
This time I will show you how to handle the failure of ajax access to Session, and what are the precautions for handling the failure of ajax access to Session. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Recently due to a project, the module switched to ajax request data. When the Session failed, there was no return value after the ajax request, only the response html: Ajax is now widely used in Web projects, almost everywhere, which brings another question: What should you do when an Ajax request encounters a Session timeout? Obviously, the traditional page jump is no longer applicable here, because the Ajax request is initiated by the XMLHTTPRequest object rather than the browser. The page jump after the verification fails cannot be reflected in the browser because the server returns (or output) information is received by JavaScript (XMLHTTPRequest object). So how should we deal with this situation?Method
Since the message returned by the server is received by the XMLHTTPRequest object, and the XMLHTTPRequest object is under the control of JavaScript, then do we Can JavaScript be used to complete page jumps? Of course you can, and it’s easy to do! But one thing is that we need to determine whether the HTTP request is an Ajax request (because AJAX requests and ordinary requests need to be processed separately), how to determine this? In fact, Ajax requests are different from ordinary HTTP requests, which is reflected in the header information of the HTTP request, as shown below: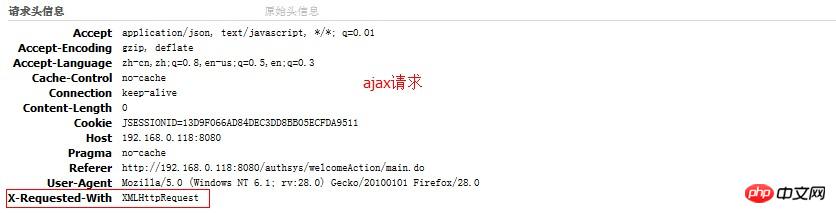
InterceptorFilter
When using Struts2, we generally use Interceptor (interceptor) to intercept permission issues.Part of the interceptor code:
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ActionContext ac = invocation.getInvocationContext();
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) ac.get(StrutsStatics.HTTP_REQUEST);
String requestType = request.getHeader("X-Requested-With");
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++reqestType:"+requestType);
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) ac.get(StrutsStatics.HTTP_RESPONSE);
// String basePath = request.getContextPath();
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path;
//获取session
Map session = ac.getSession();
//判断session是否存在及session中的user信息是否存在,如果存在不用拦截
if(session != null && session.get(Constants.FE_SESSION_BG_USER) != null && session.get(Constants.FE_SESSION_BG_AUTH) != null){
System.out.println(invocation.getProxy().getActionName()+"++++++++++++++++++++++++");
System.out.println("namespace:"+invocation.getProxy().getNamespace());
//访问路径
String visitURL = invocation.getProxy().getNamespace() + "/" + invocation.getProxy().getActionName() + Constants.FE_STRUTS_ACTION_EXTENSION;
visitURL = visitURL.substring(1);
Map<String , Object> authMap = (Map<String, Object>) session.get(Constants.FE_SESSION_BG_AUTH);
Map<Integer, String> actionMap = (Map<Integer, String>) authMap.get(Constants.FE_BG_ACTIONMAP);
if(actionMap != null && !actionMap.isEmpty() && visitURL != null){
if (actionMap.containsValue(visitURL)) {
System.out.println(visitURL+"-----------------------");
return invocation.invoke();
} else{
String forbidden = basePath + Constants.FE_BG_FORBIDDEN;
response.sendRedirect(forbidden);
return null;
}
}
return invocation.invoke();
}else{
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(requestType) && requestType.equalsIgnoreCase("XMLHttpRequest")){
response.setHeader("sessionstatus", "timeout");
response.sendError(518, "session timeout.");
return null;
}else {
String actionName = invocation.getProxy().getActionName();
System.out.println(actionName);
//如果拦截的actionName是loginUI或login,则不做处理,否则重定向到登录页面
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(actionName) && actionName.equals(Constants.FE_BG_LOGINUI)) {
return invocation.invoke();
}else if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(actionName) && actionName.equals(Constants.FE_BG_LOGIN)){
return invocation.invoke();
}else{
String login = basePath + "/" + Constants.FE_BG_LOGIN_NAMESPACE + "/" + Constants.FE_BG_LOGINUI + Constants.FE_STRUTS_ACTION_EXTENSION;
// System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++basePath:"+basePath);
// response.sendRedirect(login);
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
// out.println("<html>");
// out.println("<script>");
// out.println("window.open ('"+login+"','_top');");
// out.println("</script>");
// out.println("</html>");
out.write("<html><script type='text/javascript'>window.open('"+login+"','_top');</script></html>");
return null;
}
}
}
}Javascript code
$.ajaxSetup method is used to set the default options for AJAX requests. We can think of it as a global option setting, so it can Add this code to an external JS file and reference it on the required page./**
* 设置未来(全局)的AJAX请求默认选项
* 主要设置了AJAX请求遇到Session过期的情况
*/
$.ajaxSetup({
type: 'POST',
complete: function(xhr,status) {
var sessionStatus = xhr.getResponseHeader('sessionstatus');
if(sessionStatus == 'timeout') {
var top = getTopWinow();
var yes = confirm('由于您长时间没有操作, session已过期, 请重新登录.');
if (yes) {
top.location.href = '/skynk/index.html';
}
}
}
});
/**
* 在页面中任何嵌套层次的窗口中获取顶层窗口
* @return 当前页面的顶层窗口对象
*/
function getTopWinow(){
var p = window;
while(p != p.parent){
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}Ajax implements the function of file upload with progress bar effect
How to use the Rating control in AjaxToolKit
The above is the detailed content of How to handle session failure when ajax accesses it. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




