 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of construction, packaging and publishing of Vue project
Detailed explanation of construction, packaging and publishing of Vue project
Detailed explanation of construction, packaging and publishing of Vue project
Many friends are not familiar with the series of processes of the VUE project. Based on the questions raised by netizens, the editor has sorted out the entire process of building, packaging and releasing the vue project. This article mainly introduces in detail the construction, packaging, and release of the vue.js project. The whole process of publishing, I hope it can help everyone.
1. Creation of vue project
1. First of all, Node.js and npm must be available. Not much to say
2. Install the scaffolding
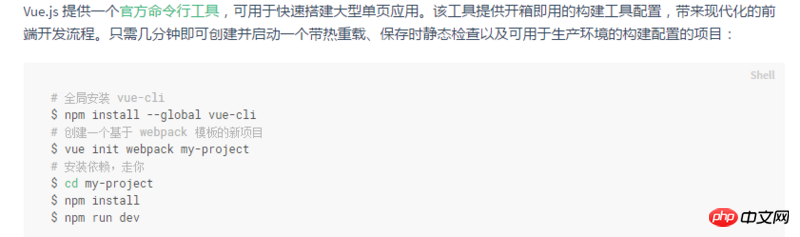
You can browse directly at this time - but now there must be many novices who want to publish it to gitHub and browse it, using vue Family Bucket makes its own blog. Now let me talk about how to publish the vue project to github. I wrote about the vue environment setup before. You can refer to: vue environment setup
2. Packaging of the vue project
1. Everyone knows that npm run build is used for packaging. At this time, if you directly open index.html under dist/, you will find that the file can be opened, but all js, css, img and other paths point to the root. Directory,
At this time, you need to modify the assetsPublicPath field in config/index.js. The initial project is /, which points to the project root directory, which is why an error occurs. At this time, it is changed to ./
./Current directory../Parent directory/Root directory
Root directory: In the computer file system, the root directory refers to the top-level directory of the logical drive, which is a relative subdirectory. In terms of directory;
It is like the "root" of a big tree. All branches start from it, so it is named the root directory. Take the Windows operating system developed by Microsoft as an example:
Open My Computer (Computer), double-click the C drive to enter the root directory of the C drive. Double-click the D drive to enter the root directory of the D drive
build: {
env: require('./prod.env'),
index: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist/index.html'),
assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist'),
assetsSubDirectory: 'static',
assetsPublicPath: './',
productionSourceMap: true,
// Gzip off by default as many popular static hosts such as
// Surge or Netlify already gzip all static assets for you.
// Before setting to `true`, make sure to:
// npm install --save-dev compression-webpack-plugin
productionGzip: false,
productionGzipExtensions: ['js', 'css'],
// Run the build command with an extra argument to
// View the bundle analyzer report after build finishes:
// `npm run build --report`
// Set to `true` or `false` to always turn it on or off
bundleAnalyzerReport: process.env.npm_config_report
}You can access it by opening the index file from the dist root directory.
3. github pages
1. Create a warehouse on the home page and ignore it directly
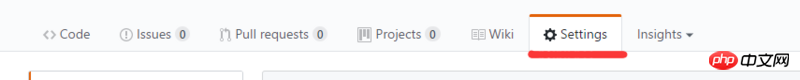
2. Select master or /doc here to upload the code to master
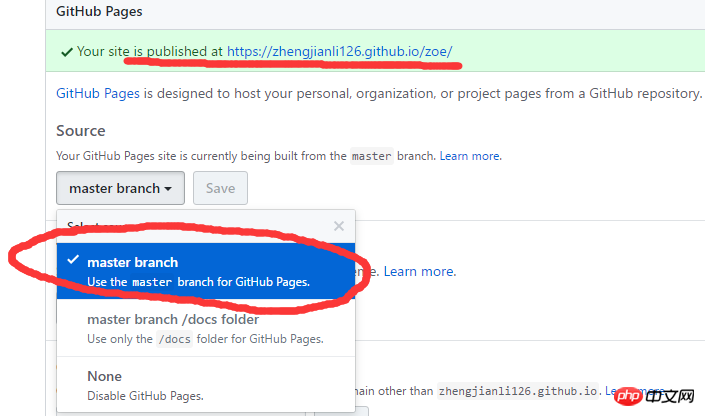
3. There is a line of domain name above which is your own page where you can see the projects you published
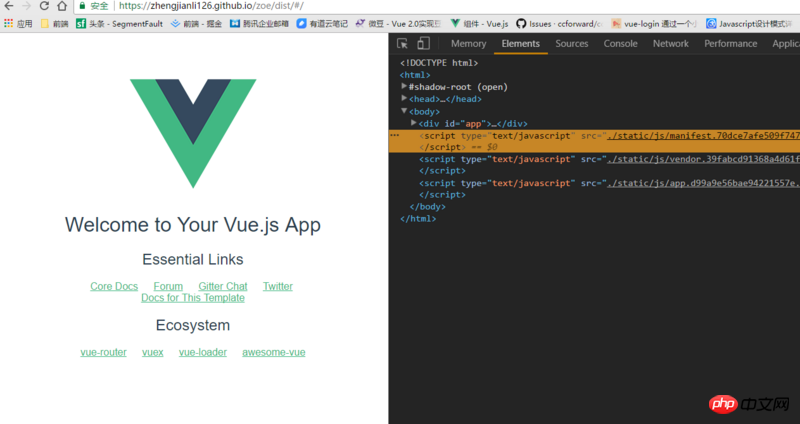
4. Custom domain name
1. You can browse your own projects at this time, but
username.github.io/xxx/dist
Such an address is really not very beautiful. You can go to Alibaba Cloud, buy a domain name yourself, and parse it. It is available online and can be customized. Use the domain name to create your own blog, and deploy the code to github.
Related recommendations:
How to create a new vue project
How to optimize the Vue project
vue project construction and practical example tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of construction, packaging and publishing of Vue project. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1657
1657
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1230
1230
 24
24
 Why can't Xiaohongshu publish videos of works? How does it publish its work?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Why can't Xiaohongshu publish videos of works? How does it publish its work?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
With the rapid development of social media, short video platforms have become the main channel for many users to express themselves and share their lives. Many users may encounter various problems when publishing videos of their works on Xiaohongshu. This article will discuss the reasons that may cause the video publishing of Xiaohongshu works to fail and provide the correct publishing method. 1. Why can’t Xiaohongshu publish videos of works? The Xiaohongshu platform may occasionally experience system failures, which may be caused by system maintenance or upgrades. In this case, users may encounter the problem of being unable to publish videos of their works. Users need to wait patiently for the platform to return to normal before trying to publish. An unstable or slow network connection may prevent users from posting videos of their work on Xiaohongshu. Users should confirm their network environment to ensure that the connection is stable and
 How to publish works on Xiaohongshu How to publish articles and pictures on Xiaohongshu
Mar 22, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
How to publish works on Xiaohongshu How to publish articles and pictures on Xiaohongshu
Mar 22, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
You can view various contents on Xiaohongshu, which can provide you with various help and help you discover a better life. If you have anything you want to share, you can post it here so that everyone can take a look. , and at the same time, it can bring you profits. It is very cost-effective. If you don’t know how to publish your works here, you can check out the tutorial. You can use this software every day and publish various contents to help everyone use it better. Don’t miss it if you need it! 1. Open Xiaohongshu and click the plus icon below. 2. There are [Video] [Picture] [Live Picture] options here; select the content you want to publish and click to check. 3. Select [Next] on the content editing page. 4. Enter the text content you want to publish and click [Publish Pen]
 Why can't Xiaohongshu be released? What should I do if the content published by Xiaohongshu cannot be displayed?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 07:47 PM
Why can't Xiaohongshu be released? What should I do if the content published by Xiaohongshu cannot be displayed?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 07:47 PM
As a lifestyle sharing platform, Xiaohongshu has attracted a large number of users to share their daily life and grow products. Many users have reported that their published content cannot be displayed. What is going on? This article will analyze the possible reasons why Xiaohongshu cannot be released and provide solutions. 1. Why can’t Xiaohongshu be released? Xiaohongshu implements strict community guidelines and has zero tolerance for publishing advertisements, spam, vulgar content, etc. If the user's content violates the regulations, the system will block it and the content will not be displayed. Xiaohongshu requires users to publish high-quality and valuable content, and the content needs to be unique and innovative. If the content is too generic and lacks innovation, it may not pass review and therefore not be displayed on the platform. 3. Account abnormality
 When is the best time to publish Xiaohongshu? Where does it post the most traffic recommendations from?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
When is the best time to publish Xiaohongshu? Where does it post the most traffic recommendations from?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
In today's social network era, Xiaohongshu has become an important platform for young people to share their lives and obtain information. Many users hope to attract more attention and traffic by publishing content on Xiaohongshu. So, when is the best time to post content? This article will explore in detail the selection of Xiaohongshu’s publishing time and the publishing location with the most traffic recommendations. 1. When is the best time to publish Xiaohongshu? The best time to publish content on Xiaohongshu is usually during periods of high user activity. According to the characteristics and behavioral habits of Xiaohongshu users, there are several time periods that are more appropriate. During the time period from 7 pm to 9 pm, most users have returned home from get off work and started browsing content on their mobile phones in search of relaxation and entertainment. Therefore, content posted during this period is more likely to attract users
 How to publish Xiaohongshu video works? What should I pay attention to when posting videos?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
How to publish Xiaohongshu video works? What should I pay attention to when posting videos?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
With the rise of short video platforms, Xiaohongshu has become a platform for many people to share their lives, express themselves, and gain traffic. On this platform, publishing video works is a very popular way of interaction. So, how to publish Xiaohongshu video works? 1. How to publish Xiaohongshu video works? First, make sure you have a video content ready to share. You can use your mobile phone or other camera equipment to shoot, but you need to pay attention to the image quality and sound clarity. 2. Edit the video: In order to make the work more attractive, you can edit the video. You can use professional video editing software, such as Douyin, Kuaishou, etc., to add filters, music, subtitles and other elements. 3. Choose a cover: The cover is the key to attracting users to click. Choose a clear and interesting picture as the cover to attract users to click on it.
 How to delete Xiaohongshu releases? How to recover after deletion?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:10 PM
How to delete Xiaohongshu releases? How to recover after deletion?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:10 PM
As a popular social e-commerce platform, Xiaohongshu has attracted a large number of users to share their daily life and shopping experiences. Sometimes we may inadvertently publish some inappropriate content, which needs to be deleted in time to better maintain our personal image or comply with platform regulations. 1. How to delete Xiaohongshu releases? 1. Log in to your Xiaohongshu account and enter your personal homepage. 2. At the bottom of the personal homepage, find the "My Creations" option and click to enter. 3. On the "My Creations" page, you can see all published content, including notes, videos, etc. 4. Find the content that needs to be deleted and click the "..." button on the right. 5. In the pop-up menu, select the "Delete" option. 6. After confirming the deletion, the content will disappear from your personal homepage and public page.
 How to publish works on Xiaohongshu app? Tutorial on publishing works on Xiaohongshu app in five minutes
Mar 12, 2024 pm 05:10 PM
How to publish works on Xiaohongshu app? Tutorial on publishing works on Xiaohongshu app in five minutes
Mar 12, 2024 pm 05:10 PM
How does the Xiaohongshu app publish works? Many friends know that there are a large number of creative works and a strong dating circle in this software. For users who are new to this software, they probably don’t know how to publish their works, so that more people can watch the other side of you. If you still don’t know how to publish the works in it, then quickly refer to the five-minute tutorial on publishing works on the Xiaohongshu app recommended by the editor of this site. Tutorial on publishing works in Xiaohongshu app in five minutes 1. Click [Three] As shown in the picture, click [Three] pointed by the red arrow in the upper left corner. 2. Click [Creation Center] As shown in the picture, click [Creation Center] pointed by the red arrow. 3. Click [Go to Publish] as shown in the picture,
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer



