 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 JS interview frequently asked questions Prototype and prototype chain
JS interview frequently asked questions Prototype and prototype chain
JS interview frequently asked questions Prototype and prototype chain
Prototype and prototype chain are one of the high-frequency front-end interview questions. I believe many friends have encountered this problem. So do you understand it clearly and completely?
[Related recommendations: Front-end interview questions]
International practice, let us first ask the question:
- What is Prototype, prototype chain
- What are their characteristics
- What can they do
- How to determine their relationship
Maybe you already have the answer, Maybe you are starting to have some doubts, whether it is get a new skill or a simple review, let us explore it together
If there are any flaws or errors in the article, please let us know. Please give me some advice if you see it, thank you in advance
Prototype
JavaScriptis based on prototypeEvery function we create has a
prototype(Prototype)Attribute, this attribute is a pointer to an object, and the purpose of this object is to contain properties and methods that can be shared by all instances of a specific type.
To put it simply, when we create a function, the system will automatically assign a prototype attribute, which can be used to store attributes and methods that can be shared by all instances.
It will be clearer if you use a picture:
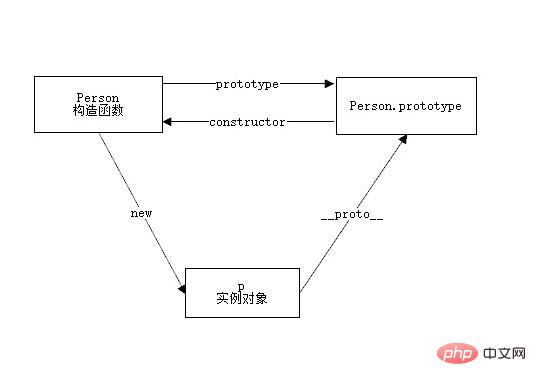
- Each constructor has a
- prototype
attribute, which points to an object, that is, the prototype objectThe prototype object has a - constructor
attribute by default, which points to Its constructorEach object has a hidden attribute - __proto__
, pointing to its prototype object
function Person(){}
var p = new Person();
p.__proto__ === Person.prototype // true
Person.prototype.constructor === Person // truefunction Person(){}
Person.prototype.name = 'tt';
Person.prototype.age = 18;
Person.prototype.sayHi = function() {
alert('Hi');
}
var person1 = new Person();
var person2 = new Person();
person1.name = 'oo';
person1.name // oo
person1.age // 18
perosn1.sayHi() // Hi
person2.age // 18
person2.sayHi() // HiCopy after login
It is not difficult to see from this code:function Person(){}
Person.prototype.name = 'tt';
Person.prototype.age = 18;
Person.prototype.sayHi = function() {
alert('Hi');
}
var person1 = new Person();
var person2 = new Person();
person1.name = 'oo';
person1.name // oo
person1.age // 18
perosn1.sayHi() // Hi
person2.age // 18
person2.sayHi() // Hi- Instances can share the properties and methods on the prototype The properties of the instance itself will block the properties of the same name on the prototype. Properties that are not on the instance will be found on the prototype.
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {
name: 'tt',
age: 18,
sayHi() {
console.log('Hi');
}
}
var p = new Person()function Person(){}
var p = new Person();
Person.prototype = {
name: 'tt',
age: 18
}
Person.prototype.constructor === Person // false
p.name // undefined 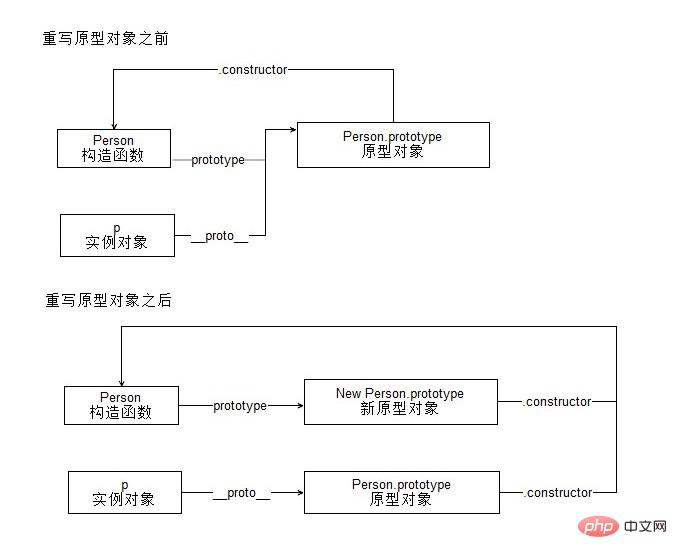
- Overwriting the prototype when an instance has already been created will cut off the connection between the existing instance and the new prototypeOverwriting the prototype object, This will cause the
- constructor
property of the prototype object to point toObject, causing confusion in the prototype chain relationship. Therefore, we should specifyconstructor(when rewriting the prototype object. instanceofwill still return the correct value)
Person.prototype = {
constructor: Person
}constructor property in this way will cause its Enumerable attribute to be Set to true (default is false)
prototype (prototype) and its characteristics, then the prototype What is a chain?
All objects in JavaScript are inherited from its prototype object. The prototype object itself is also an object, and it also has its own prototype object. In this way, a structure similar to a linked list is formed, which is the prototype chainSimilarly, we use a picture to describe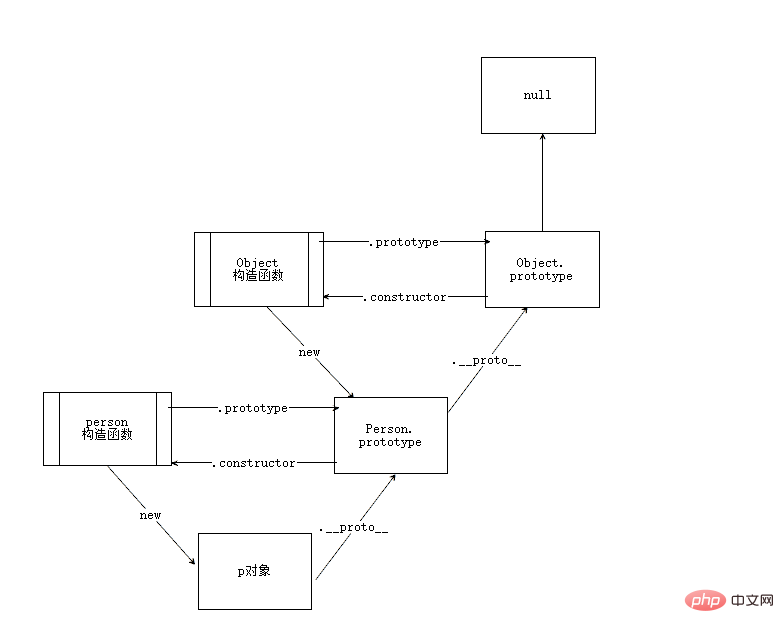
- The end point of all prototype chains is the
- prototype
attribute of theObjectfunction - Objec.prototype
The prototype object pointed to also has a prototype, but its prototype isnull, whilenullhas no prototype
p instance attribute. If this attribute does not exist in itself or in the prototype chain, Then the final value of the attribute is undefined. If it is a method, an error will be thrown.
ES6Why isprovidesClass( Class)This concept, as the template of the object, can define the class through theclasskeyword
class mentioned: ## The
of #ES6 can be regarded as just a syntactic sugar. Most of its functions can be achieved by ES5. The new class The writing method just makes the writing method of object prototype clearer and more like the syntax of object-oriented programming<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return &#39;(&#39; + this.x + &#39;, &#39; + this.y + &#39;)&#39;;
}
}
// 可以这么改写
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Point.prototype.toString = function () {
return &#39;(&#39; + this.x + &#39;, &#39; + this.y + &#39;)&#39;;
};</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><p><code>class 里面定义的方法,其实都是定义在构造函数的原型上面实现实例共享,属性定义在构造函数中,所以 ES6 中的类完全可以看作构造函数的另一种写法
除去 class 类中的一些行为可能与 ES5 存在一些不同,本质上都是通过原型、原型链去定义方法、实现共享。所以,还是文章开始那句话 JavaScript是基于原型的
更多 class 问题,参考这里
关系判断
instanceof
最常用的确定原型指向关系的关键字,检测的是原型,但是只能用来判断两个对象是否属于实例关系, 而不能判断一个对象实例具体属于哪种类型
function Person(){}
var p = new Person();
p instanceof Person // true
p instanceof Object // truehasOwnProperty
通过使用 hasOwnProperty 可以确定访问的属性是来自于实例还是原型对象
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {
name: 'tt'
}
var p = new Person();
p.age = 15;
p.hasOwnProperty('age') // true
p.hasOwnProperty('name') // false原型链的问题
由于原型链的存在,我们可以让很多实例去共享原型上面的方法和属性,方便了我们的很多操作。但是原型链并非是十分完美的
function Person(){}
Person.prototype.arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var person1 = new Person();
var person2 = new Person();
person1.arr.push(5)
person2.arr // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]引用类型,变量保存的就是一个内存中的一个指针。所以,当原型上面的属性是一个引用类型的值时,我们通过其中某一个实例对原型属性的更改,结果会反映在所有实例上面,这也是原型 共享 属性造成的最大问题
另一个问题就是我们在创建子类型(比如上面的 p)时,没有办法向超类型( Person )的构造函数中传递参数
The above is the detailed content of JS interview frequently asked questions Prototype and prototype chain. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1676
1676
 14
14
 1429
1429
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data



