G スコアを達成するために必要な最小ポイント数を調べる C++ プログラム

2 つの配列 p と c があり、各配列には D 要素があり、別の数値 G があるとします。プログラミング コンテストでは、各質問がその難易度に基づいて採点されると考えてください。質問 p[i] のスコアは 100i です。これらの p[1]...p[D] の問題はすべて競技の問題です。プログラミング Web サイトのユーザーは数値 total_score を持っています。ユーザーの total_score は、次の 2 つの要素の合計です。
基本スコア: 解決したすべての問題のスコアの合計
報酬:ユーザーがスコア 100i の問題をすべて解決すると、基本スコアに加えて、パーフェクト報酬 c[i] も獲得できます。
アマルはコンテストに初めて参加するため、まだ問題を解決していません。目標は総合評価G以上。この目標を達成するために、彼が少なくともどれだけの問題を解決する必要があるかを調べる必要があります。
したがって、入力が G = 500; P = [3, 5]; C = [500, 800] の場合、出力は 3
Steps
になります。この問題を解決するには、次の手順に従います。
D := size of p
mi := 10000
for initialize i := 0, when i < 1 << D, update (increase i by 1), do:
sum := 0
count := 0
at := 0
an array to store 10 bits b, initialize from bit value of i
for initialize j := 0, when j < D, update (increase j by 1), do:
if jth bit in b is 1, then:
count := p[j]
sum := sum + ((j + 1) * 100 * p[j] + c[j]
Otherwise
at := j
if sum < G, then:
d := (G - sum + (at + 1) * 100 - 1) / ((at + 1) * 100)
if d <= p[at], then:
sum := sum + (at + 1)
count := count + d
if sum >= G, then:
mi := minimum of mi and count
return miExample
理解を深めるために、以下の実装を見てみましょう。 -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int solve(int G, vector<int> p, vector<int> c){
int D = p.size();
int mi = 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << D; i++){
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
int at = 0;
bitset<10> b(i);
for (int j = 0; j < D; j++){
if (b.test(j)){
count += p.at(j);
sum += (j + 1) * 100 * p.at(j) + c.at(j);
} else {
at = j;
}
}
if (sum < G){
int d = (G - sum + (at + 1) * 100 - 1) / ((at + 1) * 100);
if (d <= p.at(at)){
sum += (at + 1) * 100 * d;
count += d;
}
}
if (sum >= G) {
mi = min(mi, count);
}
}
return mi;
}
int main() {
int G = 500;
vector<int> P = { 3, 5 };
vector<int> C = { 500, 800 };
cout << solve(G, P, C) << endl;
}Input
500, { 3, 5 }, { 500, 800 }出力
3
以上がG スコアを達成するために必要な最小ポイント数を調べる C++ プログラムの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7488
7488
 15
15
 1377
1377
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 19
19
 40
40
 以下を中国語に翻訳してください: ローマ数字を 10 進数に変換する C プログラム
Sep 05, 2023 pm 09:53 PM
以下を中国語に翻訳してください: ローマ数字を 10 進数に変換する C プログラム
Sep 05, 2023 pm 09:53 PM
以下に、ローマ数字を 10 進数に変換する C 言語アルゴリズムを示します。 アルゴリズム ステップ 1 - 開始 ステップ 2 - 実行時にローマ数字を読み取る ステップ 3 - 長さ: = strlen(roman) ステップ 4 - i=0 から長さ-1 の場合 ステップ4.1-switch(roman[i]) ステップ 4.1.1-case'm': &nbs
 2 つの文字列の辞書編集上の順序を比較する C++ プログラム
Sep 04, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
2 つの文字列の辞書編集上の順序を比較する C++ プログラム
Sep 04, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
辞書編集的な文字列比較とは、文字列が辞書順に比較されることを意味します。たとえば、「apple」と「appeal」という 2 つの文字列がある場合、「app」の最初の 3 文字が同じであるため、最初の文字列が最後に来ます。次に、最初の文字列の文字は「l」で、2 番目の文字列の 4 番目の文字は「e」になります。 「e」は「l」より短いため、辞書順に並べ替えると最初に表示されます。文字列は配置される前に辞書順に比較されます。この記事では、C++ を使用して 2 つの文字列を辞書編集的に比較するためのさまざまな手法を見ていきます。 C++ 文字列での Compare() 関数の使用 C++string オブジェクトには Compare() があります。
 Misty Jianghuの家のスコアの計算方法
Feb 29, 2024 pm 12:43 PM
Misty Jianghuの家のスコアの計算方法
Feb 29, 2024 pm 12:43 PM
Yanyu Jianghu には一種のハウス ゲームプレイがあります。プレイヤーは自由に自分の家を建てることができます。家が正常に建てられた後、ハウス スコアも取得します。同時に、ゲーム内のハウス スコアにも独自のものがあります。もちろんその計算方法も指定された計算方法を使って計算されるので、プレイヤーはそれを見てみることができます。燕宇江湖のハウススコアの計算方法 1. ハウススコア:外観スコア、配置スコア、スケールスコア、研究の4つの部分に分かれています 2. 外観スコア:主に建物スキンボーナスポイントと移動ボーナスポイント(200ポイント)があります。建物スキン 2 種類あり、上のホームショップで交換できるハンドパッチとターンテーブル上のスキンパッチの 2 種類があります 3. 配置ポイント: クラフト家具によって獲得できるポイント、緑の上限は10点、青の上限は15点、紫の上限は10点です。
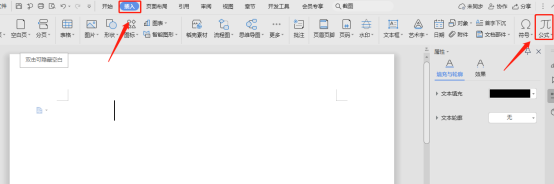 Wordで分数を挿入する方法
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:31 PM
Wordで分数を挿入する方法
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:31 PM
Wordで分数を入力する方法がわからない人も多いと思いますが、分数を入力する場面に遭遇することはあまりありません。しかし、遭遇するとさらに面倒なことになるので、Wordのスコアの入力方法を理解しておく必要があります。 Word での分数の入力は実はとても簡単なので、次に Word での分数の入力方法を紹介します。 Word で分数を入力するにはさまざまな方法がありますが、その 1 つは数式の挿入機能を使用することです。手順は次のとおりです。 Word 文書を開いた後、メニュー バーの [挿入] オプションをクリックし、ポップアップ メニューで [数式] を選択します。これにより、式エディターが開き、目的の分数を入力できます。エディターでは、分数の書式設定ボタンを使用して分数を作成するか、手動で「\frac{numerator}{」と入力できます。
 指定された値を引数として受け取る逆双曲線正弦関数の値を見つける C++ プログラム
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
指定された値を引数として受け取る逆双曲線正弦関数の値を見つける C++ プログラム
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
双曲線関数は、円の代わりに双曲線を使用して定義され、通常の三角関数と同等です。ラジアン単位で指定された角度から双曲線正弦関数の比率パラメーターを返します。しかし、その逆、つまり別の言い方をすればいいのです。双曲線正弦から角度を計算したい場合は、双曲線逆正弦演算のような逆双曲線三角関数演算が必要です。このコースでは、C++ で双曲線逆サイン (asinh) 関数を使用し、ラジアン単位の双曲線サイン値を使用して角度を計算する方法を説明します。双曲線逆正弦演算は次の式に従います -$$\mathrm{sinh^{-1}x\:=\:In(x\:+\:\sqrt{x^2\:+\:1})}ここで\:In\:is\:自然対数\:(log_e\:k)
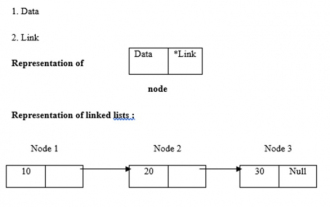 リンクリストの長さを求めるCプログラム
Sep 07, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
リンクリストの長さを求めるCプログラム
Sep 07, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
リンク リストは動的なメモリ割り当てを使用します。つまり、リンク リストはそれに応じて拡大および縮小します。これらはノードのコレクションとして定義されます。ここで、ノードにはデータとリンクという 2 つの部分があります。データ、リンク、リンクリストの表現は以下のとおりです。 ・リンクリストの種類 リンクリストには以下の4種類があります。 ・シングルリンクリスト/シングルリンクリスト ダブル/ダブルリンクリスト 循環シングルリンクリスト 循環ダブルリンクリスト再帰的メソッドを使用してリンク リストの長さを確認します。ロジックは -intlength(node *temp){ if(temp==NULL) returnl; else{&n
 辞書を印刷する C++ プログラム
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
辞書を印刷する C++ プログラム
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
マップは C++ の特別なタイプのコンテナで、各要素は 2 つの値、つまりキー値とマップ値のペアです。キー値は各項目のインデックス付けに使用され、マップされた値はキーに関連付けられた値です。マップされた値が一意であるかどうかに関係なく、キーは常に一意です。 C++ でマップ要素を出力するには、反復子を使用する必要があります。項目のセット内の要素は、反復子オブジェクトによって示されます。イテレータは主に配列や他のタイプのコンテナ (ベクトルなど) で使用され、特定の範囲内の特定の要素を識別するために使用できる特定の操作セットを備えています。イテレータをインクリメントまたはデクリメントして、範囲またはコンテナ内に存在するさまざまな要素を参照できます。イテレータは、範囲内の特定の要素のメモリ位置を指します。イテレータを使用して C++ でマップを出力する まず、定義方法を見てみましょう。
 C プログラムは rename() 関数を使用してファイル名を変更します
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
C プログラムは rename() 関数を使用してファイル名を変更します
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
名前変更機能は、ファイルまたはディレクトリを古い名前から新しい名前に変更します。この操作は移動操作と似ています。したがって、この名前変更機能を使用してファイルを移動することもできます。この関数は、stdio.h ライブラリ ヘッダー ファイルに存在します。 rename 関数の構文は次のとおりです: intrename(constchar*oldname,constchar*newname); rename() 関数は 2 つのパラメータを受け取ります。 1 つは古い名前、もう 1 つは新しい名前です。どちらのパラメータも、ファイルの古い名前と新しい名前を定義する定数文字へのポインタです。ファイルの名前が正常に変更された場合はゼロを返し、それ以外の場合はゼロ以外の整数を返します。名前変更操作中




