

51CTO オープンソース基本ソフトウェア コミュニティ をご覧ください。
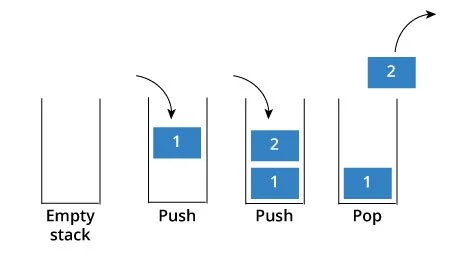
スタックは次のように構成されていますオブジェクトごとに編成された一連のオブジェクトのコレクション。これらのオブジェクトの追加および削除操作は、「後入れ先出し」(LIFO) の原則に従います。
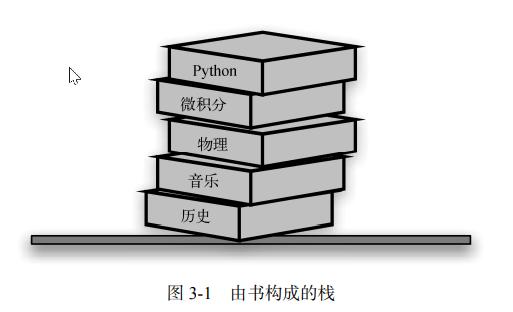
いつでもスタックに挿入できるオブジェクトは 1 つだけですが、取得または削除できるのはスタックの最上位でのみです。たとえば、本の山の中で、表紙が露出しているのは一番上の本だけです。他の本を取り出すには、図に示すように一番上の本を取り出すしかありません。
 ## スタックの実用的な応用
## スタックの実用的な応用
 Python スタックのサイズは固定されている場合もあれば、サイズの変更を許可する動的実装がある場合もあります。固定サイズのスタックの場合、すでにいっぱいのスタックに要素を追加しようとすると、スタック オーバーフロー例外が発生します。同様に、
Python スタックのサイズは固定されている場合もあれば、サイズの変更を許可する動的実装がある場合もあります。固定サイズのスタックの場合、すでにいっぱいのスタックに要素を追加しようとすると、スタック オーバーフロー例外が発生します。同様に、
操作を使用してすでに空のスタックから要素を削除しようとすることをアンダーフローと呼びます。 3. Python リストを使用してスタックを実装する
を学習している必要があります。メソッド内 スタックの関数を実装します:
 コードは以下のように表示されます:
コードは以下のように表示されます:
class ArrayStack:
""" 通过 Python 列表实现 LIFO 栈"""
def __init__(self):
self._data = []
def size(self):
""" return the number of elements in the stack"""
return len(self._data)
def is_empty(self):
""" return True if the stack is empty"""
return len(self._data) == 0
def push(self, e):
""" add element e to the top of the stack"""
self._data.append(e)
def pop(self):
""" remove and return the element from the top of the stack
"""
if self.is_empty():
raise Exception('Stack is empty')
return self._data.pop()
def top(self):
"""return the top of the stack
Raise Empty exception if the stack is empty
"""
if self.is_empty():
raise Exception('Stack is empty')
return self._data[-1]# the last item in the list
arrayStack = ArrayStack()
arrayStack.push("Python")
arrayStack.push("Learning")
arrayStack.push("Hello")
print("Stack top element: ", arrayStack.top())
print("Stack length: ", arrayStack.size())
print("Stack popped item: %s" % arrayStack.pop())
print("Stack is empty?", arrayStack.is_empty())
arrayStack.pop()
arrayStack.pop()
print("Stack is empty?", arrayStack.is_empty())
# arrayStack.pop()このプログラムを実行すると、結果は次のようになります:
Stack top element:Hello Stack length:3 Stack popped item: Hello Stack is empty? False Stack is empty? True
リストの末尾をスタックの先頭として使用することに加えて、リストの先頭をスタックの先頭として使用することもできます。ただし、この場合、pop() メソッドと append() メソッドを直接使用することはできませんが、pop() メソッドと insert() メソッドを通じて、リストの最初の要素であるインデックス 0 の要素に明示的にアクセスできます。
class ArrayStack:
""" 通过 Python 列表实现 LIFO 栈"""
def __init__(self):
self._data = []
def size(self):
""" return the number of elements in the stack"""
return len(self._data)
def is_empty(self):
""" return True if the stack is empty"""
return len(self._data) == 0
def push(self, e):
""" add element e to the top of the stack"""
self._data.insert(0, e)
def pop(self):
""" remove and return the element from the top of the stack
"""
if self.is_empty():
raise Exception('Stack is empty')
return self._data.pop(0)
def top(self):
"""return the top of the stack
Raise Empty exception if the stack is empty
"""
if self.is_empty():
raise Exception('Stack is empty')
return self._data[0]# the last item in the list抽象データ型の実装を変更しましたが、その論理特性は保持しました。この能力は抽象的思考を体現します。どちらのメソッドもスタックを実装していますが、パフォーマンス方法は異なります。
>>> from collections import deque
>>> myStack = deque()
>>> myStack.append('Apple')
>>> myStack.append('Banana')
>>> myStack.append('Orange')
>>>
>>> myStack
deque(['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'])
>>> myStack.pop()
'Orange'
>>> myStack.pop()
'Banana'
>>>
>>> len(myStack)
1
>>> myStack[0]
'Apple'
>>> myStack.pop()
'Apple'
>>>
>>> myStack.pop()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#13>", line 1, in <module>
myStack.pop()
IndexError: pop from an empty deque
>>>

>>> from queue import LifoQueue
>>> stack = LifoQueue()
>>> stack.put('H')
>>> stack.put('E')
>>> stack.put('L')
>>> stack.put('L')
>>> stack.put('O')
>>> stack
<queue.LifoQueue object at 0x00000123159F7310>
>>>
>>> stack.get()
'O'
>>> stack.get()
'L'
>>> stack.empty()
False
>>> stack.qsize()
3
>>> stack.get()
'L'
>>> stack.get()
'E'
>>> stack.qsize()
1
>>> stack.get()
'H'
>>> stack.get_nowait()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#31>", line 1, in <module>
stack.get_nowait()
_queue.Empty
>>>
>>> stack.put('Apple')
>>> stack.get_nowait()
'Apple'与 deque 不同,LifoQueue 被设计为完全线程安全的。它的所有方法都可以在线程环境中安全使用。它还为其操作添加了可选的超时功能,这在线程程序中经常是一个必须的功能。
然而,这种完全的线程安全是有代价的。为了实现这种线程安全,LifoQueue 必须在每个操作上做一些额外的工作,这意味着它将花费更长的时间。
通常情况下,这种轻微的减速对你的整体程序速度并不重要,但如果你已经测量了你的性能,并发现你的堆栈操作是瓶颈,那么小心地切换到 deque 可能是值得做的。
一般来说,如果你不使用多线程,你应该使用 deque。如果你使用多线程,那么你应该使用 LifoQueue,除非你已经测量了你的性能,发现 push 和 pop 的速度的小幅提升会带来足够的差异,以保证维护风险。
你可以对列表可能很熟悉,但需要谨慎使用它,因为它有可能存在内存重新分配的问题。deque 和 list 的接口是相同的,而且 deque 没有线程不安全问题。
本文介绍了栈这一数据结构,并介绍了在现实生活中的程序中如何使用它的情况。在文章的中,介绍了 Python 中实现栈的三种不同方式,知道了 deque 对于非多线程程序是一个更好的选择,如果你要在多线程编程环境中使用栈的话,可以使用 LifoQueue。
以上がPython でスタックを実装するいくつかの方法とその利点と欠点の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。