
This article mainly introduces the principle of Ajax cross-domain requests in detail. How does Ajax make cross-domain requests? It has a certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
The example in this article shares the specific implementation process of Ajax cross-domain request for your reference. The specific content is as follows
below Let's build two sites locally to demonstrate
The first step is to first build an Apache server locally; download address;
The second step is to configure two virtual servers locally after the server is configured. Domain name;
The third step is to create a folder on the C drive and name it "HTML5";
The fourth step is to find the configuration file of the Apache virtual host, and then open the configuration file
The fifth step is to create a folder a and a folder b respectively under the HTML5 folder created in the third step;
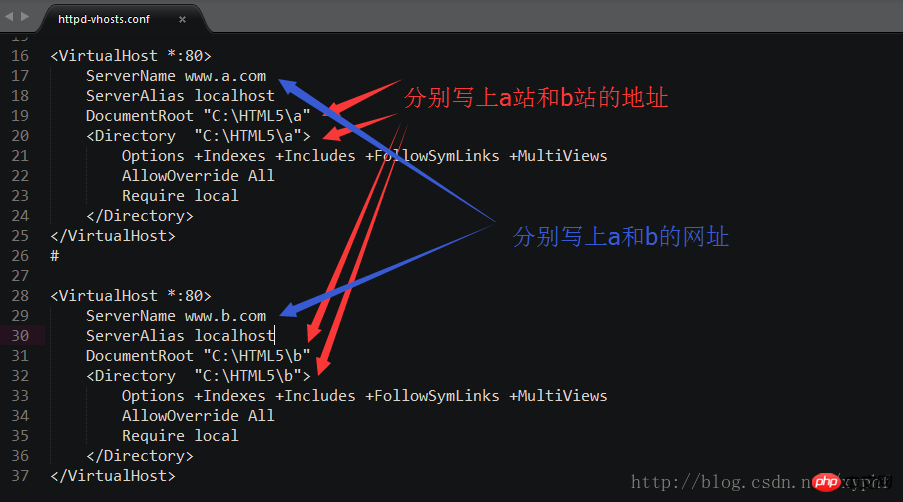
The sixth step is to modify the configuration file of the Apache virtual host, as shown in the figure
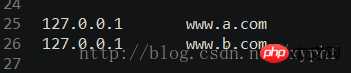
The seventh step is to modify the host file and add the URLs of a and b. Usually the host file path is under C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
We create a 7.ajax.html file under the HTML5/a folder
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>获取同域下内容</title>
<script>
window.onload = function() {
var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn');
// 忽略IE6
oBtn.onclick = function() {
//创建一个ajax对象
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//监听事件
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState == 4) {
if (xhr.status == 200) {
alert(xhr.responseText);
}
}
}
xhr.open('get', 'The principle of Ajax cross-domain request (graphic tutorial)', true);
xhr.send();
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="获取同域下内容" id="btn" />
</body>
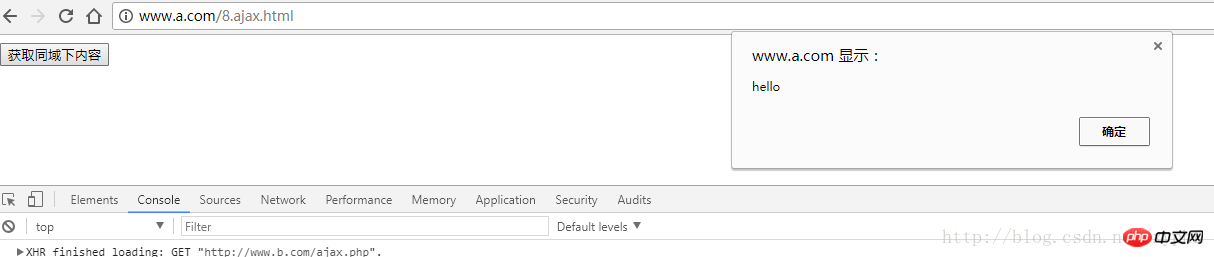
</html>Let’s first look at the requests in the same domain
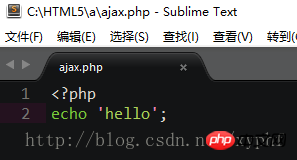
We create a php file under HTML5/a and return 'hello';
At this time we are opening the current pagehttp://www.a.com /7.ajax.html , click the button and we find that the data is requested;
The principle of Ajax cross-domain request (graphic tutorial)
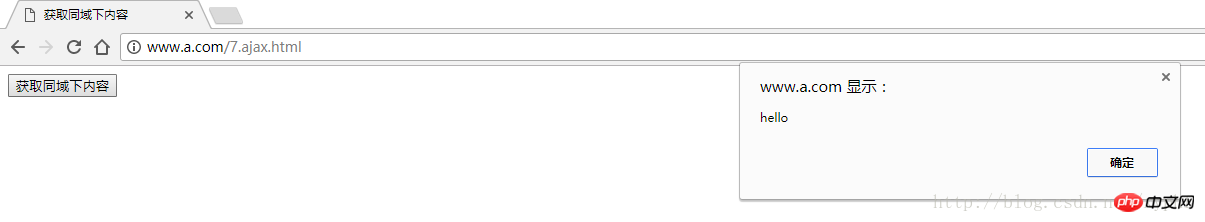
But if it is cross-domain, that is, the data you request and the current file are not under the same domain, then a cross-domain request will occur, and usually in this case you will be prohibited from accessing
For example, we now put the The principle of Ajax cross-domain request (graphic tutorial) file just in the HTML5/a folder into the b folder
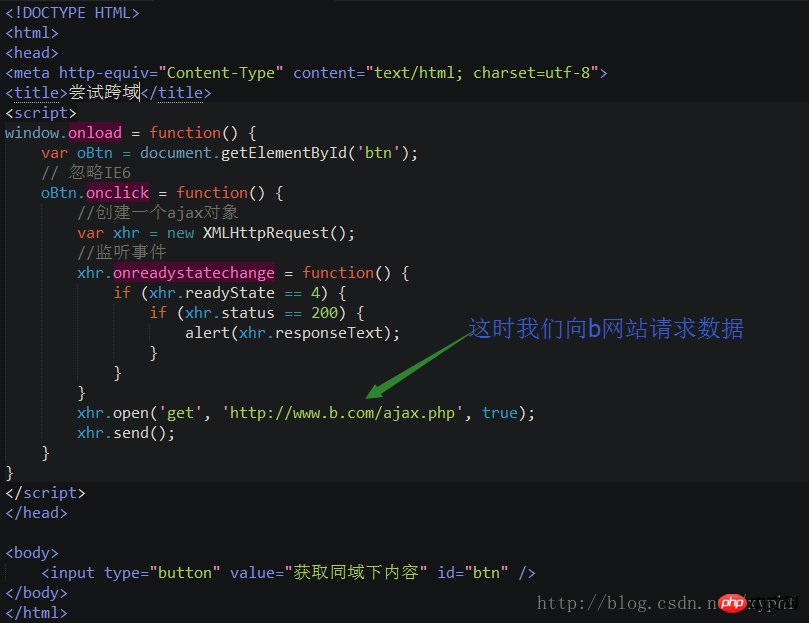
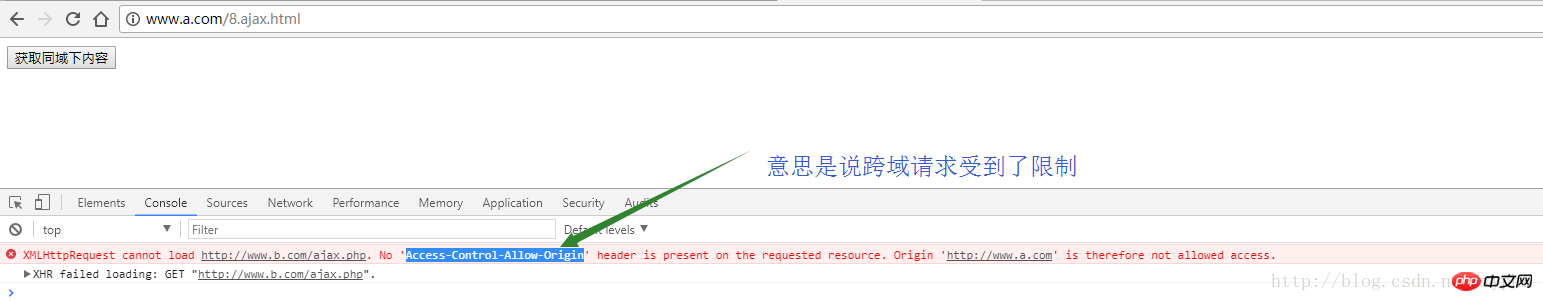
After clicking this time, we found that the request reported an error , which means that cross-domain requests are restricted
At this time we need the backend to cooperate. You need to tell the backend to add "Access-Control-Allow" when outputting -Origin” header information
For example: As shown in the figure, it means that as long as the cross-domain request of this domain name is not affected by the cross-domain policy
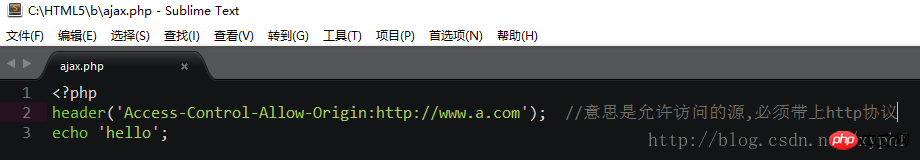
At this time I click , you can obtain cross-domain data normally
If you want to be compatible with IE, you need to
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>ajax跨域请求</title>
<script>
window.onload = function() {
/*
在标准浏览器下,XMLHttpRequest对象已经是升级版本,支持了更多的特性,可以跨域了
但是,如果想实现跨域请求,还需要后端的相关配合才可以
XMLHttpRequest : 增加很多功能,他也不推荐使用onreadystatechange这个事件来监听,推荐使用onload
*/
var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn');
oBtn.onclick = function() {
// 这是标准浏览器写法
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState == 4) {
if (xhr.status == 200) {
alert(xhr.responseText);
}
}
}
xhr.open('get', 'http://www.b.com/The principle of Ajax cross-domain request (graphic tutorial)', true);
xhr.send();
/*
如果你想兼容IE浏览器,可以特地为IE做兼容,忽略IE6
XDomainRequest : IE如果想实现跨域请求,则需要使用这个对象去实现
var oXDomainRequest = new XDomainRequest();
oXDomainRequest.onload = function() {
alert(this.responseText);
}
oXDomainRequest.open('get', 'http://www.b.com/The principle of Ajax cross-domain request (graphic tutorial)', true);
oXDomainRequest.send();
*/
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="获取同域下内容" id="btn" />
</body>
</html>The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope that in the future It will be helpful to everyone.
Related articles:
Detailed explanation of the use of AJAX request queue
jQuery ajaxUse the get() function to read Detailed explanation of page steps
ajaxDetailed explanation of steps to read properties
The above is the detailed content of The principle of Ajax cross-domain request (graphic tutorial). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




