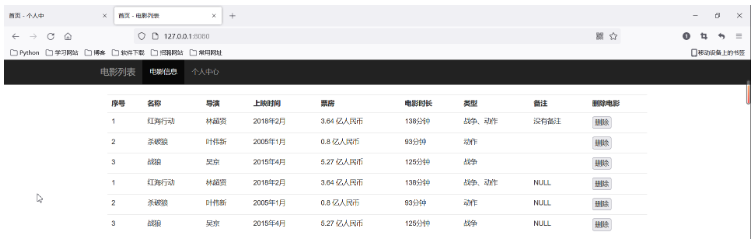
以上がPython を使用してカスタム Web フレームワークを開発する方法の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7517
7517
 15
15
 1378
1378
 52
52
 79
79
 11
11
 21
21
 66
66
 Debian Apacheログを使用してWebサイトのパフォーマンスを向上させる方法
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
Debian Apacheログを使用してWebサイトのパフォーマンスを向上させる方法
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
この記事では、Debianシステムの下でApacheログを分析することにより、Webサイトのパフォーマンスを改善する方法について説明します。 1.ログ分析の基本Apacheログは、IPアドレス、タイムスタンプ、リクエストURL、HTTPメソッド、応答コードなど、すべてのHTTP要求の詳細情報を記録します。 Debian Systemsでは、これらのログは通常、/var/log/apache2/access.logおよび/var/log/apache2/error.logディレクトリにあります。ログ構造を理解することは、効果的な分析の最初のステップです。 2。ログ分析ツールさまざまなツールを使用してApacheログを分析できます。コマンドラインツール:GREP、AWK、SED、およびその他のコマンドラインツール。
 Python:ゲーム、GUIなど
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:ゲーム、GUIなど
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
PythonはゲームとGUI開発に優れています。 1)ゲーム開発は、2Dゲームの作成に適した図面、オーディオ、その他の機能を提供し、Pygameを使用します。 2)GUI開発は、TKINTERまたはPYQTを選択できます。 TKINTERはシンプルで使いやすく、PYQTは豊富な機能を備えており、専門能力開発に適しています。
 PHPとPython:2つの一般的なプログラミング言語を比較します
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHPとPython:2つの一般的なプログラミング言語を比較します
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHPとPythonにはそれぞれ独自の利点があり、プロジェクトの要件に従って選択します。 1.PHPは、特にWebサイトの迅速な開発とメンテナンスに適しています。 2。Pythonは、データサイエンス、機械学習、人工知能に適しており、簡潔な構文を備えており、初心者に適しています。
 DDOS攻撃検出におけるDebianスニファーの役割
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
DDOS攻撃検出におけるDebianスニファーの役割
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
この記事では、DDOS攻撃検出方法について説明します。 「DebiansNiffer」の直接的なアプリケーションのケースは見つかりませんでしたが、次の方法はDDOS攻撃検出に使用できます:効果的なDDOS攻撃検出技術:トラフィック分析に基づく検出:突然のトラフィックの成長、特定のポートの接続の急増などのネットワークトラフィックの異常なパターンの識別。たとえば、PysharkライブラリとColoramaライブラリと組み合わせたPythonスクリプトは、ネットワークトラフィックをリアルタイムで監視し、アラートを発行できます。統計分析に基づく検出:データなどのネットワークトラフィックの統計的特性を分析することにより
 Nginx SSL証明書更新Debianチュートリアル
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Nginx SSL証明書更新Debianチュートリアル
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
この記事では、DebianシステムでNGINXSSL証明書を更新する方法について説明します。ステップ1:最初にCERTBOTをインストールして、システムがCERTBOTおよびPython3-Certbot-Nginxパッケージがインストールされていることを確認してください。インストールされていない場合は、次のコマンドを実行してください。sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstolcallcertbotthon3-certbot-nginxステップ2:certbotコマンドを取得して構成してlet'sencrypt証明書を取得し、let'sencryptコマンドを取得し、nginx:sudocertbot - nginxを構成します。
 Debian Readdirが他のツールと統合する方法
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
Debian Readdirが他のツールと統合する方法
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
DebianシステムのReadDir関数は、ディレクトリコンテンツの読み取りに使用されるシステムコールであり、Cプログラミングでよく使用されます。この記事では、ReadDirを他のツールと統合して機能を強化する方法について説明します。方法1:C言語プログラムを最初にパイプラインと組み合わせて、cプログラムを作成してreaddir関数を呼び出して結果をinclude#include#include inctargc、char*argv []){dir*dir; structdireant*entry; if(argc!= 2){(argc!= 2){
 Pythonと時間:勉強時間を最大限に活用する
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Pythonと時間:勉強時間を最大限に活用する
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
限られた時間でPythonの学習効率を最大化するには、PythonのDateTime、時間、およびスケジュールモジュールを使用できます。 1. DateTimeモジュールは、学習時間を記録および計画するために使用されます。 2。時間モジュールは、勉強と休息の時間を設定するのに役立ちます。 3.スケジュールモジュールは、毎週の学習タスクを自動的に配置します。
 debian opensslでHTTPSサーバーを構成する方法
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
debian opensslでHTTPSサーバーを構成する方法
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
DebianシステムでHTTPSサーバーの構成には、必要なソフトウェアのインストール、SSL証明書の生成、SSL証明書を使用するWebサーバー(ApacheやNginxなど)の構成など、いくつかのステップが含まれます。 Apachewebサーバーを使用していると仮定して、基本的なガイドです。 1.最初に必要なソフトウェアをインストールし、システムが最新であることを確認し、ApacheとOpenSSL:sudoaptupdatesudoaptupgraysudoaptinstaをインストールしてください




