
This article mainly introduces the application scenarios of Vue's built-in component components. Now I will share it with you and give you a reference.
Official instructions
Render a "meta component" as a dynamic component. Which component is rendered depends on the value of is.
<!-- 动态组件由 vm 实例的属性值 `componentId` 控制 --> <component :is="componentId"></component>
For details, please refer to the official website documentation
Dynamic components
Built-in component component
Scenario
Here is a business scenario to illustrate the application of Vue's built-in component components. As shown in the figure, the classic registration page is shown here. Registration is divided into email registration and mobile phone registration. There is a label at the top of the pop-up window to switch the registration type. In the middle is the registration form information. Email registration and mobile phone registration have different form contents. The bottom is Register button and other actions. After analysis, the mobile phone registration interface and the email registration interface are the same except for the inconsistent content of the form in the middle.
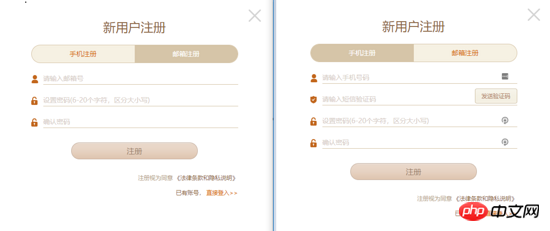
#In actual project code design, there are some feasible solutions to ensure reusability and maintainability. Here we use vue's built-in component component to achieve this.
Core code implementation
When the top tab is switched, the type value changes, and the corresponding form components also change
<template>
<p>
<a href="javascript:;" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" @click.prevent="handleCloseBtnClick"></a>
<p>
<h3>新用户注册</h3>
<p>
<span :class="{active: type === 'mobileForm'}" @click="type = mobileForm">手机注册</span>
<span :class="{active: type === 'emailForm'}" @click="type = emailForm">邮箱注册</span>
</p>
</p>
<component :is="type" ref="form">
<button @click="handleRegisterBtnClick">注册</button>
<p ><span ><span>注册视为同意</span><a> 《法律条款和隐私说明》</a></span></p>
<p><span>已有账号<a href="javascript:;" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" @click.prevent="handleLoginBtnClick">直接登入>></a></span></p>
</component>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
handleRegisterBtnClick () {
this.$refs.form.validateData().then(() => {
this.$refs.form.getFormData()
})
}
}
}
</script>mixins mixing
When using Vue’s built-in component components, generally the components that are actually rendered have certain commonalities, such as the same attributes, the same method or the same initialization and destruction process. For example, in the current scenario, both the email form and the mobile phone form have a verification method (validateData) and a method for obtaining form data (getFormData). In this case, you can use the mixing function provided by vue. Further abstraction mixins.js
export default {
methods: {
validateData() {
return Promise.resolve()
},
getFormData() {
return {}
}
}
}email-form.vue
<script>
import minx from './mixins'
export default {
mixins: [mixins],
methods: {
getFormData() {
return { email: 'example@example.com' }
}
}
}
</script>If you have custom requirements, you can override the methods in mixins.
Application of tables
In management background projects, tables are often used. We hope that the td of the table is text, progress bar, checkbox, etc., and we hope that it can be rendered by passing a json configuration. Using vue's built-in component component can play a great role.
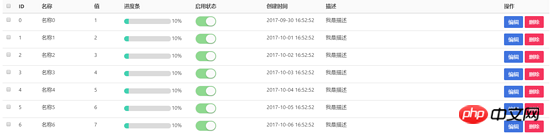
For example, how to use a table like this
<template>
<vue-table ref="table" :columns="columns" :datum="datum"></vue-table>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
columns: [
{ title: 'ID', width: '30', dataKey: 'id' },
{ title: '进度组件', dataKey: 'progress', render: { type: 'progress2', max: 100, precision: 2 } }
],
datum: [{ id: '1', name: '进度0', progress: 10 }]
}
}
}
</script>The implementation of using component in table
<td v-for="column of columns">
<component :is="`${TYPE_PRE}${columns.render.type}`" :row-data="rowData" :params="columns.render"></component>
</td>Application of forms
In management background projects, forms are often used. We also hope that one of the items in the form is a text box, a drop-down box, and a time selection. Box, rich text, etc., and hope that it can be rendered by passing a json configuration. Vue's built-in component component can still realize such a beautiful vision.
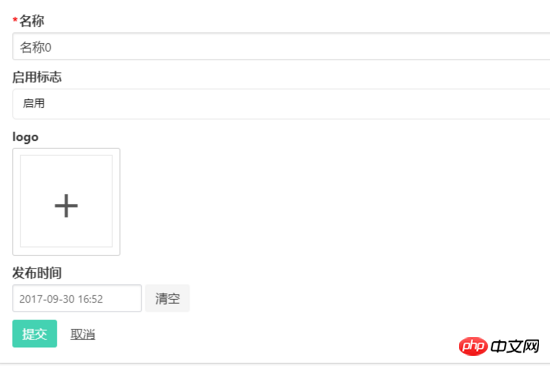
For example, how to use a form like this
<template>
<c-form :cells="cells" ref="form">
<button class="button is-primary" :class="{ 'is-disabled': isSubmitBtnDisabled }" @click.prevent="submit">提交</button>
</c-form>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed: {
cells () {
return [
{
field: 'name',
label: '名称',
type: 'textfield',
attrs: { placeholder: '名称' },
validate: { required: { message: '请输入名称'} }
},
{
field: 'enable',
label: '启用标志',
type: 'dropdown',
extra: {options: [{ label: '启用', value: 1 }, { label: '禁用', value: 2 }] }
}
]
}
}
}
</script>The implementation of using component in form
<form>
<c-form-cell v-for="cell of cellList" :key="cell.field" :field="cell.field">
<component
:is="`${TYPE_PRE}${cell.type}`"
:field="cell.field"
:attrs="cell.attrs"
:extra="cell.extra"
:validate="cell.validate"
:cells="cell.cells">
</component>
</c-form-cell>
</form>The above is I compiled it for everyone, I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
Related articles:
How to implement ASP.NET and Ajax
Ajax asynchronous upload in jquery
Detailed explanation of ajax synchronization and asynchronousness in jquery
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion on the application scenarios of Vue's built-in component components. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Vue parent component calls the method of child component
Vue parent component calls the method of child component
 Introduction to laravel components
Introduction to laravel components
 The role of vulkan
The role of vulkan
 How to use hover in css
How to use hover in css
 What are the basic data types in php
What are the basic data types in php
 The relationship between js and vue
The relationship between js and vue
 Mobile phone root
Mobile phone root
 Ranking of the top ten digital currency exchanges
Ranking of the top ten digital currency exchanges
 How to download and save today's headline videos
How to download and save today's headline videos




