Javascript_javascript スキルで継承を実装する方法についての簡単な説明
S1: js 内のすべてはオブジェクトです。プロトタイプの概念を考慮して、最初に継承を実装する方法を考えてみましょう。
function Parent(){
this.name='123';
}
Parent.prototype.getName=function(){
return this.name;
}
function Son(){
this.age=20;
}
Son.prototype=new Parent();
Son.prototype.getAge=function(){
return this.age;
}
var son=new Son();
console.log('Name :'+son.getName()+';Age: '+son.getAge());
VM1777:16 Name :123;Age: 20上記からわかるように、Parent の継承は主に Son のプロトタイプを上書きすることであり、このようにして、Parent のプロパティとメソッドが Son のプロトタイプに渡され、新しい Son を通じてオブジェクトが構築されます。 () はすべてプロトタイプ (つまり、親オブジェクト Parent) からプロパティとメソッドを継承するため、継承効果が得られますが、これには副作用が生じます。つまり、親オブジェクトに参照型属性が含まれている場合、子オブジェクトは参照型 data を変更し、すべてのサブオブジェクトに影響を与えますが、明らかにこれは必要な効果ではありません:
function Parent(){
this.name='123';
this.fruits=['apple'];
}
Parent.prototype.getName=function(){
return this.name;
}
function Son(){
this.age=20;
}
Son.prototype=new Parent();
Son.prototype.getAge=function(){
return this.age;
}
var son=new Son();
var son1=new Son();
console.log(son.fruits);//["apple"]
console.log(son1.fruits);//["apple"]
son.fruits.push('pear');
console.log(son.fruits);//["apple", "pear"]
console.log(son1.fruits);//["apple", "pear"]S2: この問題を解決するために現在考えられているのは、各子オブジェクトに親オブジェクトの属性のコピーを持たせることです。このようにして、属性を変更するときに、属性に影響を与えることなく、子オブジェクトの下の属性のみが変更されます。他の子オブジェクトの。この目標は、オブジェクト偽装の以前の方法を参照することで達成されます
function Parent(){
this.name='123';
this.fruits=['apple'];
}
Parent.prototype.getName=function(){
return this.name;
}
function Son(){
Parent.call(this);
this.age=20;
}
Son.prototype=new Parent();
Son.prototype.getAge=function(){
return this.age;
}
var son=new Son();
var son1=new Son();
console.log(son.fruits);//["apple"]
console.log(son1.fruits);//["apple"]
son.fruits.push('pear');
console.log(son.fruits);//["apple", "pear"]
console.log(son1.fruits);//["apple"]上記の Son 関数に Parent.call(this) を追加して、この [新しい Son オブジェクト] が new Son() 中に Parent() 関数を呼び出すための Parent 関数内のコンテキスト this であるかのように見せました。親オブジェクトのプロパティとメソッドのコピーを取得したため、次に親オブジェクトのプロパティとメソッドを変更すると、実際には変更されたコピーになるため、すべての子オブジェクトに影響を与えないという効果が得られます。ただし、Son.prototype=new Parent() を使用しているため、コピーを取得した後は、親オブジェクトのプロトタイプのみが必要になります。 getname();
のみが必要です。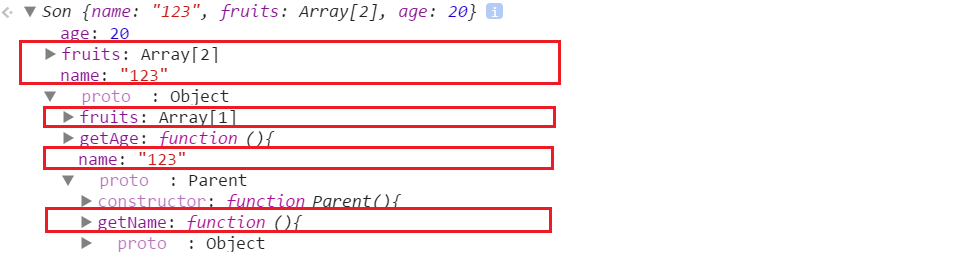
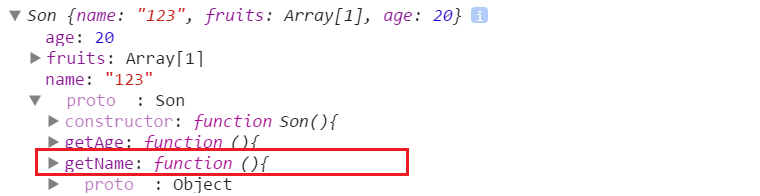
S3: 次のステップは、インスタンスの属性とメソッドを削除することです。ここでコンストラクターが登場し、Parent.prototype を子オブジェクトのプロトタイプとしてネイティブ オブジェクトに再構築します。次に、コンストラクターがサブコンストラクター
を指すようにします。
function Parent(){
this.name='123';
this.fruits=['apple'];
}
Parent.prototype.getName=function(){
return this.name;
}
function Son(){
Parent.call(this);
this.age=20;
}
function Extend(Parent,Son){
var proto = new Object(Parent.prototype);
proto.constructor = Son;
Son.prototype=proto;
}
Extend(Parent,Son);
Son.prototype.getAge=function(){
return this.age;
}
以上がこの記事の全内容です。皆さんに気に入っていただければ幸いです。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7380
7380
 15
15
 1628
1628
 14
14
 1357
1357
 52
52
 1267
1267
 25
25
 1216
1216
 29
29
 JavaScriptの文字列文字を交換します
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScriptの文字列文字を交換します
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript文字列置換法とFAQの詳細な説明 この記事では、javaScriptの文字列文字を置き換える2つの方法について説明します:内部JavaScriptコードとWebページの内部HTML。 JavaScriptコード内の文字列を交換します 最も直接的な方法は、置換()メソッドを使用することです。 str = str.replace( "find"、 "置換"); この方法は、最初の一致のみを置き換えます。すべての一致を置き換えるには、正規表現を使用して、グローバルフラグGを追加します。 str = str.replace(/fi
 8見事なjQueryページレイアウトプラグイン
Mar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AM
8見事なjQueryページレイアウトプラグイン
Mar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AM
楽なWebページレイアウトのためにjQueryを活用する:8本質的なプラグイン jQueryは、Webページのレイアウトを大幅に簡素化します。 この記事では、プロセスを合理化する8つの強力なjQueryプラグイン、特に手動のウェブサイトの作成に役立ちます
 独自のAjax Webアプリケーションを構築します
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
独自のAjax Webアプリケーションを構築します
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
それで、あなたはここで、Ajaxと呼ばれるこのことについてすべてを学ぶ準備ができています。しかし、それは正確には何ですか? Ajaxという用語は、動的でインタラクティブなWebコンテンツを作成するために使用されるテクノロジーのゆるいグループ化を指します。 Ajaxという用語は、もともとJesse Jによって造られました
 モバイル開発用のモバイルチートシート10個
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:43 AM
モバイル開発用のモバイルチートシート10個
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:43 AM
この投稿は、Android、BlackBerry、およびiPhoneアプリ開発用の有用なチートシート、リファレンスガイド、クイックレシピ、コードスニペットをコンパイルします。 開発者がいないべきではありません! タッチジェスチャーリファレンスガイド(PDF) Desigの貴重なリソース
 ソースビューアーでjQueryの知識を向上させます
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:54 AM
ソースビューアーでjQueryの知識を向上させます
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:54 AM
jQueryは素晴らしいJavaScriptフレームワークです。ただし、他のライブラリと同様に、何が起こっているのかを発見するためにフードの下に入る必要がある場合があります。おそらく、バグをトレースしているか、jQueryが特定のUIをどのように達成するかに興味があるからです
 10 jQueryの楽しみとゲームプラグイン
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM
10 jQueryの楽しみとゲームプラグイン
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM
10の楽しいjQueryゲームプラグインして、あなたのウェブサイトをより魅力的にし、ユーザーの粘着性を高めます! Flashは依然としてカジュアルなWebゲームを開発するのに最適なソフトウェアですが、jQueryは驚くべき効果を生み出すこともできます。また、純粋なアクションフラッシュゲームに匹敵するものではありませんが、場合によってはブラウザで予期せぬ楽しみもできます。 jquery tic toeゲーム ゲームプログラミングの「Hello World」には、JQueryバージョンがあります。 ソースコード jQueryクレイジーワードコンポジションゲーム これは空白のゲームであり、単語の文脈を知らないために奇妙な結果を生み出すことができます。 ソースコード jquery鉱山の掃引ゲーム
 独自のJavaScriptライブラリを作成および公開するにはどうすればよいですか?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
独自のJavaScriptライブラリを作成および公開するにはどうすればよいですか?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
記事では、JavaScriptライブラリの作成、公開、および維持について説明し、計画、開発、テスト、ドキュメント、およびプロモーション戦略に焦点を当てています。
 jQuery Parallaxチュートリアル - アニメーションヘッダーの背景
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AM
jQuery Parallaxチュートリアル - アニメーションヘッダーの背景
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AM
このチュートリアルでは、jQueryを使用して魅惑的な視差の背景効果を作成する方法を示しています。 見事な視覚的な深さを作成するレイヤー画像を備えたヘッダーバナーを構築します。 更新されたプラグインは、jQuery 1.6.4以降で動作します。 ダウンロードしてください




