迷路内のマウスのための C プログラム - バックトラッキング-2
迷路の中のネズミも、バックトラッキングを使用する一般的な問題です。 I
迷路は、いくつかのセルがブロックされている 2 次元マトリックスです。セルの 1 つはソース セルであり、そこから開始する必要があります。もう一つは目的地、つまり私たちが到達しなければならない場所です。ブロックされたセルに入らずに、送信元から宛先までのパスを見つける必要があります。未解決の迷路の写真を以下に示します。
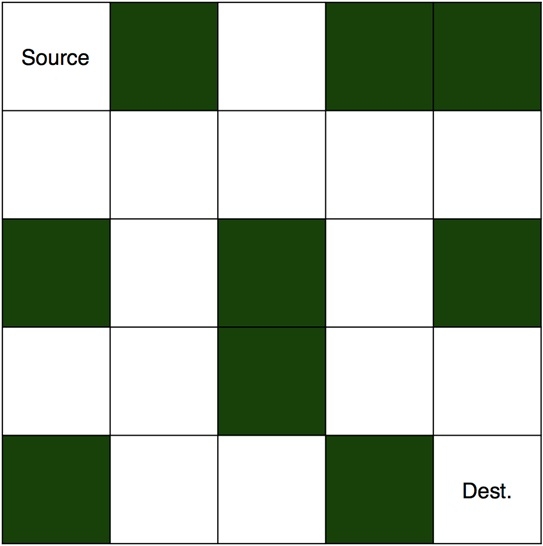
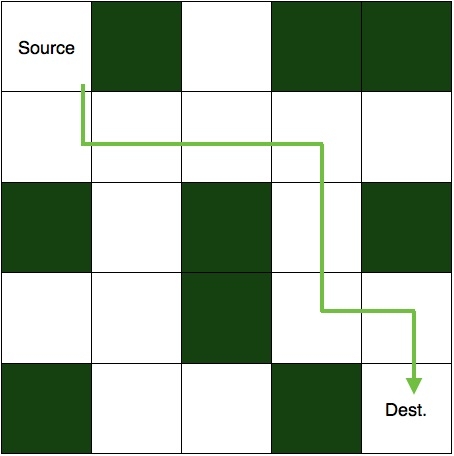
Input:
maze[][] = {
{0,1,0,1,1},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,1,0,1},
{0,0,1,0,0},
{1,0,0,1,0}}
Output:
1 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 10 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
- 現在のセルを確認し、それがターゲット セルである場合は、パズルは解けました。
- そうでない場合は、下に移動して、次のセルに移動できるかどうかを確認してください (セルに移動するには、セルが空であり、パス内にない必要があります)。
- 次のセルに移動できる場合は、パスに沿って次の下のセルまで移動を続けます。 #そうでない場合は、右に移動してみてください。右側がブロックされているか占有されている場合は、上に移動します。
- 同様に、上に移動できない場合は、単純に左のセルに移動します。
- 4 つの方向 (下、右、上、左) のいずれにも移動できない場合は、単純に戻って現在のパスを変更します (バックトラック)。
- つまり、要約すると、現在のセルから他のセル (下、右、上、左) に移動しようとし、移動できない場合は戻り、セルの方向を決定します。パスが別のセルに変更されます。
printsolution → この関数は単純に解行列を出力します。
solvemaze → これはバックトラッキングアルゴリズムを実際に実装する関数です。まず、セルがターゲット セルであるかどうかを確認します。ターゲット セルである場合は (r==SIZE-1) および (c==SIZE-1) となります。それがターゲットのセルであれば、パズルは解けたことになります。そうでない場合は、それが有効なモバイルセルであるかどうかを確認します。有効なセルが行列内に存在する必要があります。つまり、インデックスは 0 から SIZE-1 の間でなければならず、r>=0 && c>=0 && r 例#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define SIZE 5
//the maze problem
int maze[SIZE][SIZE] = {
{0,1,0,1,1},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,1,0,1},
{0,0,1,0,0},
{1,0,0,1,0}
};
//matrix to store the solution
int solution[SIZE][SIZE];
//function to print the solution matrix
void printsolution() {
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++) {
for(j=0;j<SIZE;j++) {
printf("%d\t",solution[i][j]);
}
printf("</p><p></p><p>");
}
}
//function to solve the maze
//using backtracking
int solvemaze(int r, int c) {
//if destination is reached, maze is solved
//destination is the last cell(maze[SIZE-1][SIZE-1])
if((r==SIZE-1) && (c==SIZE-1) {
solution[r][c] = 1;
return 1;
}
//checking if we can visit in this cell or not
//the indices of the cell must be in (0,SIZE-1)
//and solution[r][c] == 0 is making sure that the cell is not already visited
//maze[r][c] == 0 is making sure that the cell is not blocked
if(r>=0 && c>=0 && r<SIZE && c<SIZE && solution[r][c] == 0 && maze[r][c] == 0){
//if safe to visit then visit the cell
solution[r][c] = 1;
//going down
if(solvemaze(r+1, c))
return 1;
//going right
if(solvemaze(r, c+1))
return 1;
//going up
if(solvemaze(r-1, c))
return 1;
//going left
if(solvemaze(r, c-1))
return 1;
//backtracking
solution[r][c] = 0;
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
//making all elements of the solution matrix 0
int i,j;
for(i=0; i<SIZE; i++) {
for(j=0; j<SIZE; j++) {
solution[i][j] = 0;
}
}
if (solvemaze(0,0))
printsolution();
else
printf("No solution</p><p>");
return 0;
}
以上が迷路内のマウスのための C プログラム - バックトラッキング-2の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7328
7328
 9
9
 1626
1626
 14
14
 1350
1350
 46
46
 1262
1262
 25
25
 1209
1209
 29
29
 C言語関数によって返される値の種類は何ですか?返品値を決定するものは何ですか?
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:52 PM
C言語関数によって返される値の種類は何ですか?返品値を決定するものは何ですか?
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:52 PM
この記事では、c関数のリターンタイプ、基本(int、float、charなど)、派生(配列、ポインター、構造体)、およびvoid型を含む詳細を示します。 コンパイラは、関数宣言とreturnステートメントを介して返品タイプを決定し、強制します
 GULC:Cライブラリはゼロから構築されています
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
GULC:Cライブラリはゼロから構築されています
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
GULCは、最小限のオーバーヘッド、積極的なインライン、およびコンパイラの最適化を優先する高性能Cライブラリです。 高周波取引や組み込みシステムなどのパフォーマンスクリティカルなアプリケーションに最適な設計では、シンプルさ、モジュールが強調されています
 C言語関数の定義と呼び出しルールは何ですか、そして
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:53 PM
C言語関数の定義と呼び出しルールは何ですか、そして
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:53 PM
この記事では、C関数宣言と定義、引数の合格(価値とポインターによる)、返品値、およびメモリリークやタイプの不一致などの一般的な落とし穴について説明します。 モジュール性とProviの宣言の重要性を強調しています
 c言語関数形式文字ケース変換手順
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:53 PM
c言語関数形式文字ケース変換手順
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:53 PM
この記事では、文字列ケース変換のC関数について詳しく説明しています。 ctype.hのtoupper()とtolower()を使用し、文字列を介して繰り返し、ヌルターミネーターを処理することを説明しています。 ctype.hを忘れたり、文字列リテラルを変更するなどの一般的な落とし穴は
 メモリに保存されているC言語関数の返品値はどこにありますか?
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
メモリに保存されているC言語関数の返品値はどこにありますか?
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
この記事では、C関数の戻り値ストレージを調べます。 通常、リターン値は通常、速度のためにレジスタに保存されます。値が大きいと、ポインターをメモリ(スタックまたはヒープ)に使用し、寿命に影響を与え、手動のメモリ管理が必要になります。直接acc
 明確な使用法とフレーズ共有
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
明確な使用法とフレーズ共有
Mar 03, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
この記事では、形容詞の「個別」の多面的な使用法を分析し、その文法機能、一般的なフレーズ(例:「はっきりと異なる」とは異なる」、およびフォーマルと非公式の微妙なアプリケーションを調査します。
 STL(ソート、検索、変換など)のアルゴリズムを効率的に使用するにはどうすればよいですか?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 04:52 PM
STL(ソート、検索、変換など)のアルゴリズムを効率的に使用するにはどうすればよいですか?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 04:52 PM
この記事では、cの効率的なSTLアルゴリズムの使用について詳しく説明しています。 データ構造の選択(ベクトル対リスト)、アルゴリズムの複雑さ分析(STD :: STD :: STD :: PARTIAL_SORTなど)、イテレーターの使用、および並列実行を強調しています。 のような一般的な落とし穴
 C標準テンプレートライブラリ(STL)はどのように機能しますか?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 04:50 PM
C標準テンプレートライブラリ(STL)はどのように機能しますか?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 04:50 PM
この記事では、C標準テンプレートライブラリ(STL)について説明し、そのコアコンポーネント(コンテナ、イテレーター、アルゴリズム、およびファンクター)に焦点を当てています。 これらが一般的なプログラミングを有効にし、コード効率を向上させ、読みやすさを改善する方法を詳述しています。




