What is recursion? Detailed explanation of recursion in javascript
This article brings you what is recursion? The detailed explanation of recursion in JavaScript has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
1. What is recursion?
The concept of recursion is very simple, "call yourself" (take a function as an example below).
Before analyzing recursion, you need to understand the concept of "call stack" in JavaScript.
2. Pushing and popping the stack
What is the stack? It can be understood that it is a certain area in the memory. This area is likened to a box. If you put something into the box, this action is pushing the stack. So the first thing to put down is at the bottom of the box, and the last thing to put down is at the top of the box. Taking something out of the box can be understood as *pushing it out of the stack.
So we come to the conclusion that we have a habit of taking things from top to bottom. The first thing to put down is at the bottom of the box, and the last thing to get is.
In JavaScript, when a function is called, stack pushing occurs. Pop occurs only when a sentence containing the return keyword is encountered or execution ends.
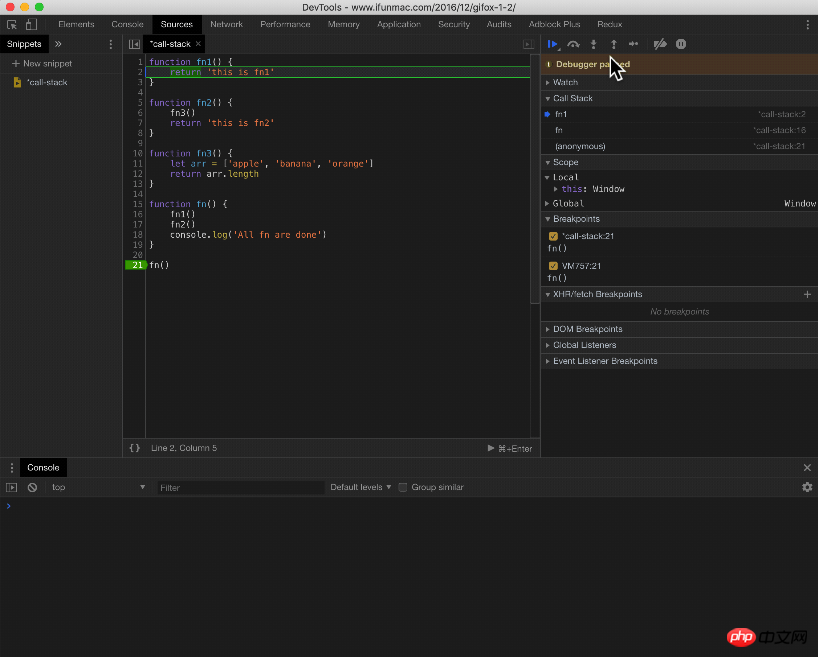
Let’s take an example. What is the execution order of this code?
function fn1() {
return 'this is fn1'
}
function fn2() {
fn3()
return 'this is fn2'
}
function fn3() {
let arr = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
return arr.length
}
function fn() {
fn1()
fn2()
console.log('All fn are done')
}
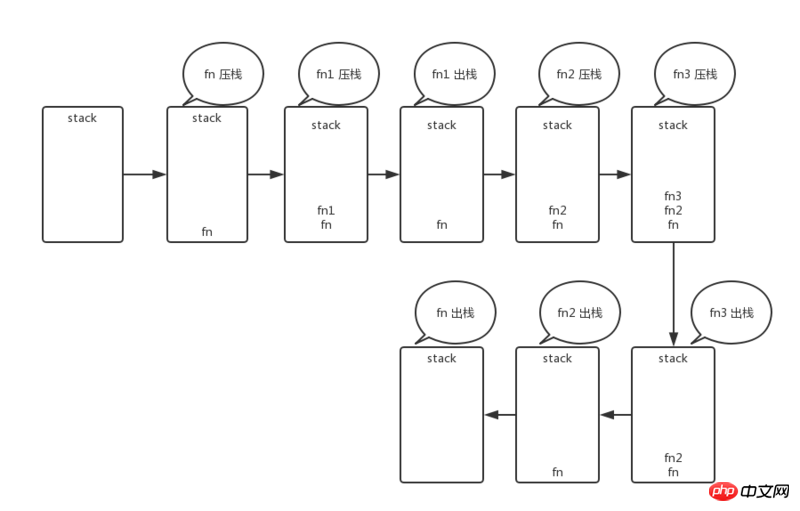
fn()A series of stack pushing and popping behaviors occurred above:
1. First, the stack (box) is empty at the beginning
2. Function fn is executed, fn is pushed onto the stack first and placed at the bottom of the stack (box)
3. Inside function fn, function fn1 is executed first, and fn1 is pushed onto the stack above fn
4. Function fn1 is executed, and when Go to the return keyword, return this is fn1, fn1 is popped off the stack, and now only fn
5 is left in the box. Return to the inside of fn, after fn1 is executed, function fn2 starts to execute, and fn2 is pushed onto the stack, but after Inside fn2, when fn3 is encountered, fn3 starts to be executed, so fn3 is pushed onto the stack
6. At this time, the order from bottom to top in the stack is: fn3
7. By analogy, when a sentence with the return keyword is encountered inside function fn3, fn3 pops out of the stack after execution and returns to function fn2. fn2 also encounters the return keyword and continues to pop out of the stack.
8. Now there is only fn in the stack. Return to the function fn. After executing the console.log('All fn are done') statement, fn pops out of the stack.
9. Now the stack is empty again.
The above steps are easy to confuse people. Here is the flow chart:
Let’s look at the execution in the chrome browser environment:
3. Recursion
Let’s first look at simple JavaScript recursion
function sumRange(num) {
if (num === 1) return 1;
return num + sumRange(num - 1)
}
sumRange(3) // 6The above code execution sequence:
1. Function sumRange(3) is executed, sumRange(3) is pushed onto the stack, and the return keyword is encountered, but it cannot be popped out of the stack immediately because the call SumRange(num - 1) is sumRange(2)
2. Therefore, sumRange(2) is pushed onto the stack, and so on, sumRange(1) is pushed onto the stack,
3. Finally, sumRange(1) pops the stack and returns 1, sumRange(2) pops the stack, returns 2, sumRange(3) pops the stack
4, so the result of 3 2 1 is 6
Look at the flow chart

So, recursion is also a process of pushing and popping the stack.
Recursion can be expressed as non-recursive. The following is the equivalent execution of the above recursive example
// for 循环
function multiple(num) {
let total = 1;
for (let i = num; i > 1; i--) {
total *= i
}
return total
}
multiple(3)4. Notes on recursion
If the above Modify the example as follows:
function multiple(num) {
if (num === 1) console.log(1)
return num * multiple(num - 1)
}
multiple(3) // Error: Maximum call stack size exceededThere is no return keyword sentence in the first line of the above code. Because there is no termination condition for recursion, it will always be pushed onto the stack, causing a memory leak.
Recursion prone error points
No termination point is set
Except for recursion, other parts Code
When is recursion appropriate
Okay, the above is the concept of recursion in JavaScript.
The following are practice questions.
6. Practice questions
1. Write a function that accepts a string and returns a string. This string is the inversion of the original string.
2. Write a function that accepts a string and compares one character from the front to the back. If the two are equal, return true; if they are not equal, return false.
3. Write a function that accepts an array and returns a flattened new array.
4. Write a function that accepts an object. If the object value is an even number, add them together and return the total value.
5. Write a function that accepts an object and returns an array. This array includes all the values in the object which are strings
7. Reference answer
Reference1
function reverse(str) {
if(str.length <p>Reference2</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">function isPalindrome(str){
if(str.length === 1) return true;
if(str.length === 2) return str[0] === str[1];
if(str[0] === str.slice(-1)) return isPalindrome(str.slice(1,-1))
return false;
}
var str = 'abba'
isPalindrome(str)Reference3
function flatten (oldArr) {
var newArr = []
for(var i = 0; i <p>Reference4</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">function nestedEvenSum(obj, sum=0) {
for (var key in obj) {
if (typeof obj[key] === 'object'){
sum += nestedEvenSum(obj[key]);
} else if (typeof obj[key] === 'number' && obj[key] % 2 === 0){
sum += obj[key];
}
}
return sum;
}
nestedEvenSum({c: 4,d: {a: 2, b:3}})Reference5
function collectStrings(obj) {
let newArr = []
for (let key in obj) {
if (typeof obj[key] === 'string') {
newArr.push(obj[key])
} else if(typeof obj[key] === 'object' && !Array.isArray(obj[key])) {
newArr = newArr.concat(collectStrings(obj[key]))
}
}
return newArr
}
var obj = {
a: '1',
b: {
c: 2,
d: 'dd'
}
}
collectStrings(obj)5. Summary
The essence of recursion is that you often have to think about the regular part first. When considering the recursive part, the following are the methods commonly used in JavaScript recursion
Array: slice, concat
String : slice, substr, substring
Object: Object.assign
The above is the detailed content of What is recursion? Detailed explanation of recursion in javascript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Is there a limit to recursion depth?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Is there a limit to recursion depth?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:30 AM
The recursion depth of C++ functions is limited, and exceeding this limit will result in a stack overflow error. The limit value varies between systems and compilers, but is usually between 1,000 and 10,000. Solutions include: 1. Tail recursion optimization; 2. Tail call; 3. Iterative implementation.
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Comparative analysis of recursive and non-recursive algorithms?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Comparative analysis of recursive and non-recursive algorithms?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
The recursive algorithm solves structured problems through function self-calling. The advantage is that it is simple and easy to understand, but the disadvantage is that it is less efficient and may cause stack overflow. The non-recursive algorithm avoids recursion by explicitly managing the stack data structure. The advantage is that it is more efficient and avoids the stack. Overflow, the disadvantage is that the code may be more complex. The choice of recursive or non-recursive depends on the problem and the specific constraints of the implementation.
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 C++ Recursion Advanced: Understanding Tail Recursion Optimization and Its Application
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:45 AM
C++ Recursion Advanced: Understanding Tail Recursion Optimization and Its Application
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:45 AM
Tail recursion optimization (TRO) improves the efficiency of certain recursive calls. It converts tail-recursive calls into jump instructions and saves the context state in registers instead of on the stack, thereby eliminating extra calls and return operations to the stack and improving algorithm efficiency. Using TRO, we can optimize tail recursive functions (such as factorial calculations). By replacing the tail recursive call with a goto statement, the compiler will convert the goto jump into TRO and optimize the execution of the recursive algorithm.
 Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
1. Background of the Construction of 58 Portraits Platform First of all, I would like to share with you the background of the construction of the 58 Portrait Platform. 1. The traditional thinking of the traditional profiling platform is no longer enough. Building a user profiling platform relies on data warehouse modeling capabilities to integrate data from multiple business lines to build accurate user portraits; it also requires data mining to understand user behavior, interests and needs, and provide algorithms. side capabilities; finally, it also needs to have data platform capabilities to efficiently store, query and share user profile data and provide profile services. The main difference between a self-built business profiling platform and a middle-office profiling platform is that the self-built profiling platform serves a single business line and can be customized on demand; the mid-office platform serves multiple business lines, has complex modeling, and provides more general capabilities. 2.58 User portraits of the background of Zhongtai portrait construction
 Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: application of recursion in string processing
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: application of recursion in string processing
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:30 AM
A recursive function is a technique that calls itself repeatedly to solve a problem in string processing. It requires a termination condition to prevent infinite recursion. Recursion is widely used in operations such as string reversal and palindrome checking.
 Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: tail recursion optimization
May 03, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: tail recursion optimization
May 03, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Recursive definition and optimization: Recursive: A function calls itself internally to solve difficult problems that can be decomposed into smaller sub-problems. Tail recursion: The function performs all calculations before making a recursive call, which can be optimized into a loop. Tail recursion optimization condition: recursive call is the last operation. The recursive call parameters are the same as the original call parameters. Practical example: Calculate factorial: The auxiliary function factorial_helper implements tail recursion optimization, eliminates the call stack, and improves efficiency. Calculate Fibonacci numbers: The tail recursive function fibonacci_helper uses optimization to efficiently calculate Fibonacci numbers.






