Nginxサーバーでのロケーション構成例の分析
まず最初に、Nginx Wiki の例を使用して、一般的な Location の種類と一致ルールを紹介します。
2, /some/other/url - を使用します。 > まず、文字列のプレフィックス部分が 2 番目の位置と一致し、次に通常のマッチングが実行されます。当然一致しないため、2 番目の位置の設定はconfigurationb
3, /images /1.jpg -> まず、 、プレフィックス 文字列の一部が 2 番目の場所と一致しましたが、その後 3 番目の場所のプレフィックスが一致しました。この時点では、これが構成ファイル内でこの URL に一致する最大の文字列であり、その場所には「^~」プレフィックスが付いていました。 . の場合、通常のマッチングは実行されなくなり、最終的に設定 c
4 が使用されます (/some/other/path/to/1.jpg -> まず、プレフィックス部分の同じ文字列が 2 番目の場所と一致し、通常のマッチングが成功したら、設定 d
location = / {
# matches the query / only.
[ configuration a ]
}
location / {
# matches any query, since all queries begin with /, but regular
# expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be
# matched first.
[ configuration b ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
# matches any query beginning with /images/ and halts searching,
# so regular expressions will not be checked.
[ configuration c ]
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
# matches any request ending in gif, jpg, or jpeg. however, all
# requests to the /images/ directory will be handled by
# configuration c.
[ configuration d ]
}
location @named {
# such locations are not used during normal processing of requests,
# they are intended only to process internally redirected requests (for example error_page, try_files).
[ configuration e ]
}ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *static_locations; (ngx_pcre) ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **regex_locations; if
location tree和regex_locations数组建立过程在ngx_http_block中:
/* create location trees */
for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) {
clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_conf_error;
}
if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_conf_error;
}
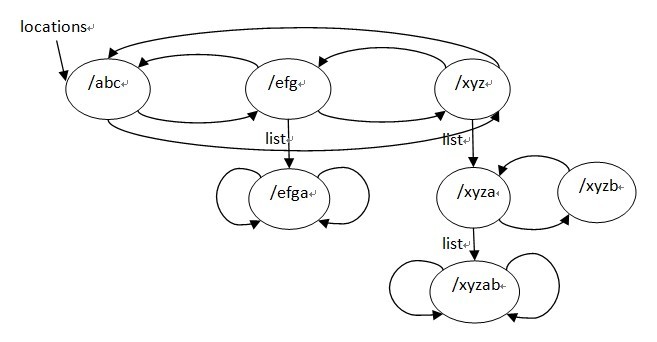
} 上記のステップは、通常の一致するロケーションに保存されます。処理後、ロケーション キューはすでに順番にあります。確立プロセスの主な作業三分ツリーは ngx_http_create_locations_list() と ngx_http_create_locations_tree() で完成します。これら 2 つの関数は両方とも再帰関数です。最初の関数はロケーション キュー内の各ノードを再帰し、現在のノードの名前がプレフィックスとして付けられたロケーションを取得し、リスト フィールドに保存されます。たとえば、次の場所:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_init_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf,
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
{
...
locations = pclcf->locations;
...
/* 按照类型排序location,排序完后的队列: (exact_match 或 inclusive) (排序好的,如果某个exact_match名字和inclusive location相同,exact_match排在前面)
| regex(未排序)| named(排序好的) | noname(未排序)*/
ngx_queue_sort(locations, ngx_http_cmp_locations);
named = null;
n = 0;
#if (ngx_pcre)
regex = null;
r = 0;
#endif
for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
/* 由于可能存在nested location,也就是location里面嵌套的location,这里需要递归的处理一下当前location下面的nested location */
if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, null, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_error;
}
#if (ngx_pcre)
if (clcf->regex) {
r++;
if (regex == null) {
regex = q;
}
continue;
}
#endif
if (clcf->named) {
n++;
if (named == null) {
named = q;
}
continue;
}
if (clcf->noname) {
break;
}
}
if (q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations)) {
ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
}
/* 如果有named location,将它们保存在所属server的named_locations数组中 */
if (named) {
clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
(n + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
if (clcfp == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
cscf->named_locations = clcfp;
for (q = named;
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
*(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
}
*clcfp = null;
ngx_queue_split(locations, named, &tail);
}
#if (ngx_pcre)
/* 如果有正则匹配location,将它们保存在所属server的http core模块的loc配置的regex_locations 数组中,
这里和named location保存位置不同的原因是由于named location只能存在server里面,而regex location可以作为nested location */
if (regex) {
clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
(r + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
if (clcfp == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
pclcf->regex_locations = clcfp;
for (q = regex;
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
*(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
}
*clcfp = null;
ngx_queue_split(locations, regex, &tail);
}
#endif
return ngx_ok;
}
static ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *
ngx_http_create_locations_tree(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations,
size_t prefix)
{
...
/* 根节点为locations队列的中间节点 */
q = ngx_queue_middle(locations);
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
len = lq->name->len - prefix;
node = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
offsetof(ngx_http_location_tree_node_t, name) + len);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
node->left = null;
node->right = null;
node->tree = null;
node->exact = lq->exact;
node->inclusive = lq->inclusive;
node->auto_redirect = (u_char) ((lq->exact && lq->exact->auto_redirect)
|| (lq->inclusive && lq->inclusive->auto_redirect));
node->len = (u_char) len;
ngx_memcpy(node->name, &lq->name->data[prefix], len);
/* 从中间节点开始断开 */
ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
/*
* ngx_queue_split() insures that if left part is empty,
* then right one is empty too
*/
goto inclusive;
}
/* 从locations左半部分得到左子树 */
node->left = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, prefix);
if (node->left == null) {
return null;
}
ngx_queue_remove(q);
if (ngx_queue_empty(&tail)) {
goto inclusive;
}
/* 从locations右半部分得到右子树 */
node->right = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &tail, prefix);
if (node->right == null) {
return null;
}
inclusive:
if (ngx_queue_empty(&lq->list)) {
return node;
}
/* 从list队列得到tree子树 */
node->tree = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &lq->list, prefix + len);
if (node->tree == null) {
return null;
}
return node;
}
location tree节点的ngx_http_location_tree_node_s结构:
struct ngx_http_location_tree_node_s {
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *left;
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *right;
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *tree;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *exact;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *inclusive;
u_char auto_redirect;
u_char len;
u_char name[1];
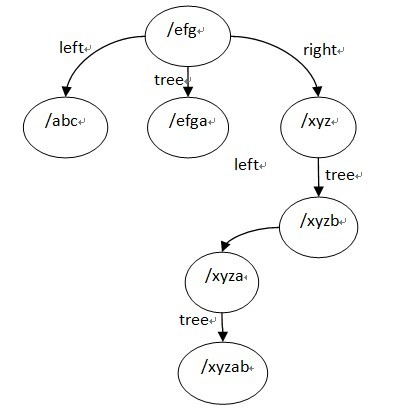
}; location tree结构用到的是left,right,tree 这3个字段, location tree实际上是一个三叉的字符串排序树,而且这里如果某个节点只考虑左,右子树,它是一颗平衡树,它的建立过程有点类似于一颗平衡排序二叉树的建立过程,先排序再用二分查找找到的节点顺序插入,ngx_http_location_tree_node_s的tree节点也是一颗平衡排序树,它是用该节点由ngx_http_create_locations_list()得到的list建立的,也就是该节点的名字是它的tree子树里面的所有节点名字的前缀,所以tree子树里面的所有节点的名字不用保存公共前缀,而且查找的时候,如果是转向tree节点的话,也是不需要再比较父节点的那段字符串了。
ngx_http_create_locations_tree()函数写的很清晰,它有一个参数是队列locations,它返回一颗三叉树,根节点为locations的中间节点,其左子树为locations队列的左半部分建立的location tree,右子树为location队列的右半部分建立的tree,tree节点为该根节点的list队列建立的tree。
最终建立的location tree如下(为了方便阅读,图中列出了tree节点的完整名字):
ps:关于 location modifier
1. =
这会完全匹配指定的 pattern ,且这里的 pattern 被限制成简单的字符串,也就是说这里不能使用正则表达式。
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location = /abcd {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 正好完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 如果运行 nginx server 的系统本身对大小写不敏感,比如 windows ,那么也匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),nginx 不认为这种情况是完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配,因为不是完全匹配
2. (none)
可以不写 location modifier ,nginx 仍然能去匹配 pattern 。这种情况下,匹配那些以指定的 patern 开头的 uri,注意这里的 uri 只能是普通字符串,不能使用正则表达式。
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location /abcd {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 正好完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 如果运行 nginx server 的系统本身对大小写不敏感,比如 windows ,那么也匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash)也属于匹配范围内 http://jb51.net/abcde # 仍然匹配,因为 uri 是以 pattern 开头的
3. ~
这个 location modifier 对大小写敏感,且 pattern 须是正则表达式
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location ~ ^/abcd$ {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 不匹配,~ 对大小写是敏感的 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),并不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$ http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$
注意:对于一些对大小写不敏感的系统,比如 windows ,~ 和 ~* 都是不起作用的,这主要是操作系统的原因。
4. ~*
与 ~ 类似,但这个 location modifier 不区分大小写,pattern 须是正则表达式
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location ~* ^/abcd$ {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 匹配,这就是它不区分大小写的特性 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),并不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$ http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$
5. ^~
匹配情况类似 2. (none) 的情况,以指定匹配模式开头的 uri 被匹配,不同的是,一旦匹配成功,那么 nginx 就停止去寻找其他的 location 块进行匹配了(与 location 匹配顺序有关)
6. @
用于定义一个 location 块,且该块不能被外部 client 所访问,只能被 nginx 内部配置指令所访问,比如 try_files or error_page
以上がNginxサーバーでのロケーション構成例の分析の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7662
7662
 15
15
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1205
1205
 24
24
 91
91
 11
11
 Nginxバージョンを確認する方法
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Nginxバージョンを確認する方法
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
nginxバージョンを照会できるメソッドは次のとおりです。nginx-vコマンドを使用します。 nginx.confファイルでバージョンディレクティブを表示します。 nginxエラーページを開き、ページタイトルを表示します。
 nginxでクラウドサーバードメイン名を構成する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
nginxでクラウドサーバードメイン名を構成する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
クラウドサーバーでnginxドメイン名を構成する方法:クラウドサーバーのパブリックIPアドレスを指すレコードを作成します。 NGINX構成ファイルに仮想ホストブロックを追加し、リスニングポート、ドメイン名、およびWebサイトルートディレクトリを指定します。 nginxを再起動して変更を適用します。ドメイン名のテスト構成にアクセスします。その他のメモ:SSL証明書をインストールしてHTTPSを有効にし、ファイアウォールがポート80トラフィックを許可し、DNS解像度が有効になることを確認します。
 Nginxが開始されるかどうかを確認する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Nginxが開始されるかどうかを確認する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
nginxが開始されるかどうかを確認する方法:1。コマンドラインを使用します:SystemCTLステータスnginx(Linux/unix)、netstat -ano | FindStr 80(Windows); 2。ポート80が開いているかどうかを確認します。 3.システムログのnginx起動メッセージを確認します。 4. Nagios、Zabbix、Icingaなどのサードパーティツールを使用します。
 Dockerコンテナの名前を確認する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Dockerコンテナの名前を確認する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
すべてのコンテナ(Docker PS)をリストする手順に従って、Dockerコンテナ名を照会できます。コンテナリストをフィルタリングします(GREPコマンドを使用)。コンテナ名(「名前」列にあります)を取得します。
 Windowsでnginxを構成する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Windowsでnginxを構成する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Windowsでnginxを構成する方法は? nginxをインストールし、仮想ホスト構成を作成します。メイン構成ファイルを変更し、仮想ホスト構成を含めます。 nginxを起動またはリロードします。構成をテストし、Webサイトを表示します。 SSLを選択的に有効にし、SSL証明書を構成します。ファイアウォールを選択的に設定して、ポート80および443のトラフィックを許可します。
 nginxサーバーを開始する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
nginxサーバーを開始する方法
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
NGINXサーバーを起動するには、異なるオペレーティングシステムに従って異なる手順が必要です。Linux/UNIXシステム:NGINXパッケージをインストールします(たとえば、APT-GetまたはYumを使用)。 SystemCtlを使用して、NGINXサービスを開始します(たとえば、Sudo SystemCtl Start NGinx)。 Windowsシステム:Windowsバイナリファイルをダウンロードしてインストールします。 nginx.exe実行可能ファイルを使用してnginxを開始します(たとえば、nginx.exe -c conf \ nginx.conf)。どのオペレーティングシステムを使用しても、サーバーIPにアクセスできます
 Docker用のコンテナを作成する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Docker用のコンテナを作成する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Dockerでコンテナを作成します。1。画像を引く:Docker Pull [ミラー名]2。コンテナを作成:Docker Run [Options] [Mirror Name] [コマンド]3。コンテナを起動:Docker Start [Container Name]
 Dockerによってコンテナを起動する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Dockerによってコンテナを起動する方法
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker Containerの起動手順:コンテナ画像を引く:「Docker Pull [Mirror Name]」を実行します。コンテナの作成:「docker create [options] [mirror name] [コマンドとパラメーター]」を使用します。コンテナを起動します:「docker start [container name or id]」を実行します。コンテナのステータスを確認してください:コンテナが「Docker PS」で実行されていることを確認します。




