Meta の公式 Prompt プロジェクト ガイド: Llama 2 はこのように使用するとより効率的になります
大規模言語モデル (LLM) テクノロジーが成熟するにつれて、プロンプト エンジニアリング (プロンプト エンジニアリング) の重要性がますます高まっています。一部の研究機関は、Microsoft、OpenAI などの LLM プロンプト エンジニアリング ガイドラインを発行しています。
最近、Meta は、Llama 2 オープン ソース モデルに特化したインタラクティブなプロンプト エンジニアリング ガイドを提供しました。このガイドでは、Llama 2 を使用するためのクイック エンジニアリングとベスト プラクティスについて説明します。
以下は、このガイドの主要な内容です。
Llama モデル
2023 年に、Meta は Llama および Llama 2 モデルを発売しました。小さいモデルは導入と実行のコストが低くなりますが、大きいモデルはより高い機能を備えています。
Llama 2 シリーズのモデル パラメーター スケールは次のとおりです:

コード Llama はコード中心です。 Llama 2 上に構築された LLM には、さまざまなパラメータ サイズと微調整バリアントもあります。

LLM のデプロイ
LLM は、次のようなさまざまな方法で展開してアクセスできます。
セルフホスティング: ローカル ハードウェアを使用して推論を実行します。たとえば、 llama.cpp を使用して Macbook Pro で Llama 2 を実行します。長所: プライバシー/セキュリティのニーズがある場合、または十分な GPU がある場合は、セルフホスト型が最適です。
クラウド ホスティング: AWS、Azure、GCP などのクラウド プロバイダーを通じて Llama 2 を実行するなど、特定のモデルをホストするインスタンスをデプロイするにはクラウド プロバイダーに依存します。利点: クラウド ホスティングは、モデルとそのランタイムをカスタマイズするための最良の方法です。
マネージ API: API を介して LLM を直接呼び出します。 AWS Bedrock、Replicate、Anyscale、Togetter など、Llama 2 推論 API を提供する企業は数多くあります。長所: ホスト型 API は全体的に最も簡単なオプションです。
ホスト型 API
マネージド API には通常、2 つの主要なエンドポイントがあります:
1. 完了: 指定されたプロンプトに対する応答を生成します。
2. chat_completion: メッセージ リスト内の次のメッセージを生成し、チャットボットなどのユースケースに対してより明確な指示とコンテキストを提供します。
token
LLM は、トークンと呼ばれるブロックの形式で入出力を処理し、各モデルにはその独自のトークン化スキーム。たとえば、次の文:
私たちの運命は星に書かれています。
ラマ 2 のトークン化は ["our", "dest", "iny 「、」、「書く」、「で」、「その」、「星」]。トークンは、API の価格設定や内部動作 (ハイパーパラメーターなど) を考慮する場合に特に重要です。各モデルには、プロンプトが超えることのできない最大コンテキスト長があり、ラマ 2 は 4096 トークン、コード ラマは 100K トークンです。
ノートブックのセットアップ
例として、Replicate を使用して Llama 2 チャットを呼び出し、LangChain を使用してチャット完了 API を簡単にセットアップします。
最初に前提条件をインストールします:
pip install langchain replicate
from typing import Dict, Listfrom langchain.llms import Replicatefrom langchain.memory import ChatMessageHistoryfrom langchain.schema.messages import get_buffer_stringimport os# Get a free API key from https://replicate.com/account/api-tokensos.environ ["REPLICATE_API_TOKEN"] = "YOUR_KEY_HERE"LLAMA2_70B_CHAT = "meta/llama-2-70b-chat:2d19859030ff705a87c746f7e96eea03aefb71f166725aee39692f1476566d48"LLAMA2_13B_CHAT = "meta/llama-2-13b-chat:f4e2de70d66816a838a89eeeb621910adffb0dd0baba3976c96980970978018d"# We'll default to the smaller 13B model for speed; change to LLAMA2_70B_CHAT for more advanced (but slower) generationsDEFAULT_MODEL = LLAMA2_13B_CHATdef completion (prompt: str,model: str = DEFAULT_MODEL,temperature: float = 0.6,top_p: float = 0.9,) -> str:llm = Replicate (model=model,model_kwargs={"temperature": temperature,"top_p": top_p, "max_new_tokens": 1000})return llm (prompt)def chat_completion (messages: List [Dict],model = DEFAULT_MODEL,temperature: float = 0.6,top_p: float = 0.9,) -> str:history = ChatMessageHistory ()for message in messages:if message ["role"] == "user":history.add_user_message (message ["content"])elif message ["role"] == "assistant":history.add_ai_message (message ["content"])else:raise Exception ("Unknown role")return completion (get_buffer_string (history.messages,human_prefix="USER",ai_prefix="ASSISTANT",),model,temperature,top_p,)def assistant (content: str):return { "role": "assistant", "content": content }def user (content: str):return { "role": "user", "content": content }def complete_and_print (prompt: str, model: str = DEFAULT_MODEL):print (f'==============\n {prompt}\n==============')response = completion (prompt, model)print (response, end='\n\n')Completion API
complete_and_print ("The typical color of the sky is:")complete_and_print ("which model version are you?")Chat Completion モデルは、LLM と対話するための追加の構造を提供し、単一のテキストの代わりに構造化メッセージ オブジェクトの配列を LLM に送信します。このメッセージ リストは、LLM に、続行するための「背景」または「履歴」情報を提供します。
通常、各メッセージには役割と内容が含まれています。
システム役割を持つメッセージは、LLM に核となる指示を提供するために開発者によって使用されます。
ユーザー ロールを持つメッセージは通常、人間が提供したメッセージです。
アシスタントの役割を持つメッセージは、通常、LLM によって生成されます。
response = chat_completion (messages=[user ("My favorite color is blue."),assistant ("That's great to hear!"),user ("What is my favorite color?"),])print (response)# "Sure, I can help you with that! Your favorite color is blue."LLM ハイパーパラメータ
LLM API 通常会采用影响输出的创造性和确定性的参数。在每一步中,LLM 都会生成 token 及其概率的列表。可能性最小的 token 会从列表中「剪切」(基于 top_p),然后从剩余候选者中随机(温度参数 temperature)选择一个 token。换句话说:top_p 控制生成中词汇的广度,温度控制词汇的随机性,温度参数 temperature 为 0 会产生几乎确定的结果。
def print_tuned_completion (temperature: float, top_p: float):response = completion ("Write a haiku about llamas", temperature=temperature, top_p=top_p)print (f'[temperature: {temperature} | top_p: {top_p}]\n {response.strip ()}\n')print_tuned_completion (0.01, 0.01)print_tuned_completion (0.01, 0.01)# These two generations are highly likely to be the sameprint_tuned_completion (1.0, 1.0)print_tuned_completion (1.0, 1.0)# These two generations are highly likely to be differentprompt 技巧
详细、明确的指令会比开放式 prompt 产生更好的结果:
complete_and_print (prompt="Describe quantum physics in one short sentence of no more than 12 words")# Returns a succinct explanation of quantum physics that mentions particles and states existing simultaneously.
我们可以给定使用规则和限制,以给出明确的指令。
- 风格化,例如:
- 向我解释一下这一点,就像儿童教育网络节目中教授小学生一样;
- 我是一名软件工程师,使用大型语言模型进行摘要。用 250 字概括以下文字;
- 像私家侦探一样一步步追查案件,给出你的答案。
- 格式化
使用要点;
以 JSON 对象形式返回;
使用较少的技术术语并用于工作交流中。
- 限制
- 仅使用学术论文;
- 切勿提供 2020 年之前的来源;
- 如果你不知道答案,就说你不知道。
以下是给出明确指令的例子:
complete_and_print ("Explain the latest advances in large language models to me.")# More likely to cite sources from 2017complete_and_print ("Explain the latest advances in large language models to me. Always cite your sources. Never cite sources older than 2020.")# Gives more specific advances and only cites sources from 2020零样本 prompting
一些大型语言模型(例如 Llama 2)能够遵循指令并产生响应,而无需事先看过任务示例。没有示例的 prompting 称为「零样本 prompting(zero-shot prompting)」。例如:
complete_and_print ("Text: This was the best movie I've ever seen! \n The sentiment of the text is:")# Returns positive sentimentcomplete_and_print ("Text: The director was trying too hard. \n The sentiment of the text is:")# Returns negative sentiment少样本 prompting
添加所需输出的具体示例通常会产生更加准确、一致的输出。这种方法称为「少样本 prompting(few-shot prompting)」。例如:
def sentiment (text):response = chat_completion (messages=[user ("You are a sentiment classifier. For each message, give the percentage of positive/netural/negative."),user ("I liked it"),assistant ("70% positive 30% neutral 0% negative"),user ("It could be better"),assistant ("0% positive 50% neutral 50% negative"),user ("It's fine"),assistant ("25% positive 50% neutral 25% negative"),user (text),])return responsedef print_sentiment (text):print (f'INPUT: {text}')print (sentiment (text))print_sentiment ("I thought it was okay")# More likely to return a balanced mix of positive, neutral, and negativeprint_sentiment ("I loved it!")# More likely to return 100% positiveprint_sentiment ("Terrible service 0/10")# More likely to return 100% negativeRole Prompting
Llama 2 在指定角色时通常会给出更一致的响应,角色为 LLM 提供了所需答案类型的背景信息。
例如,让 Llama 2 对使用 PyTorch 的利弊问题创建更有针对性的技术回答:
complete_and_print ("Explain the pros and cons of using PyTorch.")# More likely to explain the pros and cons of PyTorch covers general areas like documentation, the PyTorch community, and mentions a steep learning curvecomplete_and_print ("Your role is a machine learning expert who gives highly technical advice to senior engineers who work with complicated datasets. Explain the pros and cons of using PyTorch.")# Often results in more technical benefits and drawbacks that provide more technical details on how model layers思维链
简单地添加一个「鼓励逐步思考」的短语可以显著提高大型语言模型执行复杂推理的能力(Wei et al. (2022)),这种方法称为 CoT 或思维链 prompting:
complete_and_print ("Who lived longer Elvis Presley or Mozart?")# Often gives incorrect answer of "Mozart"complete_and_print ("Who lived longer Elvis Presley or Mozart? Let's think through this carefully, step by step.")# Gives the correct answer "Elvis"自洽性(Self-Consistency)
LLM 是概率性的,因此即使使用思维链,一次生成也可能会产生不正确的结果。自洽性通过从多次生成中选择最常见的答案来提高准确性(以更高的计算成本为代价):
import refrom statistics import modedef gen_answer ():response = completion ("John found that the average of 15 numbers is 40.""If 10 is added to each number then the mean of the numbers is?""Report the answer surrounded by three backticks, for example:```123```",model = LLAMA2_70B_CHAT)match = re.search (r'```(\d+)```', response)if match is None:return Nonereturn match.group (1)answers = [gen_answer () for i in range (5)]print (f"Answers: {answers}\n",f"Final answer: {mode (answers)}",)# Sample runs of Llama-2-70B (all correct):# [50, 50, 750, 50, 50]-> 50# [130, 10, 750, 50, 50] -> 50# [50, None, 10, 50, 50] -> 50检索增强生成
有时我们可能希望在应用程序中使用事实知识,那么可以从开箱即用(即仅使用模型权重)的大模型中提取常见事实:
complete_and_print ("What is the capital of the California?", model = LLAMA2_70B_CHAT)# Gives the correct answer "Sacramento"然而,LLM 往往无法可靠地检索更具体的事实或私人信息。模型要么声明它不知道,要么幻想出一个错误的答案:
complete_and_print ("What was the temperature in Menlo Park on December 12th, 2023?")# "I'm just an AI, I don't have access to real-time weather data or historical weather records."complete_and_print ("What time is my dinner reservation on Saturday and what should I wear?")# "I'm not able to access your personal information [..] I can provide some general guidance"检索增强生成(RAG)是指在 prompt 中包含从外部数据库检索的信息(Lewis et al. (2020))。RAG 是将事实纳入 LLM 应用的有效方法,并且比微调更经济实惠,微调可能成本高昂并对基础模型的功能产生负面影响。
MENLO_PARK_TEMPS = {"2023-12-11": "52 degrees Fahrenheit","2023-12-12": "51 degrees Fahrenheit","2023-12-13": "51 degrees Fahrenheit",}def prompt_with_rag (retrived_info, question):complete_and_print (f"Given the following information: '{retrived_info}', respond to: '{question}'")def ask_for_temperature (day):temp_on_day = MENLO_PARK_TEMPS.get (day) or "unknown temperature"prompt_with_rag (f"The temperature in Menlo Park was {temp_on_day} on {day}'",# Retrieved factf"What is the temperature in Menlo Park on {day}?",# User question)ask_for_temperature ("2023-12-12")# "Sure! The temperature in Menlo Park on 2023-12-12 was 51 degrees Fahrenheit."ask_for_temperature ("2023-07-18")# "I'm not able to provide the temperature in Menlo Park on 2023-07-18 as the information provided states that the temperature was unknown."程序辅助语言模型
LLM 本质上不擅长执行计算,例如:
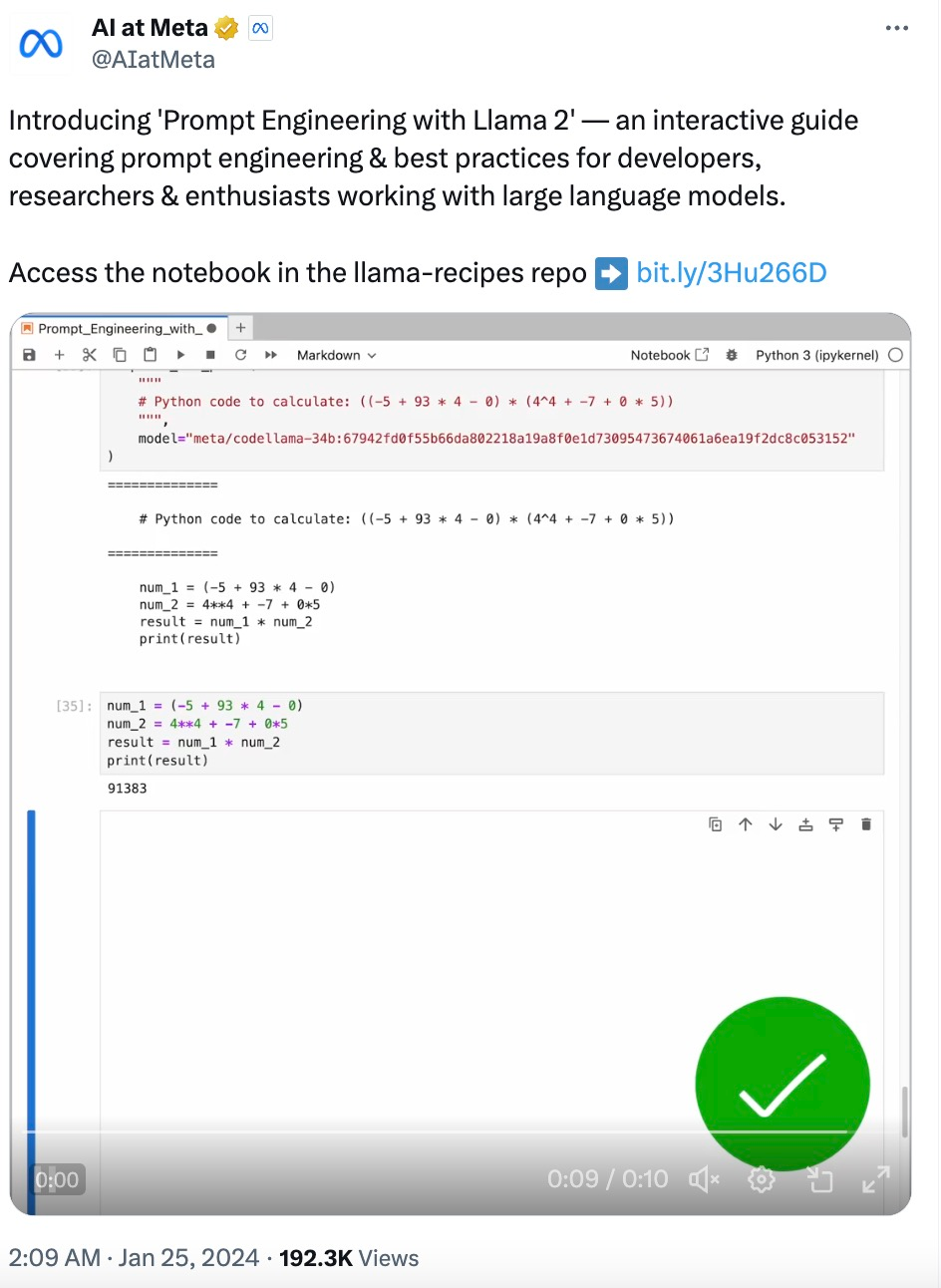
complete_and_print ("""Calculate the answer to the following math problem:((-5 + 93 * 4 - 0) * (4^4 + -7 + 0 * 5))""")# Gives incorrect answers like 92448, 92648, 95463Gao et al. (2022) 提出「程序辅助语言模型(Program-aided Language Models,PAL)」的概念。虽然 LLM 不擅长算术,但它们非常擅长代码生成。PAL 通过指示 LLM 编写代码来解决计算任务。
complete_and_print ("""# Python code to calculate: ((-5 + 93 * 4 - 0) * (4^4 + -7 + 0 * 5))""",model="meta/codellama-34b:67942fd0f55b66da802218a19a8f0e1d73095473674061a6ea19f2dc8c053152")# The following code was generated by Code Llama 34B:num1 = (-5 + 93 * 4 - 0)num2 = (4**4 + -7 + 0 * 5)answer = num1 * num2print (answer)
以上がMeta の公式 Prompt プロジェクト ガイド: Llama 2 はこのように使用するとより効率的になりますの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7681
7681
 15
15
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1209
1209
 24
24
 91
91
 11
11
 オープンソース!ゾーイデプスを超えて! DepthFM: 高速かつ正確な単眼深度推定!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
オープンソース!ゾーイデプスを超えて! DepthFM: 高速かつ正確な単眼深度推定!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
0.この記事は何をするのですか?私たちは、多用途かつ高速な最先端の生成単眼深度推定モデルである DepthFM を提案します。従来の深度推定タスクに加えて、DepthFM は深度修復などの下流タスクでも最先端の機能を実証します。 DepthFM は効率的で、いくつかの推論ステップ内で深度マップを合成できます。この作品について一緒に読みましょう〜 1. 論文情報タイトル: DepthFM: FastMonocularDepthEstimationwithFlowMatching 著者: MingGui、JohannesS.Fischer、UlrichPrestel、PingchuanMa、Dmytr
 世界で最も強力なオープンソース MoE モデルが登場。GPT-4 に匹敵する中国語機能を備え、価格は GPT-4-Turbo のわずか 1% 近くです
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
世界で最も強力なオープンソース MoE モデルが登場。GPT-4 に匹敵する中国語機能を備え、価格は GPT-4-Turbo のわずか 1% 近くです
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
従来のコンピューティングを超える能力を備えているだけでなく、より低コストでより効率的なパフォーマンスを実現する人工知能モデルを想像してみてください。これは SF ではありません。世界で最も強力なオープンソース MoE モデルである DeepSeek-V2[1] が登場しました。 DeepSeek-V2 は、経済的なトレーニングと効率的な推論の特徴を備えた強力な専門家混合 (MoE) 言語モデルです。これは 236B のパラメータで構成されており、そのうち 21B は各マーカーをアクティブにするために使用されます。 DeepSeek67B と比較して、DeepSeek-V2 はパフォーマンスが優れていると同時に、トレーニング コストを 42.5% 節約し、KV キャッシュを 93.3% 削減し、最大生成スループットを 5.76 倍に高めます。 DeepSeek は一般的な人工知能を研究する会社です
 AI が数学研究を破壊する!フィールズ賞受賞者で中国系アメリカ人の数学者が上位 11 件の論文を主導 | テレンス・タオが「いいね!」しました
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI が数学研究を破壊する!フィールズ賞受賞者で中国系アメリカ人の数学者が上位 11 件の論文を主導 | テレンス・タオが「いいね!」しました
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI は確かに数学を変えつつあります。最近、この問題に細心の注意を払っている陶哲軒氏が『米国数学協会会報』(米国数学協会会報)の最新号を送ってくれた。 「機械は数学を変えるのか?」というテーマを中心に、多くの数学者が意見を述べ、そのプロセス全体は火花に満ち、ハードコアで刺激的でした。著者には、フィールズ賞受賞者のアクシャイ・ベンカテシュ氏、中国の数学者鄭楽軍氏、ニューヨーク大学のコンピューター科学者アーネスト・デイビス氏、その他業界で著名な学者を含む強力な顔ぶれが揃っている。 AI の世界は劇的に変化しています。これらの記事の多くは 1 年前に投稿されたものです。
 こんにちは、電気アトラスです!ボストン・ダイナミクスのロボットが復活、180度の奇妙な動きにマスク氏も恐怖
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
こんにちは、電気アトラスです!ボストン・ダイナミクスのロボットが復活、180度の奇妙な動きにマスク氏も恐怖
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Boston Dynamics Atlas は正式に電動ロボットの時代に突入します!昨日、油圧式アトラスが歴史の舞台から「涙ながらに」撤退したばかりですが、今日、ボストン・ダイナミクスは電動式アトラスが稼働することを発表しました。ボストン・ダイナミクス社は商用人型ロボットの分野でテスラ社と競争する決意を持っているようだ。新しいビデオが公開されてから、わずか 10 時間ですでに 100 万人以上が視聴しました。古い人が去り、新しい役割が現れるのは歴史的な必然です。今年が人型ロボットの爆発的な年であることは間違いありません。ネットユーザーは「ロボットの進歩により、今年の開会式は人間のように見え、人間よりもはるかに自由度が高い。しかし、これは本当にホラー映画ではないのか?」とコメントした。ビデオの冒頭では、アトラスは仰向けに見えるように地面に静かに横たわっています。次に続くのは驚くべきことです
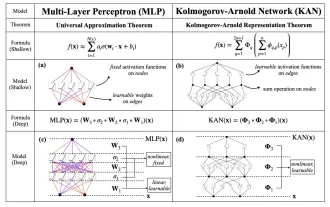 MLP に代わる KAN は、オープンソース プロジェクトによって畳み込みまで拡張されました
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
MLP に代わる KAN は、オープンソース プロジェクトによって畳み込みまで拡張されました
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
今月初め、MIT やその他の機関の研究者らは、MLP に代わる非常に有望な代替案である KAN を提案しました。 KAN は、精度と解釈可能性の点で MLP よりも優れています。また、非常に少数のパラメーターを使用して、多数のパラメーターを使用して実行する MLP よりも優れたパフォーマンスを発揮できます。たとえば、著者らは、KAN を使用して、より小規模なネットワークと高度な自動化で DeepMind の結果を再現したと述べています。具体的には、DeepMind の MLP には約 300,000 個のパラメーターがありますが、KAN には約 200 個のパラメーターしかありません。 KAN は、MLP が普遍近似定理に基づいているのに対し、KAN はコルモゴロフ-アーノルド表現定理に基づいているのと同様に、強力な数学的基礎を持っています。以下の図に示すように、KAN は
 超知性の生命力が覚醒する!しかし、自己更新 AI の登場により、母親はデータのボトルネックを心配する必要がなくなりました。
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
超知性の生命力が覚醒する!しかし、自己更新 AI の登場により、母親はデータのボトルネックを心配する必要がなくなりました。
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
世界は狂ったように大きなモデルを構築していますが、インターネット上のデータだけではまったく不十分です。このトレーニング モデルは「ハンガー ゲーム」のようであり、世界中の AI 研究者は、データを貪欲に食べる人たちにどのように餌を与えるかを心配しています。この問題は、マルチモーダル タスクで特に顕著です。何もできなかった当時、中国人民大学学部のスタートアップチームは、独自の新しいモデルを使用して、中国で初めて「モデル生成データフィード自体」を実現しました。さらに、これは理解側と生成側の 2 つの側面からのアプローチであり、両方の側で高品質のマルチモーダルな新しいデータを生成し、モデル自体にデータのフィードバックを提供できます。モデルとは何ですか? Awaker 1.0 は、中関村フォーラムに登場したばかりの大型マルチモーダル モデルです。チームは誰ですか?ソフォンエンジン。人民大学ヒルハウス人工知能大学院の博士課程学生、ガオ・イージャオ氏によって設立されました。
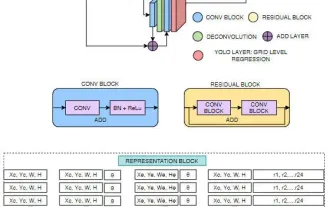 FisheyeDetNet: 魚眼カメラに基づいた最初のターゲット検出アルゴリズム
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
FisheyeDetNet: 魚眼カメラに基づいた最初のターゲット検出アルゴリズム
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
目標検出は自動運転システムにおいて比較的成熟した問題であり、その中でも歩行者検出は最も初期に導入されたアルゴリズムの 1 つです。ほとんどの論文では非常に包括的な研究が行われています。ただし、サラウンドビューに魚眼カメラを使用した距離認識については、あまり研究されていません。放射状の歪みが大きいため、標準のバウンディング ボックス表現を魚眼カメラに実装するのは困難です。上記の説明を軽減するために、拡張バウンディング ボックス、楕円、および一般的な多角形の設計を極/角度表現に探索し、これらの表現を分析するためのインスタンス セグメンテーション mIOU メトリックを定義します。提案された多角形モデルの FisheyeDetNet は、他のモデルよりも優れたパフォーマンスを示し、同時に自動運転用の Valeo 魚眼カメラ データセットで 49.5% の mAP を達成しました。
 Kuaishou バージョンの Sora「Ke Ling」がテスト用に公開されています。120 秒以上のビデオを生成し、物理学をより深く理解し、複雑な動きを正確にモデル化できます。
Jun 11, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Kuaishou バージョンの Sora「Ke Ling」がテスト用に公開されています。120 秒以上のビデオを生成し、物理学をより深く理解し、複雑な動きを正確にモデル化できます。
Jun 11, 2024 am 09:51 AM
何?ズートピアは国産AIによって実現するのか?ビデオとともに公開されたのは、「Keling」と呼ばれる新しい大規模な国産ビデオ生成モデルです。 Sora も同様の技術的ルートを使用し、自社開発の技術革新を多数組み合わせて、大きく合理的な動きをするだけでなく、物理世界の特性をシミュレートし、強力な概念的結合能力と想像力を備えたビデオを制作します。データによると、Keling は、最大 1080p の解像度で 30fps で最大 2 分の超長時間ビデオの生成をサポートし、複数のアスペクト比をサポートします。もう 1 つの重要な点は、Keling は研究所が公開したデモやビデオ結果のデモンストレーションではなく、ショートビデオ分野のリーダーである Kuaishou が立ち上げた製品レベルのアプリケーションであるということです。さらに、主な焦点は実用的であり、白紙小切手を書かず、リリースされたらすぐにオンラインに移行することです。Ke Ling の大型モデルは Kuaiying でリリースされました。




