PythonのRegEx正規表現の使い方
RegEx または正規表現は、検索パターンを形成する一連の文字です。
RegEx を使用すると、文字列に指定した検索パターンが含まれているかどうかを確認できます。
RegEx モジュール
Python には、正規表現の処理に使用できる re という名前の組み込みパッケージが用意されています。
re モジュールをインポートします:
import re
Python の RegEx
re モジュールをインポートした後、正規表現の使用を開始できます:
例
文字列を取得して、「中国」で始まり「国」で終わるかどうかを確認します。
import re
txt = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("^China.*country$", txt)実行例
import re
txt = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("^China.*country$", txt)
if (x):
print("YES! We have a match!")
else:
print("No match")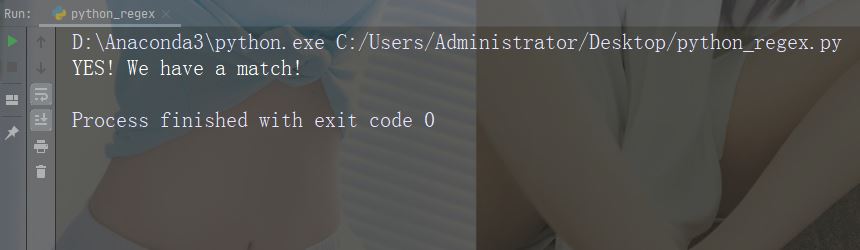
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Find all lower case characters alphabetically between "a" and "m":
x = re.findall("[a-m]", str)
print(x) 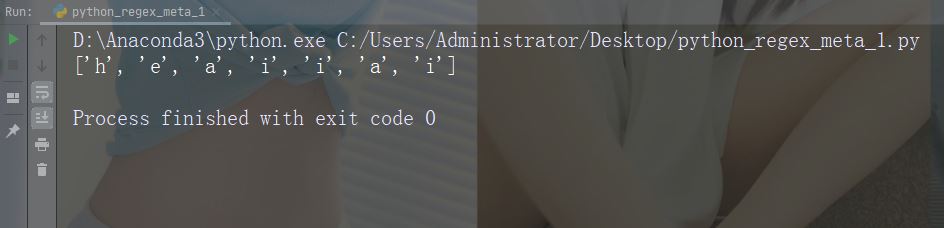
import re
str = "That will be 59 dollars"
#Find all digit characters:
x = re.findall("\d", str)
print(x)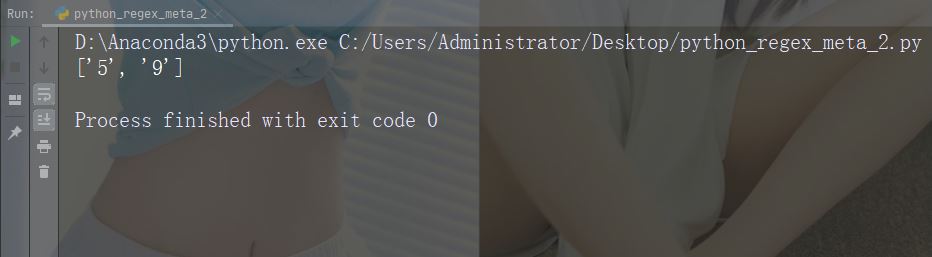 ## 文字: . 説明: 任意の文字 (改行を除く) 例: "he…o"
## 文字: . 説明: 任意の文字 (改行を除く) 例: "he…o"
import re
str = "hello world"
#Search for a sequence that starts with "he", followed by two (any) characters, and an "o":
x = re.findall("he..o", str)
print(x)サンプルを実行
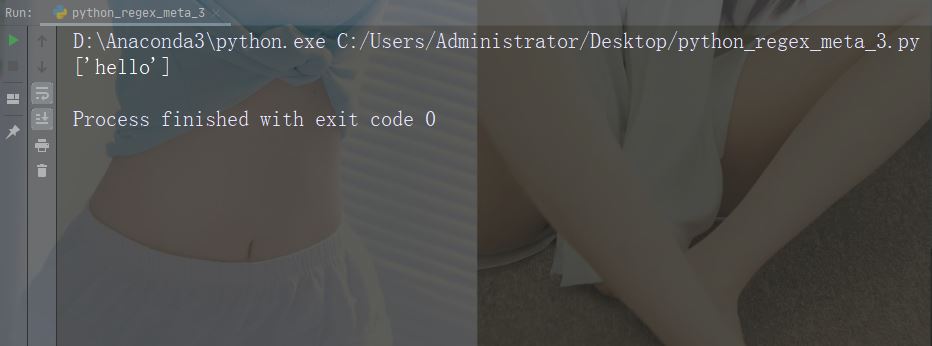 文字: ^ 説明:例で開始: "^hello"
文字: ^ 説明:例で開始: "^hello"
import re
str = "hello world"
#Check if the string starts with 'hello':
x = re.findall("^hello", str)
if (x):
print("Yes, the string starts with 'hello'")
else:
print("No match")実行例
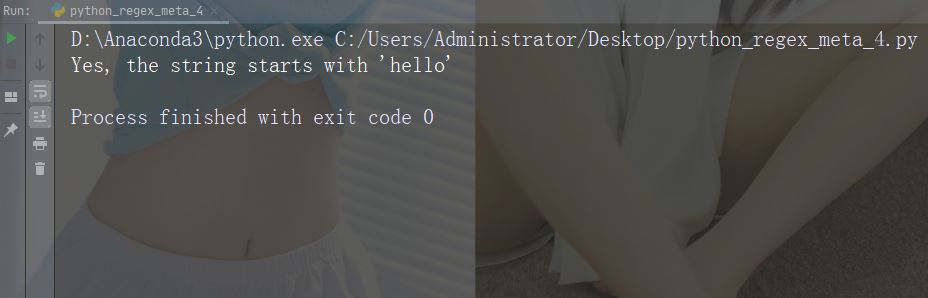 文字: $ 説明: 例で終了: "world$"
文字: $ 説明: 例で終了: "world$"
import re
str = "hello world"
#Check if the string ends with 'world':
x = re.findall("world$", str)
if (x):
print("Yes, the string ends with 'world'")
else:
print("No match")実行例
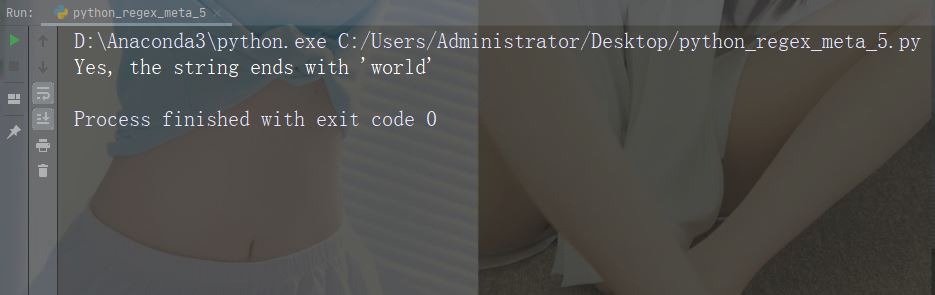 文字: * 説明: 0 個以上の出現例: "aix*"
文字: * 説明: 0 個以上の出現例: "aix*"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "ai" followed by 0 or more "x" characters:
x = re.findall("aix*", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")実行例
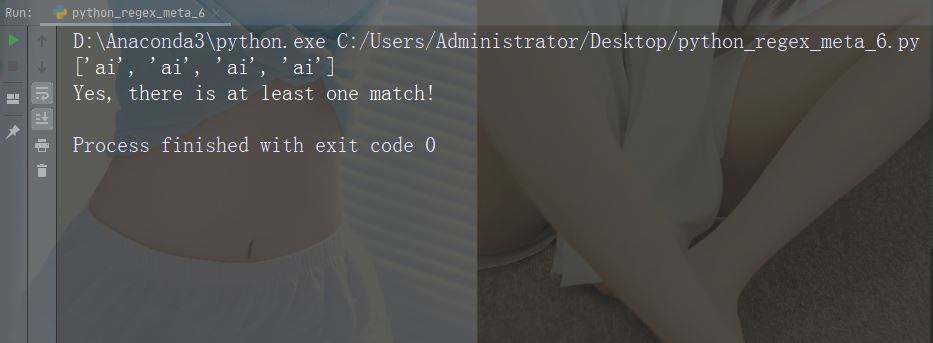 文字: 説明: 1 つ以上の例: "aix"
文字: 説明: 1 つ以上の例: "aix"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "ai" followed by 1 or more "x" characters:
x = re.findall("aix+", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")例の実行
 文字 :{ } 説明: 正確に指定された出現回数 例: "al{2}"
文字 :{ } 説明: 正確に指定された出現回数 例: "al{2}"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "a" followed by exactly two "l" characters:
x = re.findall("al{2}", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")実行例
 文字: | 説明: 両方 いずれかの例: " fall|stays"
文字: | 説明: 両方 いずれかの例: " fall|stays"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains either "falls" or "stays":
x = re.findall("falls|stays", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")実行例
##文字: () 説明: 
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string starts with "The":
x = re.findall("\AThe", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is a match!")
else:
print("No match") 説明: 指定された文字が単語の先頭または末尾にある一致を返します。
説明: 指定された文字が単語の先頭または末尾にある一致を返します。
例: r"\bain"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present at the beginning of a WORD:
x = re.findall(r"\bain", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")例の実行
例: r"ain\b"import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present at the end of a WORD:
x = re.findall(r"ain\b", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")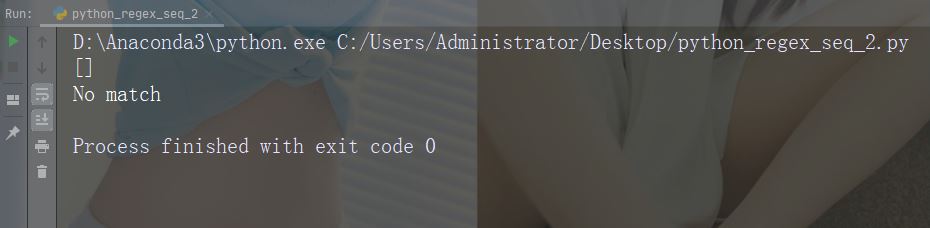 例の実行
例の実行文字: \B
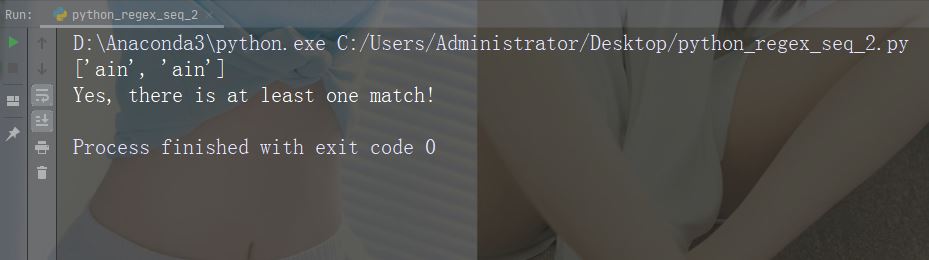 説明: 指定された文字が存在するが、単語の先頭 (または末尾) にない一致を返します。
説明: 指定された文字が存在するが、単語の先頭 (または末尾) にない一致を返します。
例: r"\Bain"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present, but NOT at the beginning of a word:
x = re.findall(r"\Bain", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")サンプルを実行
##例: r"ain\B"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present, but NOT at the end of a word:
x = re.findall(r"ain\B", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")サンプルを実行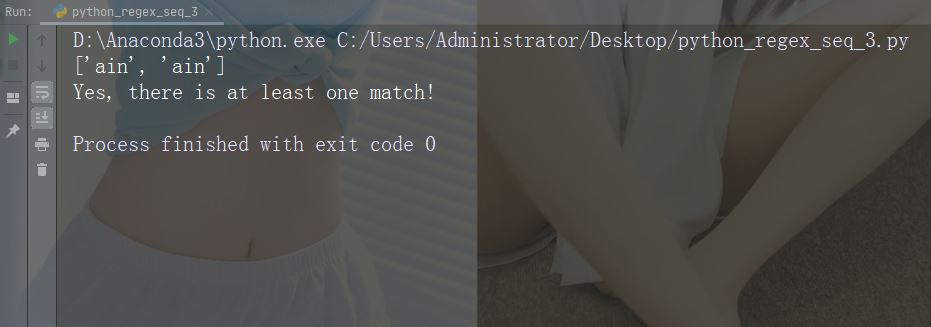
文字: \d
説明: 文字列に数字 (0 ~ 9 の数字) が含まれる一致を返します。 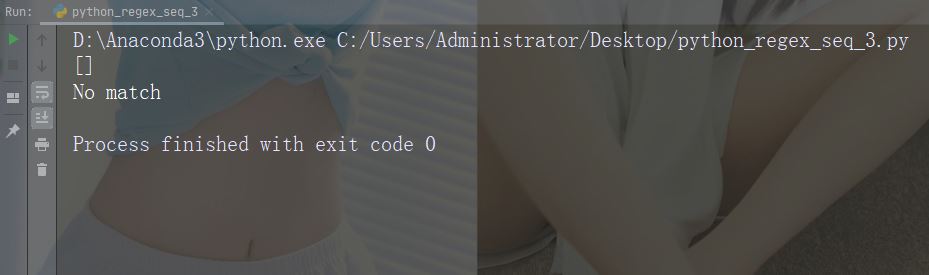
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string contains any digits (numbers from 0-9):
x = re.findall("\d", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")文字: \D
説明: 文字列に数字が含まれていない一致を返します。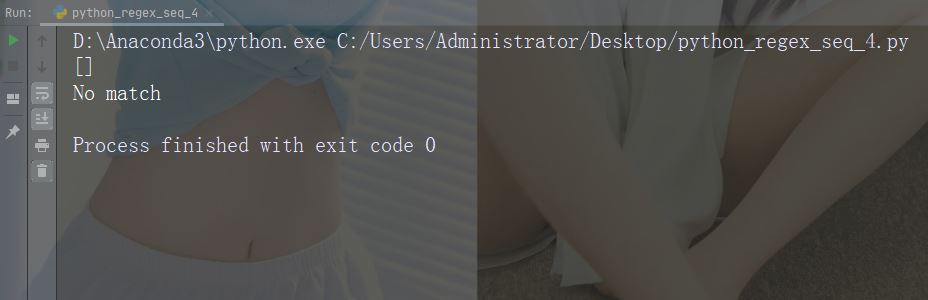
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every no-digit character:
x = re.findall("\D", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")文字: \s
描述:返回字符串包含空白字符的匹配项
示例:“\s”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every white-space character:
x = re.findall("\s", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
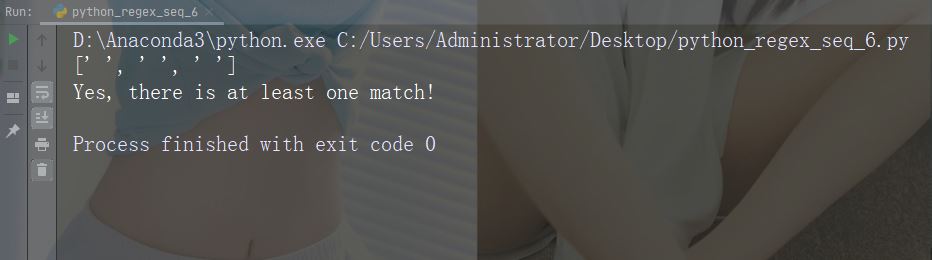
字符:\S
描述:返回字符串不包含空白字符的匹配项
示例:“\S”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every NON white-space character:
x = re.findall("\S", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
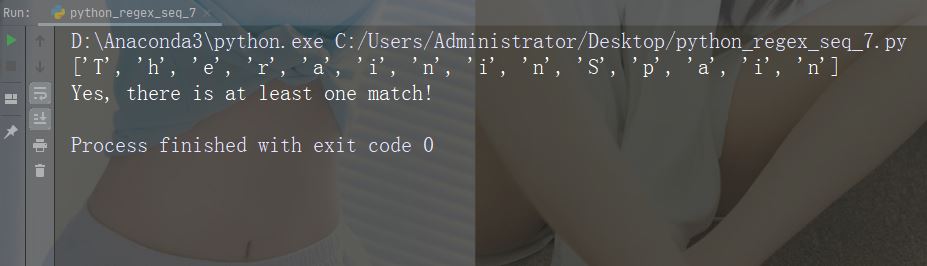
字符:\w
描述: 返回一个匹配项,其中字符串包含任何单词字符 (从 a 到 Z 的字符,从 0 到 9 的数字和下划线 _ 字符)
示例:“\w”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every word character (characters from a to Z, digits from 0-9, and the underscore _ character):
x = re.findall("\w", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
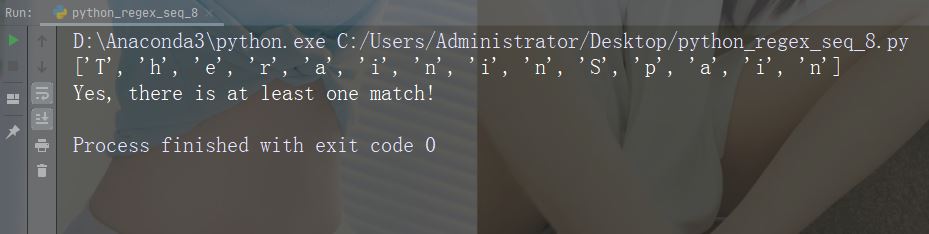
字符:\W
描述:返回一个匹配项,其中字符串不包含任何单词字符
示例:“\W”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every NON word character (characters NOT between a and Z. Like "!", "?" white-space etc.):
x = re.findall("\W", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
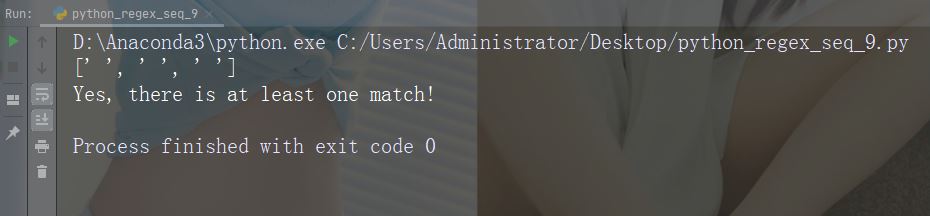
字符:\Z
描述:如果指定的字符位于字符串的末尾,则返回匹配项 。
示例:“Spain\Z”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string ends with "Spain":
x = re.findall("Spain\Z", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is a match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
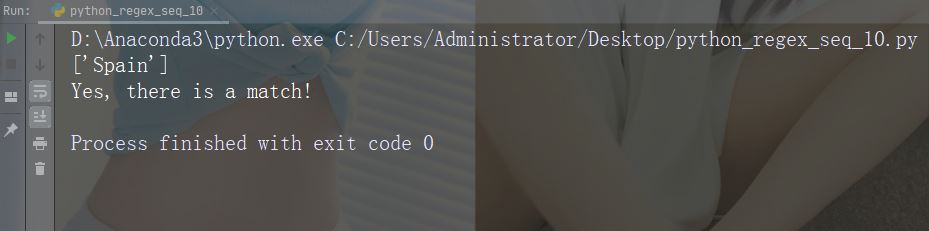
集合(Set)
集合(Set)是一对方括号 [] 内的一组字符,具有特殊含义。
字符:[arn]
描述:返回一个匹配项,其中存在指定字符(a,r 或 n)之一
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any a, r, or n characters:
x = re.findall("[arn]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
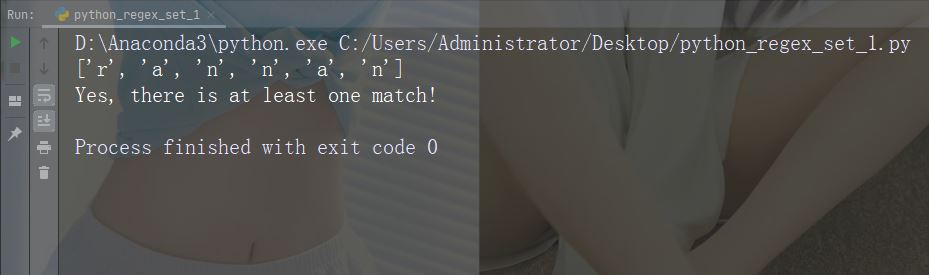
字符:[a-n]
描述:返回字母顺序 a 和 n 之间的任意小写字符匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any characters between a and n:
x = re.findall("[a-n]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
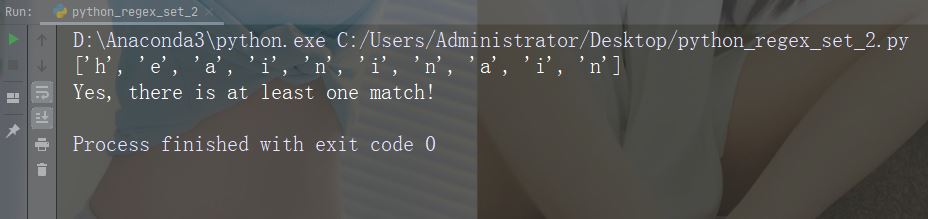
字符:[^arn]
描述:返回除 a、r 和 n 之外的任意字符的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has other characters than a, r, or n:
x = re.findall("[^arn]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
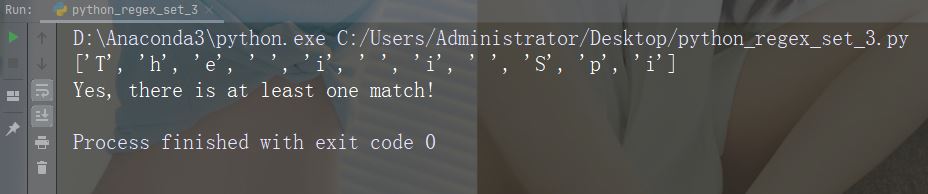
字符:[0123]
描述:返回存在任何指定数字(0、1、2 或 3)的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any 0, 1, 2, or 3 digits:
x = re.findall("[0123]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
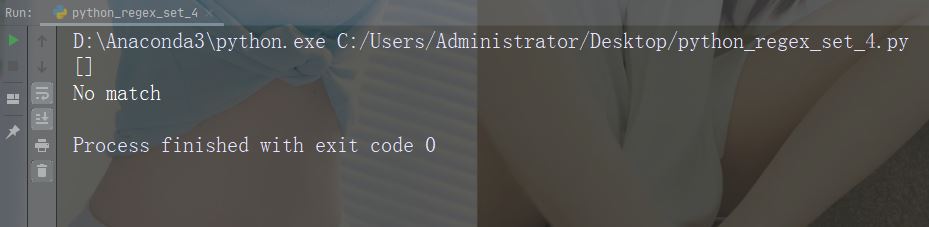
字符:[0-9]
描述:返回 0 与 9 之间任意数字的匹配
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any digits:
x = re.findall("[0-9]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
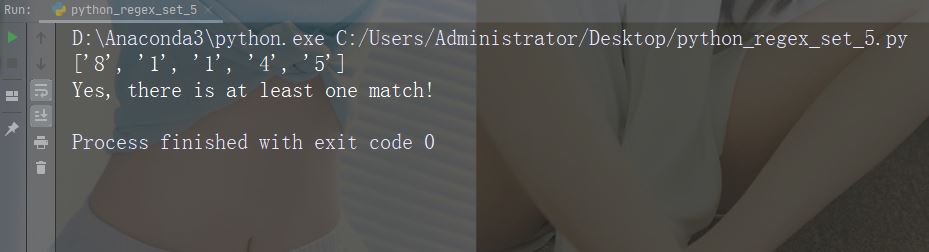
字符:[0-5][0-9]
描述:返回介于 0 到 9 之间的任何数字的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any two-digit numbers, from 00 to 59:
x = re.findall("[0-5][0-9]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
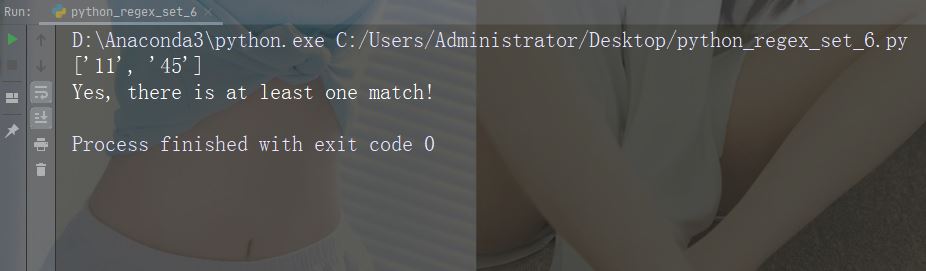
字符:[a-zA-Z]
描述:返回字母顺序 a 和 z 之间的任何字符的匹配,小写或大写
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any characters from a to z lower case, and A to Z upper case:
x = re.findall("[a-zA-Z]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
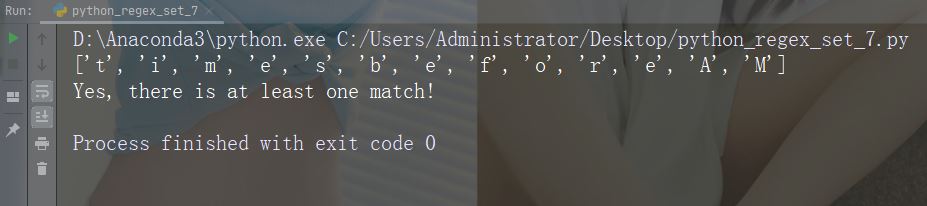
字符:[+]
描述:在集合中,+、*、.、|、()、$、{} 没有特殊含义,因此 [+] 表示:返回字符串中任何 + 字符的匹配项。
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any + characters:
x = re.findall("[+]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
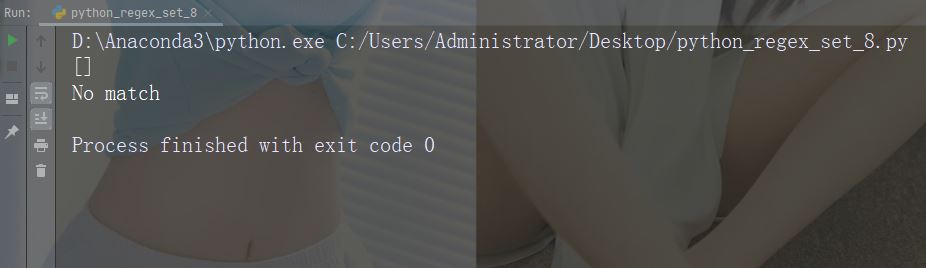
findall() 函数
findall() 函数返回包含所有匹配项的列表。
实例
打印所有匹配的列表
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.findall("a", str)
print(x)运行实例
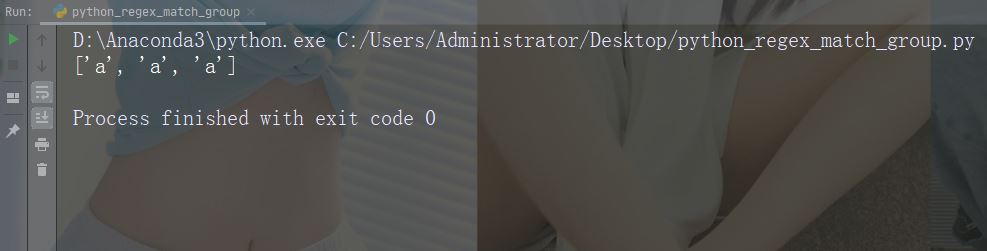
这个列表以被找到的顺序包含匹配项。
如果未找到匹配项,则返回空列表。
实例
如果未找到匹配,则返回空列表:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.findall("USA", str)
print(x)运行实例
search() 函数
search() 函数搜索字符串中的匹配项,如果存在匹配则返回 Match 对象。
如果有多个匹配,则仅返回首个匹配项。
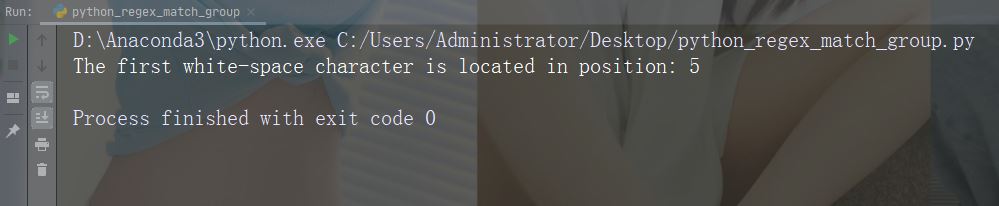
实例
在字符串中搜索第一个空白字符
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("\s", str)
print("The first white-space character is located in position:", x.start())运行实例
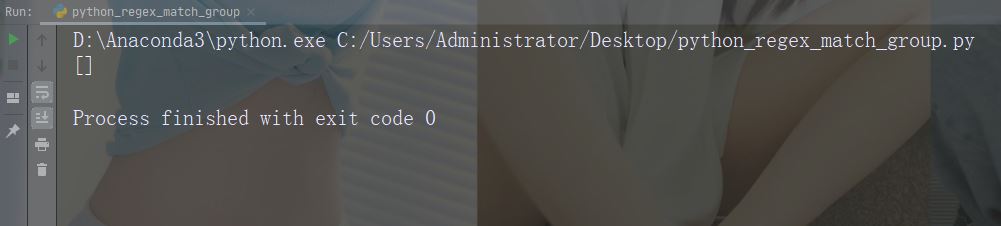
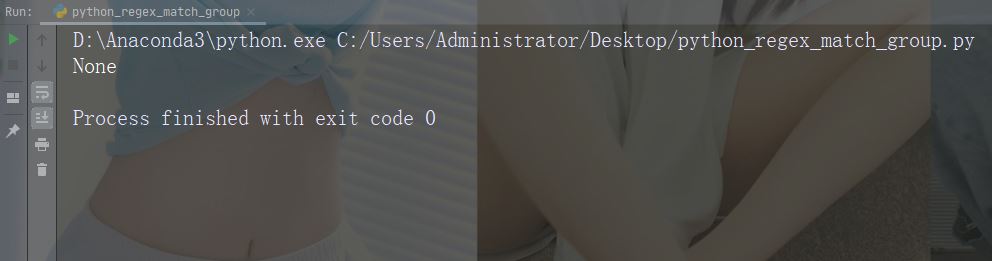
如果未找到匹配,则返回值 None:
实例
进行不返回匹配的检索
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("USA", str)
print(x)运行实例
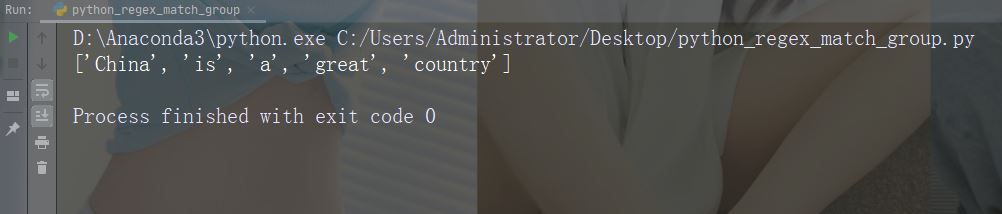
split() 函数
split() 函数返回一个列表,其中字符串在每次匹配时被拆分。
实例
在每个空白字符处进行拆分
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.split("\s", str)
print(x)运行实例
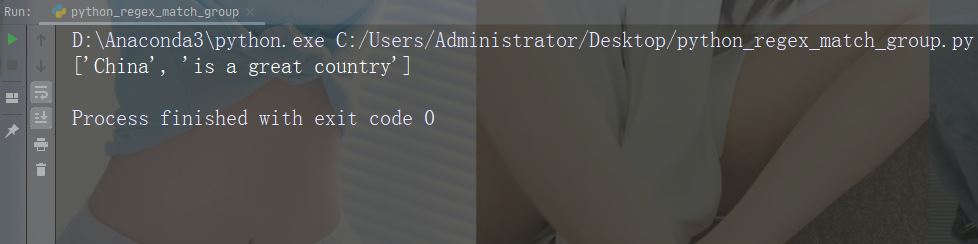
可以通过指定 maxsplit 参数来控制出现次数:
实例
仅在首次出现时拆分字符串:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.split("\s", str, 1)
print(x)运行实例
sub() 函数
sub() 函数把匹配替换为您选择的文本
实例
用数字 9 替换每个空白字符
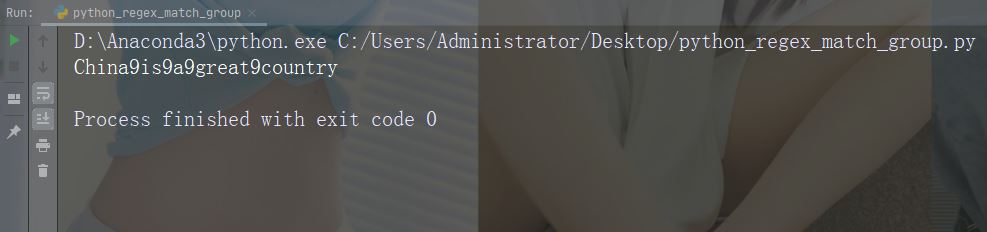
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.sub("\s", "9", str)
print(x)运行实例
可以通过指定 count 参数来控制替换次数:
实例
替换前两次出现
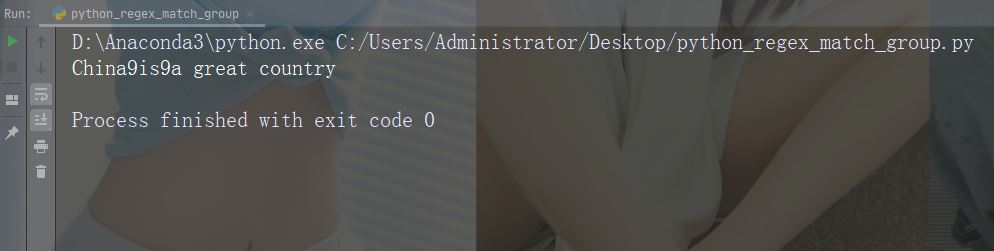
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.sub("\s", "9", str, 2)
print(x)运行实例
Match 对象
Match 对象是包含有关搜索和结果信息的对象。
注释:如果没有匹配,则返回值 None,而不是 Match 对象。
实例
执行会返回 Match 对象的搜索:
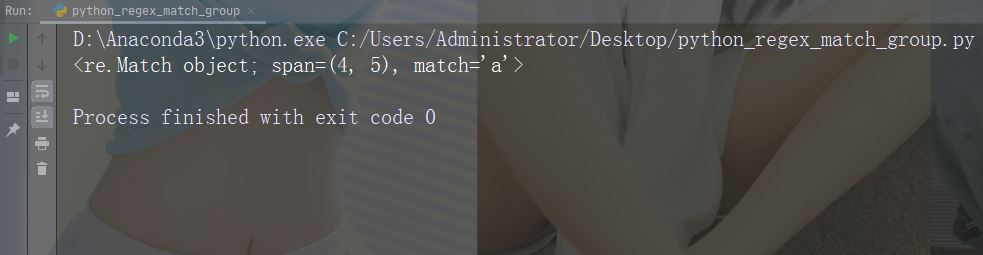
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("a", str)
print(x) # 将打印一个对象运行实例
Match 对象提供了用于取回有关搜索及结果信息的属性和方法:
span()返回的元组包含了匹配的开始和结束位置.string返回传入函数的字符串group()返回匹配的字符串部分
实例
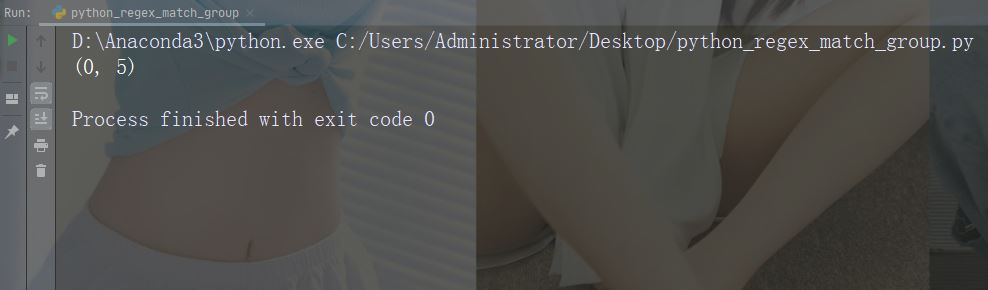
打印首个匹配出现的位置(开始和结束位置)。
正则表达式查找以大写 “C” 开头的任何单词:
import re str = "China is a great country" x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str) print(x.span())
运行实例
实例
打印传入函数的字符串
import re str = "China is a great country" x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str) print(x.string)
运行实例
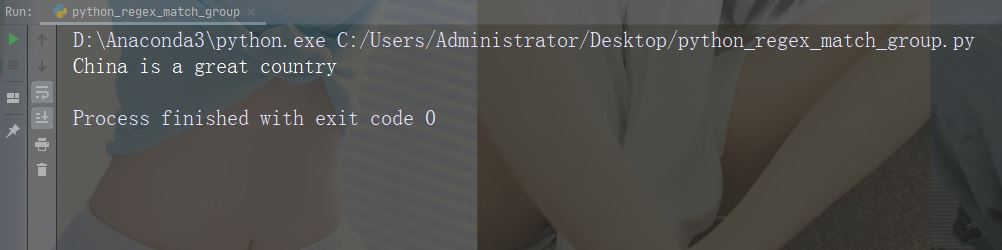
实例
打印匹配的字符串部分
正则表达式查找以大写 “C” 开头的任何单词:
import re str = "China is a great country" x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str) print(x.group())
运行实例
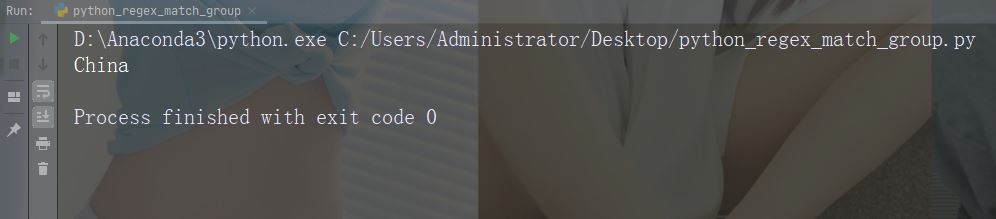
注释:如果没有匹配项,则返回值 None,而不是 Match 对象。
以上がPythonのRegEx正規表現の使い方の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7629
7629
 15
15
 1389
1389
 52
52
 89
89
 11
11
 31
31
 141
141
 PHPとPythonの選択:ガイド
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHPとPythonの選択:ガイド
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHPはWeb開発と迅速なプロトタイピングに適しており、Pythonはデータサイエンスと機械学習に適しています。 1.PHPは、単純な構文と迅速な開発に適した動的なWeb開発に使用されます。 2。Pythonには簡潔な構文があり、複数のフィールドに適しており、強力なライブラリエコシステムがあります。
 PHPおよびPython:さまざまなパラダイムが説明されています
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHPおよびPython:さまざまなパラダイムが説明されています
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHPは主に手順プログラミングですが、オブジェクト指向プログラミング(OOP)もサポートしています。 Pythonは、OOP、機能、手続き上のプログラミングなど、さまざまなパラダイムをサポートしています。 PHPはWeb開発に適しており、Pythonはデータ分析や機械学習などのさまざまなアプリケーションに適しています。
 Windows 8でコードを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Windows 8でコードを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VSコードはWindows 8で実行できますが、エクスペリエンスは大きくない場合があります。まず、システムが最新のパッチに更新されていることを確認してから、システムアーキテクチャに一致するVSコードインストールパッケージをダウンロードして、プロンプトとしてインストールします。インストール後、一部の拡張機能はWindows 8と互換性があり、代替拡張機能を探すか、仮想マシンで新しいWindowsシステムを使用する必要があることに注意してください。必要な拡張機能をインストールして、適切に動作するかどうかを確認します。 Windows 8ではVSコードは実行可能ですが、開発エクスペリエンスとセキュリティを向上させるために、新しいWindowsシステムにアップグレードすることをお勧めします。
 VSCODE拡張機能は悪意がありますか?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VSCODE拡張機能は悪意がありますか?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VSコード拡張機能は、悪意のあるコードの隠れ、脆弱性の活用、合法的な拡張機能としての自慰行為など、悪意のあるリスクを引き起こします。悪意のある拡張機能を識別する方法には、パブリッシャーのチェック、コメントの読み取り、コードのチェック、およびインストールに注意してください。セキュリティ対策には、セキュリティ認識、良好な習慣、定期的な更新、ウイルス対策ソフトウェアも含まれます。
 ターミナルVSCODEでプログラムを実行する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
ターミナルVSCODEでプログラムを実行する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
VSコードでは、次の手順を通じて端末でプログラムを実行できます。コードを準備し、統合端子を開き、コードディレクトリが端末作業ディレクトリと一致していることを確認します。プログラミング言語(pythonのpython your_file_name.pyなど)に従って実行コマンドを選択して、それが正常に実行されるかどうかを確認し、エラーを解決します。デバッガーを使用して、デバッグ効率を向上させます。
 Visual StudioコードはPythonで使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Visual StudioコードはPythonで使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VSコードはPythonの書き込みに使用でき、Pythonアプリケーションを開発するための理想的なツールになる多くの機能を提供できます。ユーザーは以下を可能にします。Python拡張機能をインストールして、コードの完了、構文の強調表示、デバッグなどの関数を取得できます。デバッガーを使用して、コードを段階的に追跡し、エラーを見つけて修正します。バージョンコントロールのためにGitを統合します。コードフォーマットツールを使用して、コードの一貫性を維持します。糸くずツールを使用して、事前に潜在的な問題を発見します。
 vscodeはMacに使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
vscodeはMacに使用できますか
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VSコードはMacで利用できます。強力な拡張機能、GIT統合、ターミナル、デバッガーがあり、豊富なセットアップオプションも提供しています。ただし、特に大規模なプロジェクトまたは非常に専門的な開発の場合、コードと機能的な制限がある場合があります。
 vscodeはipynbを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
vscodeはipynbを実行できます
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
VSコードでJupyterノートブックを実行するための鍵は、Python環境が適切に構成されていることを確認し、コードの実行順序がセルの順序と一致していることを理解し、パフォーマンスに影響を与える可能性のある大きなファイルまたは外部ライブラリに注意することです。 VSコードで提供されるコードの完了とデバッグ機能は、コーディング効率を大幅に改善し、エラーを減らすことができます。




