
This time I will bring you JavaScript Detailed explanation of the steps to implement regular verification of ID number with Regex. What are the precautions for using JavaScript Regex to implement regular verification of ID number. Here is the actual combat Let’s take a look at the case.

ID card number description
Resident ID card number, the correct and formal title should be "citizen identity number". According to the regulations on citizen identity numbers in [National Standard of the People's Republic of China GB 11643-1999], the citizen identity number is a characteristic combination code, consisting of a seventeen-digit body code and a one-digit check code. The order from left to right is: six-digit address code, eight-digit date of birth code, three-digit sequence code and one-digit check code.
Take the ID number of a woman in Chaoyang District, Beijing as an example. The meaning of the ID number is as shown below:
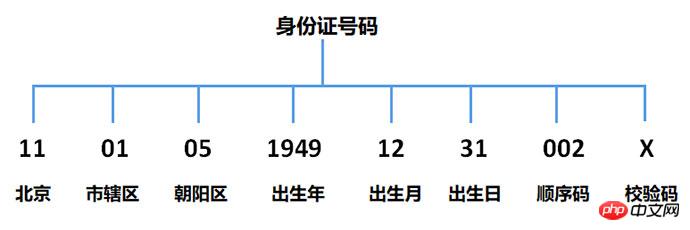
Note: This identity The certificate number comes from the national standard [GB 11643-1999].
Next we will complete a complete ID number verification process from scratch.
Option 1 (simple)
1.1 Division rules
1.1.1 Address code Rules: The address code is 6 digits long
Starts with numbers 1-9
The last 5 digits are numbers 0-9
According to the above rules, write the regular pattern of the address code Expression : /^[1-9]\d{5}/
1.1.2 Year code rules: The year code is 4 digits long
Start with the number 18, 19 or 20
The remaining two digits are 0-9
According to the above rules, write the regular expression of the year code: /(18|19| 20)\d{2}/. If you don't need a year starting with 18, you can remove 18.
1.1.3 Month code rules:
The month code is 2 digits long
The first digit is 0, the second digit is 1-9
or One digit is 1, and the second digit is 0-2
According to the above rules, write the regular expression of the month code: /((0[1-9])|(1[ 0-2]))/.
1.1.4 Date code rules:
The date code is 2 digits long
The first digit is 0-2, the second digit is 1-9
Or 10, 20, 30, 31
According to the above rules, write the regular expression of the date code: /(([0-2][1-9])|10|20| 30|31)/.
1.1.5 Sequential code rules:
The sequence code is 3 digits long
The sequence code is a number
According to the above rules, write the regular code of the sequence code Expression: /\d{3}/.
1.1.6 Check code rules:
The check code is 1 digit long
can be a number, the letter x or the letter X
According to the above rules, Write the regular expression of the check code: /[0-9Xx]/.
1.2 Option 1 Regular Expression
Based on the above 6 rules, the complete regular expression and test program are given as follows:
var p = /^[1-9]\d{5}(18|19|20)\d{2}((0[1-9])|(1[0-2]))(([0-2][1-9])|10|20|30|31)\d{3}[0-9Xx]$/;
//输出 true
console.log(p.test("11010519491231002X"));
//输出 false 不能以0开头
console.log(p.test("01010519491231002X"));
//输出 false 年份不能以17开头
console.log(p.test("11010517491231002X"));
//输出 false 月份不能为13
console.log(p.test("11010519491331002X"));
//输出 false 日期不能为32
console.log(p.test("11010519491232002X"));
//输出 false 不能以a结尾
console.log(p.test("11010519491232002a"));1.3 Analysis of Option 1
Option 1 only makes basic format determination, and there are three main shortcomings:
The address code determination is not accurate enough. For example: There are no areas starting with 16 or 26 in our country, but it can be determined by verifying the date that it is not accurate enough. Example: 19490231 can also pass the verification, but there is no 31-day check code in February. It is calculated from the 17-bit ontology code. Scheme 1 does not verify this code. Scheme 2 (Comprehensive)
Based on the shortcomings of Scheme 1 , introduce Scheme 2 to improve the shortcomings of Scheme 1.
2.1 Provincial address code verification
North China: Beijing 11, Tianjin 12, Hebei 13, Shanxi 14, Inner Mongolia 15
Northeast: Liaoning 21, Jilin 22, Heilongjiang 23
East China: Shanghai 31, Jiangsu 32, Zhejiang 33, Anhui 34, Fujian 35, Jiangxi 36, Shandong 37
Central China: Henan 41, Hubei 42, Hunan 43
South China: Guangdong 44, Guangxi 45, Hainan 46
Southwest: Sichuan 51, Guizhou 52, Yunnan 53, Tibet 54, Chongqing 50
Northwest: Shaanxi 61, Gansu 62, Qinghai 63, Ningxia 64, Xinjiang 65
Special: Taiwan 71 , Hong Kong 81, Macau 82
根据上述地址码做身份证号码的前两位校验,进一步的提高准确率。当前的地址码以2013版的行政区划代码【GB/T2260】为标准。由于区划代码的历史演变,使得地址码后四位校验变得不太可能。以三胖的身份证号为例,本人号码是2321开头,而当前行政区划代码表中并无此代码。因此本文只做前两位省级地址码的校验。
也有说法表述91开头是外国人取得中国身份证号码的前两位编码,但本人并未得到证实。如有持91开头身份证或认识马布里的,请帮忙确认相关信息。
根据以上分析,给出省级地址码校验及测试程序如下:
var checkProv = function (val) {
var pattern = /^[1-9][0-9]/;
var provs = {11:"北京",12:"天津",13:"河北",14:"山西",15:"内蒙古",21:"辽宁",22:"吉林",23:"黑龙江 ",31:"上海",32:"江苏",33:"浙江",34:"安徽",35:"福建",36:"江西",37:"山东",41:"河南",42:"湖北 ",43:"湖南",44:"广东",45:"广西",46:"海南",50:"重庆",51:"四川",52:"贵州",53:"云南",54:"西藏 ",61:"陕西",62:"甘肃",63:"青海",64:"宁夏",65:"新疆",71:"台湾",81:"香港",82:"澳门"};
if(pattern.test(val)) {
if(provs[val]) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//输出 true,37是山东
console.log(checkProv(37));
//输出 false,16不存在
console.log(checkProv(16));2.2 出生日期码校验
出生日期码的校验不做解释,直接给出如下函数及测试程序:
var checkDate = function (val) {
var pattern = /^(18|19|20)\d{2}((0[1-9])|(1[0-2]))(([0-2][1-9])|10|20|30|31)$/;
if(pattern.test(val)) {
var year = val.substring(0, 4);
var month = val.substring(4, 6);
var date = val.substring(6, 8);
var date2 = new Date(year+"-"+month+"-"+date);
if(date2 && date2.getMonth() == (parseInt(month) - 1)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//输出 true
console.log(checkDate("20180212"));
//输出 false 2月没有31日
console.log(checkDate("20180231"));2.3 校验码校验
校验码的计算略复杂,先给出如下公式:
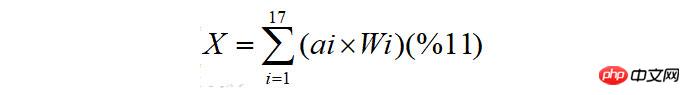
其中 ai 表示身份证本体码的第 i 位值,而 Wi 表示第 i 位的加权因子值。
加权因子表 【表1】:
| i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi | 7 | 9 | 10 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 6 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 2 |
X与校验码换算表 【表2】
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a18 | 1 | 0 | X | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
算法过程:
根据身份证主体码(前17位)分别与对应的加权因子(表1)计算乘积再求和,根据所得结果与11取模得到X值。
根据 X 值查询表2,得出a18即校验码值。
校验码计算程序及测试见如下代码:
var checkCode = function (val) {
var p = /^[1-9]\d{5}(18|19|20)\d{2}((0[1-9])|(1[0-2]))(([0-2][1-9])|10|20|30|31)\d{3}[0-9Xx]$/;
var factor = [ 7, 9, 10, 5, 8, 4, 2, 1, 6, 3, 7, 9, 10, 5, 8, 4, 2 ];
var parity = [ 1, 0, 'X', 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2 ];
var code = val.substring(17);
if(p.test(val)) {
var sum = 0;
for(var i=0;i<p style="text-align: left;"><strong>2.4 方案2整体代码</strong></p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">var checkID = function (val) {
if(checkCode(val)) {
var date = val.substring(6,14);
if(checkDate(date)) {
if(checkProv(val.substring(0,2))) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//输出 true
console.log(checkID("11010519491231002X"));
//输出 false,校验码不符
console.log(checkID("110105194912310021"));
//输出 false,日期码不符
console.log(checkID("110105194902310026"));
//输出 false,地区码不符
console.log(checkID("160105194912310029"));相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the steps for regular verification of ID number using JavaScript+Regex. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




