Python foliumの機能の使い方
1. レンダリング
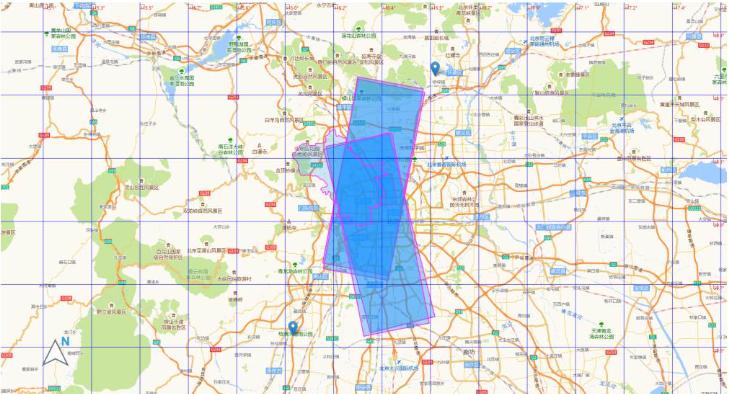
2. レイヤー制御
Folium 公式は、私たちが使用できるいくつかの明確な方法も提供しています。レイヤーコントロールと同じです。正式なメソッド名はFeatureGroupで、インポートメソッドはfolium import FeatureGroup、またはfolium.FeatureGroup()からのものです。ここでは特定の原則については詳しく説明しませんが、主に例を見ていきます。
import folium
def map2png(map_data,out_file='pdf.png'):
# 1.直接构造,默认底图
mo = folium.Map(location=[0, 0])
# 2.图层1-高德底图+数据
fg = folium.FeatureGroup()
# 2.1 高德地图
fg.add_child(folium.TileLayer(
tiles='http://webrd02.is.autonavi.com/appmaptile?lang=zh_cn&size=1&scale=1&style=8&x={x}&y={y}&z={z}',
attr="© <a href=http://ditu.amap.com/>高德地图</a>",
min_zoom=0,
max_zoom=19,
control=True,
zoom_control=False,
show=True))
# 2.2添加一个点
fg.add_child(folium.Marker(
location=[45.3311, -121.7113],
popup="Timberline Lodge",
icon=folium.Icon(color="green")))
# 2.3添加一个线形
fg.add_child(folium.PolyLine(
locations=[[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]],
color='green', weight=2, opacity=1))
# 2.4添加一个面
fg.add_child(folium.Polygon(
locations=[[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]],
color='green', weight=2,
fill=True,fill_color = 'red'))
# 2.5将我们的图层加入map
mo.add_child(fg)
# 3.图层2-重点数据+最上层
fg2 = folium.FeatureGroup()
fg2.add_child(folium.Polygon(
locations=[[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]],
color='green', weight=2,
fill=True,fill_color = 'red'))
mo.add_child(fg2)
# 4.将图层fg2显示在最上层,keep_in_front的参数必须是FeatureGroup或TileLayer对象
mo.keep_in_front(fg2)
# 5.根据范围缩放地图
mo.fit_bounds([[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]])
root = mo.get_root()
html = root.render() # 这个拿到的就是一个html的内容
# mo.save('text.html')3. ノース アロー
ノース アロー関数はマップには必ずしも必要ではありませんが、追加するものは次のとおりです。上がるのはいつも良いことだ。 FloatImage を使用するとこの機能を実現できますが、関連する内容は公式ドキュメントやソース コード分析には記載されていません。公式ドキュメントで提供されているプラグインは数多くありますが、その中で最も広く使われているのがヒートマップと呼ばれるHeatMap方式です。
FloatImage メソッドは、画面上に画像を配置し、画像のサイズと画面上の位置を指定する処理を実装します。パラメータは整数です (FloatImage メソッドはパーセント変換を実装します)。 2 番目のコードに基づいて、画像を左下隅に追加しました。
fg.add_child(FloatImage(os.path.join(base, 'map_png', 'image', 'compass.png'), left=5, bottom=10, width=5))
4. folium への js と css の追加
folium 公式では、js と css を追加するための関連メソッドは提供されていません。インターネット上の多くのメソッドは、ソース コードの解釈に基づいて抽出する必要があります。言ってみれば、それは比較的単純であり、js と css を追加する方法についての関連した指示はありません。
ソース コードから、folium のマップ関数は、データとマップの HTML をロードするために jinjia2 を通じて実装されていることがわかります。
ソース コードで使用されるデータとマップを追加するには、主に 3 つの方法があります。これらのメソッドには欠点があります (先頭にしか追加できない)。これらのメソッドはほとんどのシナリオで使用できます。マップ オブジェクトに対する操作が含まれない場合、これら 3 つのメソッドで要件を満たすことができます。
1.ヘッダーに js と css を追加
init_script = """
var mapsPlaceholder = [];
L.Map.addInitHook(function () {mapsPlaceholder.push(this);});
"""
# 加在header最上边
mo.get_root().header.add_child(folium.Element(init_script))
2.body に js と css を追加
init_script = """
var mapsPlaceholder = [];
L.Map.addInitHook(function () {mapsPlaceholder.push(this);});
"""
# 加在body中
mo.get_root().html.add_child(folium.Element(init_script))
3.js と css を追加するスクリプト
init_script = """
var mapsPlaceholder = [];
L.Map.addInitHook(function () {mapsPlaceholder.push(this);});
"""
# 加在script中
mo.get_root().script.add_child(folium.Element(init_script))
5. 経度と緯度のグリッド線
前のステップでは、別の場所に js と css を追加する実装が行われました。 htmlファイル方式の場合、地図オブジェクトの操作を伴う場合、経度・緯度のグリッド線の追加など満足できない場合があります。緯度と経度のグリッド ラインの機能を実装するのは、主に次の問題により面倒です:
1. 関連する公式のメソッドやプラグインはありません (現在はありません);
2.folium は実装のために leadlet.js に依存します 緯度と経度のサードパーティ ライブラリを実装したい場合は、リーフレットに精通する必要があります (インターネット上で関連記事が 1 つだけ見つかりました);
3. 上記の記事はフロントエンドによって完了しており、バックエンドに直接実装する方法はありません。
4. フロントエンドの実装方法はマップを直接構築することであり、ここではマップ作成オブジェクトは利用できません (マップ オブジェクトはランダムに生成されます)。
緯度と経度のグリッド線を決定するにはどうすればよいですか?
マップ オブジェクトの作成時にオブジェクトを保存し、次にマップ オブジェクトを取得して、ズーム レベルに応じてグリッド ラインを実装する必要があります。重要なタスクは、マップ オブジェクトの作成前後に JavaScript コードが HTML ページに適切に埋め込まれていることを確認することです。
マップオブジェクト作成時にオブジェクトを4つに格納するように実装されていましたが、foliumのソースコードを調べてjsを追加するメソッドをマップオブジェクト作成後にjsを追加するように書き換えました。
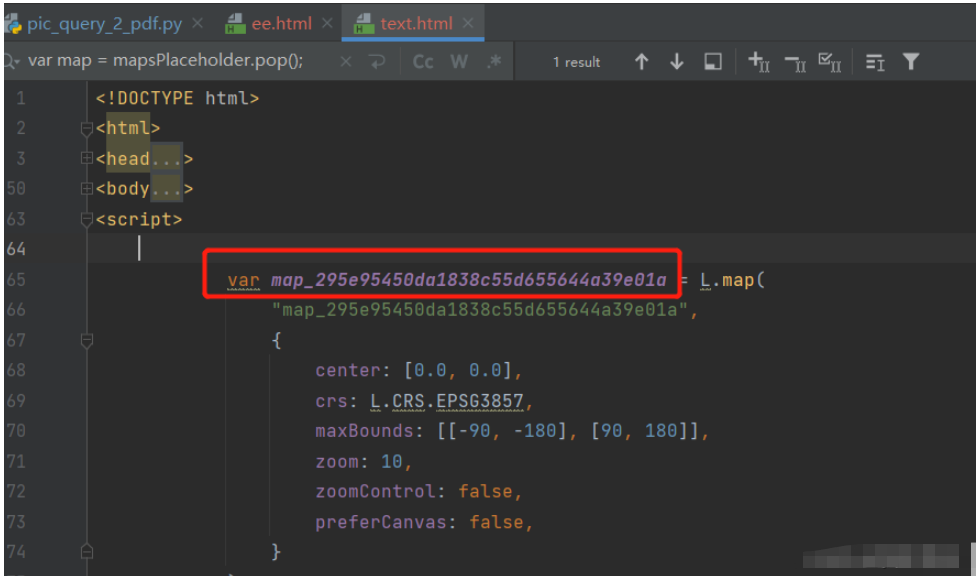
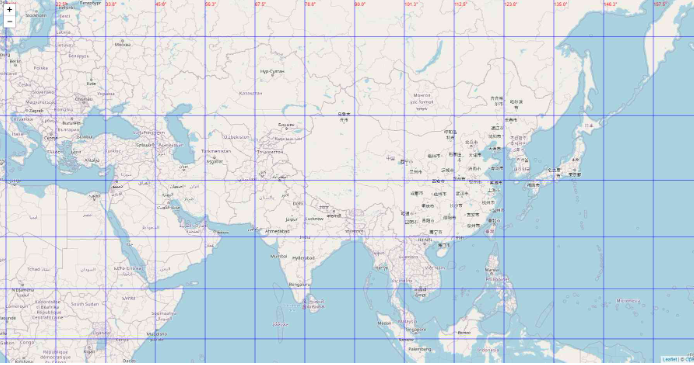
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://unpkg.com/leaflet@1.7.1/dist/leaflet.css" rel="external nofollow"
/>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/leaflet@1.7.1/dist/leaflet.js"></script>
<title>leaflet-经纬网格</title>
<style>
html,
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.leaflet-div-icon {
background: none;
border: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map" ></div>
<script>
let map = L.map("map", { renderer: L.canvas({ padding: 0.5 }) }).setView(
[25.127879288597576, 118.37905883789064],
4
);
// 添加背景图层
L.tileLayer("https://{s}.tile.openstreetmap.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png", {
attribution:
'© <a href="https://www.openstreetmap.org/copyright" rel="external nofollow" >OpenStreetMap</a> contributors',
}).addTo(map);
// 创建图层
let lonLatGridLineLayer = L.featureGroup().addTo(map);
// 经纬网格生成方法
let addLonLatLine = () => {
let zoom = map.getZoom();
let bounds = map.getBounds();
let north = bounds.getNorth();
let east = bounds.getEast();
// 经纬度间隔
let d = 90 / Math.pow(2, zoom - 1);
// 经线网格
for (let index = -180; index <= 360; index += d) {
// 判断当前视野内
if (bounds.contains([north, index])) {
// 绘制经线
let lonLine = L.polyline(
[
[-90, index],
[90, index],
],
{ weight: 1, color: "blue" }
);
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(lonLine);
// 标注
let text = index.toFixed(1) + "°";
// 动态计算小数位数
if (zoom > 10) {
text = index.toFixed((zoom - 8) / 2) + "°";
}
let divIcon = L.divIcon({
html: `<div >${text}</div>`,
iconAnchor: [0, -5],
});
let textMarker = L.marker([north, index], { icon: divIcon });
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(textMarker);
}
}
if(d>90)d=90;
// 纬线网格
for (let index = -90; index <= 90; index += d) {
if (bounds.contains([index, east])) {
let lonLine = L.polyline(
[
[index, -180],
[index, 360],
],
{ weight: 1, color: "blue" }
);
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(lonLine);
// 标注
let text = index.toFixed(1) + "°";
if (zoom > 10) {
text = index.toFixed((zoom - 8) / 2) + "°";
}
let divIcon = L.divIcon({
html: `<div >${text}</div>`,
iconAnchor: [(text.length + 1) * 6, 0],
});
let textMarker = L.marker([index, east], { icon: divIcon });
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(textMarker);
}
}
};
addLonLatLine();
map.on("zoomend move", () => {
lonLatGridLineLayer.clearLayers();
addLonLatLine();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>from branca.element import MacroElement,
from jinja2 import Template
from folium.vector_layers import path_options
class Jwwg(MacroElement):
"""自定义经纬线网格"""
_template = Template("""
{% macro script(this, kwargs) %}
var map = mapsPlaceholder.pop();
// 创建图层
let lonLatGridLineLayer = L.featureGroup().addTo(map);
// 经纬网格生成方法
let addLonLatLine = () => {
let zoom = map.getZoom();
let bounds = map.getBounds();
let north = bounds.getNorth();
let east = bounds.getEast();
// 经纬度间隔
let d = 90 / Math.pow(2, zoom - 1);
// 经线网格
for (let index = -180; index <= 360; index += d) {
// 判断当前视野内
if (bounds.contains([north, index])) {
// 绘制经线
let lonLine = L.polyline(
[
[-90, index],
[90, index],
],
{weight: 1, color: "blue"}
);
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(lonLine);
// 标注
let text = index.toFixed(1) + "°";
// 动态计算小数位数
if (zoom > 10) {
text = index.toFixed((zoom - 8) / 2) + "°";
}
let divIcon = L.divIcon({
html: `<div >${text}</div>`,
iconAnchor: [0, -5],
});
let textMarker = L.marker([north, index], {icon: divIcon});
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(textMarker);
}
}
if (d > 90) d = 90;
// 纬线网格
for (let index = -90; index <= 90; index += d) {
if (bounds.contains([index, east])) {
let lonLine = L.polyline(
[
[index, -180],
[index, 360],
],
{weight: 1, color: "blue"}
);
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(lonLine);
// 标注
let text = index.toFixed(1) + "°";
if (zoom > 10) {
text = index.toFixed((zoom - 8) / 2) + "°";
}
let divIcon = L.divIcon({
html: `<div >${text}</div>`,
iconAnchor: [(text.length + 1) * 6, 0],
});
let textMarker = L.marker([index, east], {icon: divIcon});
lonLatGridLineLayer.addLayer(textMarker);
}
}
};
addLonLatLine();
map.on("zoomend move", () => {
lonLatGridLineLayer.clearLayers();
addLonLatLine();
});
{% endmacro %}
""")
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Jwwg, self).__init__()
self._name = 'Jwwg'
self.options = path_options(line=True, **kwargs)import folium
def map2png(map_data,out_file='pdf.png'):
# 1.直接构造,默认底图
mo = folium.Map(location=[0, 0])
# 2.图层1-高德底图+数据
fg = folium.FeatureGroup()
# 2.1 高德地图
fg.add_child(folium.TileLayer(
tiles='http://webrd02.is.autonavi.com/appmaptile?lang=zh_cn&size=1&scale=1&style=8&x={x}&y={y}&z={z}',
attr="© <a href=http://ditu.amap.com/>高德地图</a>",
min_zoom=0,
max_zoom=19,
control=True,
zoom_control=False,
show=True))
# 2.2添加一个点
fg.add_child(folium.Marker(
location=[45.3311, -121.7113],
popup="Timberline Lodge",
icon=folium.Icon(color="green")))
# 2.3添加一个线形
fg.add_child(folium.PolyLine(
locations=[[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]],
color='green', weight=2, opacity=1))
# 2.4添加一个面
fg.add_child(folium.Polygon(
locations=[[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]],
color='green', weight=2,
fill=True,fill_color = 'red'))
# 2.5将我们的图层加入map
mo.add_child(fg)
# 5.根据范围缩放地图
mo.fit_bounds([[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]])
# 网格线
init_script = """
var mapsPlaceholder = [];
L.Map.addInitHook(function () {mapsPlaceholder.push(this);});
"""
mo.get_root().script.add_child(folium.Element(init_script))
Jwwg().add_to(mo)
root = mo.get_root()
html = root.render() # 这个拿到的就是一个html的内容
# mo.save('text.html')ログイン後にコピー
import folium
def map2png(map_data,out_file='pdf.png'):
# 1.直接构造,默认底图
mo = folium.Map(location=[0, 0])
# 2.图层1-高德底图+数据
fg = folium.FeatureGroup()
# 2.1 高德地图
fg.add_child(folium.TileLayer(
tiles='http://webrd02.is.autonavi.com/appmaptile?lang=zh_cn&size=1&scale=1&style=8&x={x}&y={y}&z={z}',
attr="© <a href=http://ditu.amap.com/>高德地图</a>",
min_zoom=0,
max_zoom=19,
control=True,
zoom_control=False,
show=True))
# 2.2添加一个点
fg.add_child(folium.Marker(
location=[45.3311, -121.7113],
popup="Timberline Lodge",
icon=folium.Icon(color="green")))
# 2.3添加一个线形
fg.add_child(folium.PolyLine(
locations=[[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]],
color='green', weight=2, opacity=1))
# 2.4添加一个面
fg.add_child(folium.Polygon(
locations=[[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]],
color='green', weight=2,
fill=True,fill_color = 'red'))
# 2.5将我们的图层加入map
mo.add_child(fg)
# 5.根据范围缩放地图
mo.fit_bounds([[38.68,115.67],
[38.85,115.48],
[38.65,115.37],
[38.68,115.67]])
# 网格线
init_script = """
var mapsPlaceholder = [];
L.Map.addInitHook(function () {mapsPlaceholder.push(this);});
"""
mo.get_root().script.add_child(folium.Element(init_script))
Jwwg().add_to(mo)
root = mo.get_root()
html = root.render() # 这个拿到的就是一个html的内容
# mo.save('text.html')以上がPython foliumの機能の使い方の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7316
7316
 9
9
 1625
1625
 14
14
 1349
1349
 46
46
 1261
1261
 25
25
 1208
1208
 29
29
 Deepseek Xiaomiをダウンロードする方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
Deepseek Xiaomiをダウンロードする方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
Deepseek Xiaomiをダウンロードする方法は? Xiaomi App Storeで「Deepseek」を検索します。ニーズ(検索ファイル、データ分析)を特定し、DeepSeek関数を含む対応するツール(ファイルマネージャー、データ分析ソフトウェアなど)を見つけます。
 どうやって彼にdeepseekに尋ねますか
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:42 PM
どうやって彼にdeepseekに尋ねますか
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:42 PM
DeepSeekを効果的に使用する鍵は、質問を明確にすることです。質問を直接および具体的に表現してください。特定の詳細と背景情報を提供します。複雑な問い合わせのために、複数の角度と反論の意見が含まれています。コードのパフォーマンスボトルネックなどの特定の側面に焦点を当てます。あなたが得る答えについて批判的な考えを維持し、あなたの専門知識に基づいて判断を下します。
 DeepSeekを検索する方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
DeepSeekを検索する方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
DeepSeekに付属する検索機能を使用するだけです。ただし、不人気で最新の情報または考慮する必要がある検索の場合、キーワードを調整したり、より具体的な説明を使用したり、他のリアルタイム情報源と組み合わせたり、DeepSeekが必要なツールであることを理解する必要があります。アクティブで明確で洗練された検索戦略。
 DeepSeekをプログラムする方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
DeepSeekをプログラムする方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
DeepSeekはプログラミング言語ではなく、深い検索の概念です。 DeepSeekの実装には、既存の言語に基づいて選択が必要です。さまざまなアプリケーションシナリオでは、適切な言語とアルゴリズムを選択し、機械学習技術を組み合わせる必要があります。コードの品質、保守性、テストが重要です。適切なプログラミング言語、アルゴリズム、ツールをお客様のニーズに応じて選択し、高品質のコードを作成することにより、DeepSeekを正常に実装できます。
 DeepSeekを使用してアカウントを解決する方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
DeepSeekを使用してアカウントを解決する方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
質問:DeepSeekは会計に利用できますか?回答:いいえ、それは財務データの分析に使用できるデータマイニングおよび分析ツールですが、会計レコードと会計ソフトウェアの生成機能をレポートしていません。 DeepSeekを使用して財務データを分析するには、データ構造、アルゴリズム、DeepSeek APIの知識を持つデータを処理するためにコードを作成する必要があります。
 コーディングの鍵: 初心者のための Python の力を解き放つ
Oct 11, 2024 pm 12:17 PM
コーディングの鍵: 初心者のための Python の力を解き放つ
Oct 11, 2024 pm 12:17 PM
Python は、学習の容易さと強力な機能により、初心者にとって理想的なプログラミング入門言語です。その基本は次のとおりです。 変数: データ (数値、文字列、リストなど) を保存するために使用されます。データ型: 変数内のデータの型 (整数、浮動小数点など) を定義します。演算子: 数学的な演算と比較に使用されます。制御フロー: コード実行のフロー (条件文、ループ) を制御します。
 Python による問題解決: 初心者プログラマーとして強力なソリューションをアンロックする
Oct 11, 2024 pm 08:58 PM
Python による問題解決: 初心者プログラマーとして強力なソリューションをアンロックする
Oct 11, 2024 pm 08:58 PM
Python は、問題解決の初心者に力を与えます。ユーザーフレンドリーな構文、広範なライブラリ、変数、条件文、ループによる効率的なコード開発などの機能を備えています。データの管理からプログラム フローの制御、反復的なタスクの実行まで、Python が提供します
 Deepseekapiにアクセスする方法-Deepseekapiアクセスコールチュートリアル
Mar 12, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Deepseekapiにアクセスする方法-Deepseekapiアクセスコールチュートリアル
Mar 12, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Deepseekapiアクセスと電話の詳細な説明:クイックスタートガイドこの記事では、Deepseekapiにアクセスして呼び出す方法を詳しく説明し、強力なAIモデルを簡単に使用するのに役立ちます。ステップ1:APIキーを取得して、DeepSeekの公式Webサイトにアクセスし、右上隅の「オープンプラットフォーム」をクリックします。一定数の無料トークン(API使用量を測定するために使用)が得られます。左側のメニューで、[apikeys]をクリックし、[Apikeyの作成]をクリックします。 Apikey(たとえば、「テスト」)に名前を付け、生成されたキーをすぐにコピーします。このキーは一度しか表示されないため、必ず適切に保存してください




