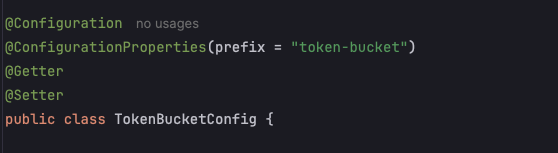
이러한 주석은 Spring Boot의 전체 프로젝트를 채웁니다.
그런데 이 주석이 어떤 문제를 해결하는지 아시나요?
애초에 맞춤 특수효과가 도입된 이유는 무엇인가요?
맞춤 주석을 만드는 방법은 무엇입니까?
오늘 다룰 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
Spring Boot에서 주석은 단순한 메타데이터를 추가하는 방법 그 이상입니다. 그들은
Spring이 사용자 정의 주석을 도입하기 전에 개발자는 XML 구성 파일을 사용하여 이메일 검증과 같은 구성을 관리해야 했습니다.
XML 구성은 이메일 주소 확인과 같은 작업을 수행하는 데 필요한 빈, 유효성 검사기 및 기타 필수 구성 요소를 정의합니다.
다음은 Spring 애플리케이션에서 XML을 사용하여 이메일 검증을 구성한 방법에 대한 예입니다.
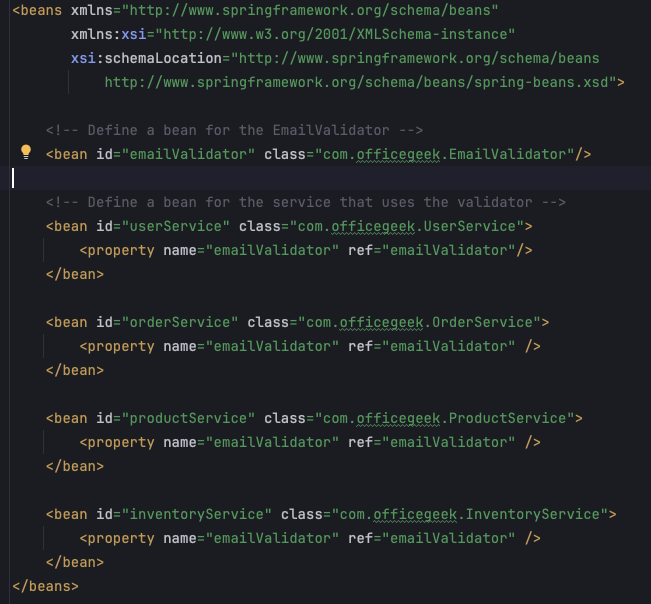
보시다시피, 수백 개의 클래스가 서로 의존하고 있는 경우 이는 쉽게 악몽이 될 수 있습니다.
또한 이는 개발자가 새 종속성을 추가해야 할 때마다 이 XML을 찾아야 함을 의미합니다.
Spring에서는 개발자가 코드에서 직접 주석을 사용할 수 있도록 하여 구성을 단순화하는 사용자 정의 주석을 도입했습니다.
이로 인해 광범위한 XML 구성의 필요성이 줄어들어 코드베이스가 더욱 깔끔하고 유지 관리가 쉬워졌습니다.
Spring의 사용자 정의 주석을 사용하면 선언적 접근 방식이 가능합니다.
개발자는 @Transactional, @Cacheable 또는 @Scheduled와 같은 주석을 사용하여 기본 논리를 작성하지 않고도 원하는 동작을 선언할 수 있습니다.
이렇게 하면 코드를 더 읽기 쉽고 유지 관리하기 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다.
AOP(관점 지향 프로그래밍)와 함께 자주 사용되는 Spring의 사용자 정의 주석을 사용하면 개발자가 중앙 집중식으로 교차 편집 문제를 처리할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 @Transactional 주석은 코드 전체에 트랜잭션 관리 논리를 분산시키지 않고 여러 메서드나 클래스에 걸쳐 트랜잭션을 관리합니다.
일반적인 동작을 캡슐화하여 상용구 코드의 필요성을 줄입니다.
예를 들어 @Autowired 주석은 종속성 주입을 단순화하여 명시적인 생성자나 설정자 메서드를 요구하지 않고 Spring이 자동으로 종속성을 주입할 수 있도록 합니다
@Autowired를 사용해야 하는지 아닌지는 별개의 논의입니다.
Spring은 구성 및 교차 절단 문제를 주석으로 추상화하여 코드의 가독성을 향상시킵니다.
귀하와 동료 개발자는 주석을 보고 메서드나 클래스의 목적을 빠르게 이해할 수 있으며 주석은 코드베이스 전체에서 일관성을 유지하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
사용자 정의 주석을 사용하면 개발자가 특정 요구 사항에 맞는 주석을 생성하여 표준화된 방식으로 프레임워크의 기능을 확장할 수 있습니다.
이러한 유연성 덕분에 Spring은 여러 애플리케이션과 아키텍처 전반에 걸쳐 관련성과 강력한 성능을 유지할 수 있었습니다.
package co.officegeek.tokenratelimiter;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // Annotation available at runtime
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // Can be applied to methods
public @interface LogExecutionTime {
}
Spring의 BeanPostProcessor, Aspect 또는 사용자 정의 주석 처리 로직을 사용하여 주석을 처리하는 사용자 정의 로직을 생성할 수 있습니다.
package co.officegeek.tokenratelimiter;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogExecutionTimeAspect {
@Around("@annotation(LogExecutionTime)")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature() + " executed in " + executionTime + "ms");
return proceed;
}
}
정의된 대로 메소드, 필드 또는 클래스에 사용자 정의 주석을 적용합니다.
package co.officegeek.tokenratelimiter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TestService {
@LogExecutionTime
public void serve() throws InterruptedException {
// Simulate some work
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}

When you apply a custom annotation to a method, class, or field, the annotation itself doesn't directly cause any method to be called.
Instead, the logic associated with the annotation is typically implemented using reflection or aspect-oriented programming (AOP) in frameworks like Spring.
Here's a breakdown of how the compiler and runtime environment know what method to call when an annotation is applied:
Some annotations are handled at compile time by annotation processors.
Java's javax.annotation.processing package allows developers to create custom annotation processors that generate code, validate annotations, or even modify the abstract syntax tree (AST) of the code being compiled.
The annotation processor reads the annotations during compilation and executes code based on those annotations.
This can include generating new classes or methods that the code will use later.
The @Override annotation is a compile-time annotation that doesn't invoke a method but instead tells the compiler to check if the method actually overrides a superclass method.
Custom annotations can be processed at runtime using reflection.
The runtime system (e.g., a framework like Spring) uses reflection to detect the presence of annotations on methods, classes, or fields, and then applies the corresponding behavior.
A custom annotation like @LogExecutionTime doesn't directly trigger any method call.
Instead, an aspect or some other reflective mechanism checks for the presence of the annotation at runtime and then wraps the method call with additional logic.
In frameworks like Spring, AOP is commonly used to handle custom annotations.
AOP allows you to define "aspects" that can intercept method calls and perform additional processing before or after the method execution.
When the AOP framework (e.g. Spring AOP) detects an annotation, it triggers the execution of an advice method associated with the aspect.
This advice method contains the logic that the AOP framework executes when the annotated method is called.
A @Transactional annotation in Spring doesn't execute any logic by itself.
Instead, the Spring framework's AOP infrastructure intercepts calls to methods annotated with @Transactional and wraps them with transaction management logic.
Custom annotations are ideal for handling cross-cutting concerns like logging, security, transaction management, and caching.
These are concerns that affect multiple parts of an application but are not related to the core business logic.
위의 @LogExecutionTime 주석은 모든 메서드에 걸쳐 사용할 수 있고 비즈니스 로직이 없다는 점에서 좋은 예입니다.
어떻게 발생해야 하는지가 아니라 어떻게 발생해야 하는지 지정하려는 경우 맞춤 주석을 사용하면 명확하고 표현력이 풍부한 방법을 제공할 수 있습니다.
@Cacheable 또는 @Retry와 같은 주석을 사용하면 개발자가 구현 코드를 수동으로 작성하지 않고도 선언적으로 캐싱 또는 재시도 논리를 활성화할 수 있습니다.
사용자 정의 주석은 사용하기 쉬운 주석 뒤에 복잡성을 숨겨 프레임워크 또는 라이브러리의 통합을 단순화할 수 있습니다.
Spring의 @Autowired와 같은 주석은 수동으로 인스턴스화하지 않고도 종속성을 주입하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
복잡한 로직을 재사용 가능한 방식으로 캡슐화해야 하는 경우 맞춤 주석이 이 로직을 적용하기 위한 깔끔한 API를 제공할 수 있습니다.
@RateLimit와 같은 주석은 메소드 본문을 이 로직으로 복잡하게 만들지 않고도 메소드 호출 횟수를 제한하는 로직을 캡슐화할 수 있습니다.
로직이 단순하거나 한 곳에만 적용해야 하는 경우 맞춤 주석을 만드는 것은 과도하고 코드를 불필요하게 복잡하게 만들 수 있습니다.
주석은 컴파일 타임에 정적으로 정의되므로 런타임에 동작을 동적으로 결정해야 하는 시나리오에는 적합하지 않습니다.
사용자 입력이나 외부 구성에 따라 메소드의 동작이 변경되어야 하는 경우 이를 사용자 정의 주석으로 처리하면 복잡한 솔루션이 발생할 수 있습니다.
핵심 비즈니스 로직을 사용자 정의 주석으로 추상화해서는 안 됩니다. 이렇게 하면 로직의 투명성이 떨어지고 유지 관리가 더 어려워질 수 있습니다.
@ProcessOrder와 같은 비즈니스 프로세스를 캡슐화하기 위해 주석을 사용하면 중요한 비즈니스 규칙이 숨겨져 코드를 이해하고 유지 관리하기가 더 어려워질 수 있습니다.
동작이 여러 주석 간의 복잡한 상호 작용에 따라 달라지는 경우 예상치 못한 결과가 발생하고 코드를 이해하고 디버깅하기 어렵게 만들 수 있습니다.
동일한 메소드(예: @Retry, @Cacheable, @LogExecutionTime)에 영향을 미치는 여러 사용자 정의 주석을 결합하면 예측할 수 없는 동작이 발생할 수 있으며 관리하기가 어렵습니다
맞춤 주석은 리플렉션이나 프록시 메커니즘에 의존하는 경우가 많으며 이로 인해 성능 오버헤드가 발생할 수 있습니다.
성능이 중요한 코드 섹션에서는 사용하면 안 됩니다.
단단한 루프에서 수백만 번 호출되는 메소드에 로깅을 추가하기 위해 사용자 정의 주석을 사용하면 성능이 크게 저하될 수 있습니다.
맞춤 주석은 로깅, 보안, 트랜잭션 관리와 같은 교차 문제를 처리하는 데 적합합니다.
애플리케이션의 여러 부분에 동일한 동작을 적용해야 하는 시나리오에도 적합합니다.
그러나 단순한 일회성 로직이나 세밀한 제어와 유연성이 필요한 경우에는 맞춤 주석이 최선의 접근 방식이 아닐 수도 있습니다.
구현을 결정하기 전에 장단점을 고려하세요.
사용자 정의 주석은 Spring Boot 무기고의 강력한 도구이지만 다른 도구와 마찬가지로 신중하게 사용해야 합니다.
반복적인 작업을 처리하고 코드베이스 전체에 일관성을 강화할 수 있는 깔끔하고 재사용 가능한 방법을 제공합니다.
그러나 특히 복잡성과 성능 면에서 잠재적인 단점에 유의하세요.
소프트웨어 개발자와 주목받는 마이크로서비스 설계자를 대상으로 Spring Boot 및 Bucket4j를 사용하여 속도 제한 서비스를 설계하고 구현하는 방법에 대한 10일 코호트 기반 과정을 시작합니다.
알게 될 내용:
✅ 프로덕션에 바로 사용할 수 있는 마이크로서비스를 설계하고 구축하는 방법
✅ 속도 제한 알고리즘 및 구현에 대한 심층적인 지식
✅ Spring Boot 개발, 테스트 및 컨테이너화 모범 사례
하지만 그것도
✅ 프로젝트를 특정 작업으로 나누기
✅ 자신에게 책임을 지기
✅ 프로젝트를 올바르게 설계하고 구축하기
대부분의 회사와 관련된 사용 사례인 마이크로서비스를 설계하고 개발하려는 소프트웨어 개발자를 대상으로 합니다.
특히 "프로젝트 경험"은 없지만 열정과 야망이 넘치는 소프트웨어 개발자 경력 초기의 사람들에게 적합합니다.
이 내용이 도움이 될 것이라고 생각하거나 더 알고 싶은 경우:
관심 등록하시면 워크숍 세부사항을 알려드리겠습니다.
이 내용은 내 하위 스택에 처음 게시되었습니다. 먼저 업데이트를 받으려면 내 Substack - Weekend Developer를 구독하세요.
당신이 작성한 코드에 대한 피드백이 필요한 개발자이신가요?
아니면 당신이 올바른 일을 할 수 있도록 누군가가 당신의 코드를 검토하길 원하시나요?
저는 사람들이 조기에 피드백을 받고 더 나은 코드를 작성할 수 있도록 무료 코드 검토 세션을 제공합니다
Twitter(X) 또는 LinkedIn으로 DM을 보내주시면 코드 작성에 도움을 드리겠습니다.
위 내용은 Spring Boot에서 맞춤 주석을 생성하기 위한 최종 가이드의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!