Python实现控制台进度条功能
本文实例讲述了Python显示进度条的方法,是Python程序设计中非常实用的技巧。分享给大家供大家参考。具体方法如下:
首先,进度条和一般的print区别在哪里呢?
答案就是print会输出一个\n,也就是换行符,这样光标移动到了下一行行首,接着输出,之前已经通过stdout输出的东西依旧保留,而且保证我们在下面看到最新的输出结果。
进度条不然,我们必须再原地输出才能保证他是一个进度条,否则换行了怎么还叫进度条?
最简单的办法就是,再输出完毕后,把光标移动到行首,继续在那里输出更长的进度条即可实现,新的更长的进度条把旧的短覆盖,就形成了动画效果。
可以想到那个转义符了吧,那就是\ r。
转义符r就可以把光标移动到行首而不换行,转义符n就把光标移动到行首并且换行。
在python中,输出stdout(标准输出)可以使用sys.stdout.write
例如:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
j = '#'
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1,61):
j += '#'
sys.stdout.write(str(int((i/60)*100))+'% ||'+j+'->'+"\r")
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(0.5)
print
第二种思路是用转义符\b
转义符\b是退格键,也就是说把输出的光标往回退格子,这样就可以不用+=了,例如:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1,61):
sys.stdout.write('#'+'->'+"\b\b")
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(0.5)
print
光标回退2格,写个#再回退,再写,达到增长的目的了
不过写这么多似乎是废话,在耳边常常听到一句话:那就是不要重复造轮子。实际上python有丰富发lib帮你实现这个东西,你完全可以把心思放在逻辑开发上而不用注意这些小细节
下面要介绍的就是这个类“progressbar”(http://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/),使用easy_install可以方便的安装这个类库,其实就一个文件,拿过来放到文件同一个目录下面也直接可以import过来
如下图所示:
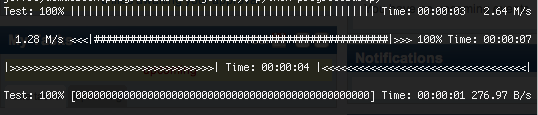
下面就是基本使用举例:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
from progressbar import *
total = 1000
#基本用法
progress = ProgressBar()
for i in progress(range(total)):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar = ProgressBar().start()
for i in range(1,1000):
pbar.update(int((i/(total-1))*100))
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.finish()
#高级用法
widgets = ['Progress: ', Percentage(), ' ', Bar(marker=RotatingMarker('>-=')),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10*i+1)
time.sleep(0.0001)
pbar.finish()
官方示例:http://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/source/browse/progressbar/examples.py
Python
# coding:utf-8
import sys
import time
from progressbar import AnimatedMarker, Bar, BouncingBar, Counter, ETA, \
FileTransferSpeed, FormatLabel, Percentage, \
ProgressBar, ReverseBar, RotatingMarker, \
SimpleProgress, Timer
examples = []
def example(fn):
try:
name = 'Example %d' % int(fn.__name__[7:])
except:
name = fn.__name__
def wrapped():
try:
sys.stdout.write('Running: %s\n' % name)
fn()
sys.stdout.write('\n')
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.stdout.write('\nSkipping example.\n\n')
examples.append(wrapped)
return wrapped
@example
def example0():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=[Percentage(), Bar()], maxval=300).start()
for i in range(300):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example1():
widgets = ['Test: ', Percentage(), ' ', Bar(marker=RotatingMarker()),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10 * i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example2():
class CrazyFileTransferSpeed(FileTransferSpeed):
"""It's bigger between 45 and 80 percent."""
def update(self, pbar):
if 45 < pbar.percentage() < 80:
return 'Bigger Now ' + FileTransferSpeed.update(self, pbar)
else:
return FileTransferSpeed.update(self, pbar)
widgets = [CrazyFileTransferSpeed(), ' <<<', Bar(), '>>> ',
Percentage(), ' ', ETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000)
# maybe do something
pbar.start()
for i in range(2000000):
# do something
pbar.update(5 * i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example3():
widgets = [Bar('>'), ' ', ETA(), ' ', ReverseBar('<')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10 * i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example4():
widgets = ['Test: ', Percentage(), ' ',
Bar(marker='0', left='[', right=']'),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=500)
pbar.start()
for i in range(100, 500 + 1, 50):
time.sleep(0.2)
pbar.update(i)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example5():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=[SimpleProgress()], maxval=17).start()
for i in range(17):
time.sleep(0.2)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example6():
pbar = ProgressBar().start()
for i in range(100):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example7():
pbar = ProgressBar() # Progressbar can guess maxval automatically.
for i in pbar(range(80)):
time.sleep(0.01)
@example
def example8():
pbar = ProgressBar(maxval=80) # Progressbar can't guess maxval.
for i in pbar((i for i in range(80))):
time.sleep(0.01)
@example
def example9():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=['Working: ', AnimatedMarker()])
for i in pbar((i for i in range(50))):
time.sleep(.08)
@example
def example10():
widgets = ['Processed: ', Counter(), ' lines (', Timer(), ')']
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(150))):
time.sleep(0.1)
@example
def example11():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Processed: %(value)d lines (in: %(elapsed)s)')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(150))):
time.sleep(0.1)
@example
def example12():
widgets = ['Balloon: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='.oO<a href="http://www.jobbole.com/members/weiboyes8848">@*</a> ')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
@example
def example13():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Arrows: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='←↖↑↗→↘↓↙')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError:
sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example14():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Arrows: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='◢◣◤◥')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError:
sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example15():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Wheels: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='◐◓◑◒')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError:
sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example16():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Bouncer: value %(value)d - '), BouncingBar()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(180))):
time.sleep(0.05)
@example
def example17():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Animated Bouncer: value %(value)d - '),
BouncingBar(marker=RotatingMarker())]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(180))):
time.sleep(0.05)
@example
def example18():
widgets = [Percentage(),
' ', Bar(),
' ', ETA(),
' ', AdaptiveETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=500)
pbar.start()
for i in range(500):
time.sleep(0.01 + (i < 100) * 0.01 + (i > 400) * 0.9)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example19():
pbar = ProgressBar()
for i in pbar([]):
pass
pbar.finish()
try:
for example in examples:
example()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.stdout('\nQuitting examples.\n')
再发一个类:
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
class progressbarClass:
def __init__(self, finalcount, progresschar=None):
import sys
self.finalcount=finalcount
self.blockcount=0
#
# See if caller passed me a character to use on the
# progress bar (like "*"). If not use the block
# character that makes it look like a real progress
# bar.
#
if not progresschar: self.block=chr(178)
else: self.block=progresschar
#
# Get pointer to sys.stdout so I can use the write/flush
# methods to display the progress bar.
#
self.f=sys.stdout
#
# If the final count is zero, don't start the progress gauge
#
if not self.finalcount : return
self.f.write('\n------------------- % Progress -------------------\n')
return
def progress(self, count):
#
# Make sure I don't try to go off the end (e.g. >100%)
#
count=min(count, self.finalcount)
#
# If finalcount is zero, I'm done
#
if self.finalcount:
percentcomplete=int(round(100*count/self.finalcount))
if percentcomplete < 1: percentcomplete=1
else:
percentcomplete=100
#print "percentcomplete=",percentcomplete
blockcount=int(percentcomplete/2)
#print "blockcount=",blockcount
if blockcount > self.blockcount:
for i in range(self.blockcount,blockcount):
self.f.write(self.block)
self.f.flush()
if percentcomplete == 100: self.f.write("\n")
self.blockcount=blockcount
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
from time import sleep
pb=progressbarClass(8,"*")
count=0
while count<9:
count+=1
pb.progress(count)
sleep(0.2)
另外,python cookbook中11.1节也提供了一个不错的进度条类,代码如下:
Python
import sys
class progressbar(object):
def __init__(self, finalcount, block_char='.'):
self.finalcount = finalcount
self.blockcount = 0
self.block = block_char
self.f = sys.stdout
if not self.finalcount:
return
self.f.write('\n------------------ % Progress -------------------1\n')
self.f.write(' 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0\n')
self.f.write('----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0\n')
def progress(self, count):
count = min(count, self.finalcount)
if self.finalcount:
percentcomplete = int(round(100.0 * count / self.finalcount))
if percentcomplete < 1:
percentcomplete = 1
else:
percentcomplete = 100
blockcount = int(percentcomplete // 2)
if blockcount <= self.blockcount:
return
for i in range(self.blockcount, blockcount):
self.f.write(self.block)
self.f.flush()
self.blockcount = blockcount
if percentcomplete == 100:
self.f.write("\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
from time import sleep
pb = progressbar(8, "*")
for count in range(1, 9):
pb.progress(count)
sleep(0.2)
pb = progressbar(100)
pb.progress(20)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(47)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(90)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(100)
print "testing 1:"
pb = progressbar(1)
pb.progress(1)
运行结果如下图所示:
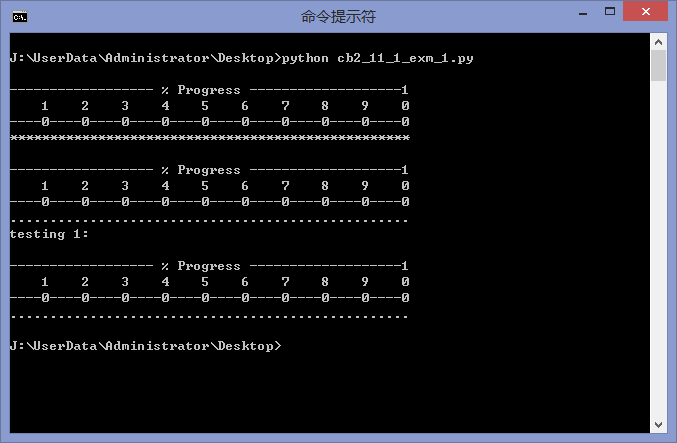
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计的学习有所帮助。

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7457
7457
 15
15
 1376
1376
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 44
44
 19
19
 17
17
 10
10
 PS가 계속 로딩을 보여주는 이유는 무엇입니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS가 계속 로딩을 보여주는 이유는 무엇입니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS "로드"문제는 자원 액세스 또는 처리 문제로 인한 것입니다. 하드 디스크 판독 속도는 느리거나 나쁘다 : CrystalDiskinfo를 사용하여 하드 디스크 건강을 확인하고 문제가있는 하드 디스크를 교체하십시오. 불충분 한 메모리 : 고해상도 이미지 및 복잡한 레이어 처리에 대한 PS의 요구를 충족시키기 위해 메모리 업그레이드 메모리. 그래픽 카드 드라이버는 구식 또는 손상됩니다. 운전자를 업데이트하여 PS와 그래픽 카드 간의 통신을 최적화하십시오. 파일 경로는 너무 길거나 파일 이름에는 특수 문자가 있습니다. 짧은 경로를 사용하고 특수 문자를 피하십시오. PS 자체 문제 : PS 설치 프로그램을 다시 설치하거나 수리하십시오.
 PS가 시작될 때 로딩 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
PS가 시작될 때 로딩 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
부팅 할 때 "로드"에 PS가 붙어있는 여러 가지 이유로 인해 발생할 수 있습니다. 손상되거나 충돌하는 플러그인을 비활성화합니다. 손상된 구성 파일을 삭제하거나 바꾸십시오. 불충분 한 메모리를 피하기 위해 불필요한 프로그램을 닫거나 메모리를 업그레이드하십시오. 하드 드라이브 독서 속도를 높이기 위해 솔리드 스테이트 드라이브로 업그레이드하십시오. 손상된 시스템 파일 또는 설치 패키지 문제를 복구하기 위해 PS를 다시 설치합니다. 시작 오류 로그 분석의 시작 과정에서 오류 정보를 봅니다.
 PS가 파일을 열 때로드 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
PS가 파일을 열 때로드 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
"로드"는 PS에서 파일을 열 때 말더듬이 발생합니다. 그 이유에는 너무 크거나 손상된 파일, 메모리 불충분, 하드 디스크 속도가 느리게, 그래픽 카드 드라이버 문제, PS 버전 또는 플러그인 충돌이 포함될 수 있습니다. 솔루션은 다음과 같습니다. 파일 크기 및 무결성 확인, 메모리 증가, 하드 디스크 업그레이드, 그래픽 카드 드라이버 업데이트, 의심스러운 플러그인 제거 또는 비활성화 및 PS를 다시 설치하십시오. 이 문제는 PS 성능 설정을 점차적으로 확인하고 잘 활용하고 우수한 파일 관리 습관을 개발함으로써 효과적으로 해결할 수 있습니다.
 설치 후 MySQL을 사용하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
설치 후 MySQL을 사용하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
이 기사는 MySQL 데이터베이스의 작동을 소개합니다. 먼저 MySQLworkBench 또는 명령 줄 클라이언트와 같은 MySQL 클라이언트를 설치해야합니다. 1. MySQL-Uroot-P 명령을 사용하여 서버에 연결하고 루트 계정 암호로 로그인하십시오. 2. CreateABase를 사용하여 데이터베이스를 작성하고 데이터베이스를 선택하십시오. 3. CreateTable을 사용하여 테이블을 만들고 필드 및 데이터 유형을 정의하십시오. 4. InsertInto를 사용하여 데이터를 삽입하고 데이터를 쿼리하고 업데이트를 통해 데이터를 업데이트하고 DELETE를 통해 데이터를 삭제하십시오. 이러한 단계를 마스터하고 일반적인 문제를 처리하는 법을 배우고 데이터베이스 성능을 최적화하면 MySQL을 효율적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
 PS 페더 링은 어떻게 전환의 부드러움을 제어합니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
PS 페더 링은 어떻게 전환의 부드러움을 제어합니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
깃털 통제의 열쇠는 점진적인 성격을 이해하는 것입니다. PS 자체는 그라디언트 곡선을 직접 제어하는 옵션을 제공하지 않지만 여러 깃털, 일치하는 마스크 및 미세 선택으로 반경 및 구배 소프트를 유연하게 조정하여 자연스럽게 전이 효과를 달성 할 수 있습니다.
 MySQL 설치 후 데이터베이스 성능을 최적화하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL 설치 후 데이터베이스 성능을 최적화하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL 성능 최적화는 설치 구성, 인덱싱 및 쿼리 최적화, 모니터링 및 튜닝의 세 가지 측면에서 시작해야합니다. 1. 설치 후 innodb_buffer_pool_size 매개 변수와 같은 서버 구성에 따라 my.cnf 파일을 조정해야합니다. 2. 과도한 인덱스를 피하기 위해 적절한 색인을 작성하고 Execution 명령을 사용하여 실행 계획을 분석하는 것과 같은 쿼리 문을 최적화합니다. 3. MySQL의 자체 모니터링 도구 (showprocesslist, showstatus)를 사용하여 데이터베이스 건강을 모니터링하고 정기적으로 백업 및 데이터베이스를 구성하십시오. 이러한 단계를 지속적으로 최적화함으로써 MySQL 데이터베이스의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
 PS 카드가 로딩 인터페이스에 있으면 어떻게해야합니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
PS 카드가 로딩 인터페이스에 있으면 어떻게해야합니까?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
PS 카드의로드 인터페이스는 소프트웨어 자체 (파일 손상 또는 플러그인 충돌), 시스템 환경 (DIFE 드라이버 또는 시스템 파일 손상) 또는 하드웨어 (하드 디스크 손상 또는 메모리 스틱 고장)로 인해 발생할 수 있습니다. 먼저 컴퓨터 자원이 충분한 지 확인하고 배경 프로그램을 닫고 메모리 및 CPU 리소스를 릴리스하십시오. PS 설치를 수정하거나 플러그인의 호환성 문제를 확인하십시오. PS 버전을 업데이트하거나 폴백합니다. 그래픽 카드 드라이버를 확인하고 업데이트하고 시스템 파일 확인을 실행하십시오. 위의 문제를 해결하면 하드 디스크 감지 및 메모리 테스트를 시도 할 수 있습니다.
 MySQL은 지불해야합니다
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL은 지불해야합니다
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL에는 무료 커뮤니티 버전과 유료 엔터프라이즈 버전이 있습니다. 커뮤니티 버전은 무료로 사용 및 수정할 수 있지만 지원은 제한되어 있으며 안정성이 낮은 응용 프로그램에 적합하며 기술 기능이 강합니다. Enterprise Edition은 안정적이고 신뢰할 수있는 고성능 데이터베이스가 필요하고 지원 비용을 기꺼이 지불하는 응용 프로그램에 대한 포괄적 인 상업적 지원을 제공합니다. 버전을 선택할 때 고려 된 요소에는 응용 프로그램 중요도, 예산 책정 및 기술 기술이 포함됩니다. 완벽한 옵션은없고 가장 적합한 옵션 만 있으므로 특정 상황에 따라 신중하게 선택해야합니다.




