 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (3) - Garbage collection mechanism
Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (3) - Garbage collection mechanism
Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (3) - Garbage collection mechanism
In the previous article, we said that automatic memory management is divided into two parts: allocating memory to objects and recycling the memory allocated to objects. In this article we talk about the latter, that is, recycling the memory allocated to the object. Recycling memory requires the use of a garbage collection mechanism, whose English name is GC (Garbage Collection).
In this part we have to solve the following questions:
1. Which memory needs to be recycled?
2. When will it be recycled?
3. How to recycle?
Which memory needs to be recycled?
The memory in the heap and method area needs to be recycled, and the rest does not need to be recycled.
Because only the heap and method area are shared by threads, the rest "live and die" with the thread. When the thread ends, the memory will naturally be recycled, so don't worry about them.
When will it be recycled?
(1) In the heap:
When the object "dies", its memory must be recycled. What does it mean that the object is dead? There's just no place to reference it, it's useless. So how do you tell if it's dead?
There are two methods:
Reference counting algorithm
Add a reference counter to the object. Whenever there is a reference to it, the counter's The value is 1. When the reference fails, the value of the counter is -1. When the value of the counter is 0, it means that the object is no longer referenced, that is, "it can die."
But there is a drawback, which is the problem of circular references. Just like the picture below, even if the two objects in the heap are useless, they cannot be recycled because they refer to each other and the counter value is at least 1.
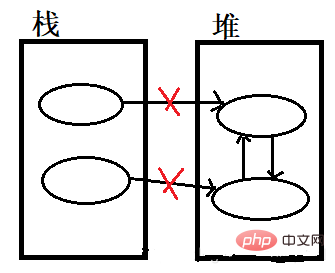
reachability analysis
All generated objects are subtrees of a root called "GC Roots". Starting from GC Roots and searching downward, the path traveled by the search is called the reference chain. When an object has no reference chain to reach GC Roots, the object is said to be unreachable, that is, it can be recycled by GC. This is a commonly used method in Java.
Just like the unreferenced objects in the heap in the figure below, they can be recycled.
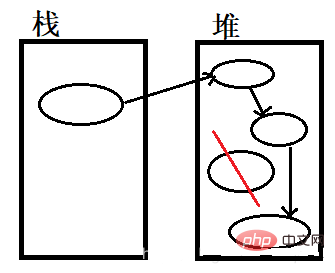
How to determine whether an object still has a reference? There are four types of references in Java:
Strong reference: Object o=new Object(). As long as the strong reference exists, the GC will never reclaim the referenced object.
Soft reference: describes some objects that are useful but not necessary. When the system is about to overflow memory, it will be recycled.
Weak reference: As long as GC is performed, it will be recycled.
Virtual reference: This is the weakest reference relationship. An object instance cannot be obtained through a virtual reference. Its function is to receive a system notification when this object is recycled by the collector.
(2) In the method area:
We know that what is stored in the method area has been loaded by the virtual machine Class information, constants, static variables, code compiled by the just-in-time compiler and other data. So we perform garbage collection in the method area, recycling some abandoned constants and useless classes.
How to determine whether a constant is obsolete?
Just look at the reference count. If no object refers to the constant, it means that the constant has been abandoned and can be recycled.
How to determine whether a class is useless?
There are three situations:
a. All instances of this class have been recycled.
b. The ClassLoader that loaded this class has been recycled.
c. The java.lang.Class object corresponding to this class is not referenced anywhere, and the methods of this class cannot be accessed through reflection anywhere.
How to recycle?
There are 4 algorithms as theories:
• Mark-Sweep Algorithm
• Copy Algorithm
• Mark-Collation Algorithm
• Generational Collection Algorithm
There are 5 types of collectors as implementations:
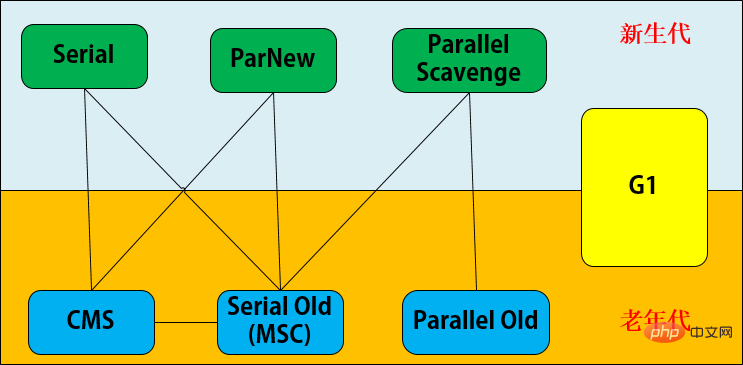
Postscript
Memory overflow: The system cannot allocate any more Take out the space you need. For example, no more memory can be allocated to new objects in the heap, and if the stack is full, new stack frames cannot be pushed onto the stack.
Memory leak: If the memory is occupied by an object and is not returned, it is called a memory leak.
The above is a detailed explanation of the garbage collection mechanism in JVM. For more related questions, please visit the PHP Chinese website: JAVA Video Tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (3) - Garbage collection mechanism. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 A distributed JVM monitoring tool, very practical!
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:15 PM
A distributed JVM monitoring tool, very practical!
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:15 PM
This project is designed to facilitate developers to monitor multiple remote host JVMs faster. If your project is Spring boot, it is very easy to integrate. Just introduce the jar package. If it is not Spring boot, don’t be discouraged. You can quickly initialize a Spring boot program and introduce it yourself. Jar package is enough
 JVM memory management key points and precautions
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:26 AM
JVM memory management key points and precautions
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:26 AM
Key points and precautions for mastering JVM memory usage JVM (JavaVirtualMachine) is the environment in which Java applications run, and the most important one is the memory management of the JVM. Properly managing JVM memory can not only improve application performance, but also avoid problems such as memory leaks and memory overflows. This article will introduce the key points and considerations of JVM memory usage and provide some specific code examples. JVM memory partitions JVM memory is mainly divided into the following areas: Heap (He
 Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
JVM command line parameters allow you to adjust JVM behavior at a fine-grained level. The common parameters include: Set the Java heap size (-Xms, -Xmx) Set the new generation size (-Xmn) Enable the parallel garbage collector (-XX:+UseParallelGC) Reduce the memory usage of the Survivor area (-XX:-ReduceSurvivorSetInMemory) Eliminate redundancy Eliminate garbage collection (-XX:-EliminateRedundantGCs) Print garbage collection information (-XX:+PrintGC) Use the G1 garbage collector (-XX:-UseG1GC) Set the maximum garbage collection pause time (-XX:MaxGCPau
 Java Error: JVM memory overflow error, how to deal with and avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
Java Error: JVM memory overflow error, how to deal with and avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
Java is a popular programming language. During the development of Java applications, you may encounter JVM memory overflow errors. This error usually causes the application to crash, affecting the user experience. This article will explore the causes of JVM memory overflow errors and how to deal with and avoid such errors. What is JVM memory overflow error? The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is the running environment for Java applications. In the JVM, memory is divided into multiple areas, including heap, method area, stack, etc. The heap is used to store created objects
 Analysis of the functions and principles of JVM virtual machine
Feb 22, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Analysis of the functions and principles of JVM virtual machine
Feb 22, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
An introduction to the analysis of the functions and principles of the JVM virtual machine: The JVM (JavaVirtualMachine) virtual machine is one of the core components of the Java programming language, and it is one of the biggest selling points of Java. The role of the JVM is to compile Java source code into bytecodes and be responsible for executing these bytecodes. This article will introduce the role of JVM and how it works, and provide some code examples to help readers understand better. Function: The main function of JVM is to solve the problem of portability of Java programs on different platforms.
 Demystifying the working principle of JVM: In-depth exploration of the principles of Java virtual machine
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:28 PM
Demystifying the working principle of JVM: In-depth exploration of the principles of Java virtual machine
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:28 PM
Detailed explanation of JVM principles: In-depth exploration of the working principle of the Java virtual machine requires specific code examples 1. Introduction With the rapid development and widespread application of the Java programming language, the Java Virtual Machine (JavaVirtualMachine, referred to as JVM) has also become indispensable in software development. a part of. As the running environment for Java programs, JVM can provide cross-platform features, allowing Java programs to run on different operating systems. In this article, we will delve into how the JVM works
 How to adjust JVM heap memory size efficiently?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
How to adjust JVM heap memory size efficiently?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
JVM memory parameter settings: How to reasonably adjust the heap memory size? In Java applications, the JVM is the key component responsible for managing memory. Among them, heap memory is used to store object instances. The size setting of heap memory has an important impact on the performance and stability of the application. This article will introduce how to reasonably adjust the heap memory size, with specific code examples. First, we need to understand some basic knowledge about JVM memory. The JVM's memory is divided into several areas, including heap memory, stack memory, method area, etc. in
 Java program to check if JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit
Sep 05, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Java program to check if JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit
Sep 05, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Before writing a java program to check whether the JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit, let us first discuss about the JVM. JVM is a java virtual machine, responsible for executing bytecode. It is part of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). We all know that java is platform independent, but JVM is platform dependent. We need separate JVM for each operating system. If we have the bytecode of any java source code, we can easily run it on any platform due to JVM. The entire process of java file execution is as follows - First, we save the java source code with .java extension and the compiler converts it into bytecode with .class extension. This happens at compile time. Now, at runtime, J



