연산자는 변수나 값(피연산자)에 대해 특정 연산을 수행하는 데 사용되는 특수 문자나 기호로 간주됩니다. Java에는 변수를 조작하는 데 사용되는 여러 연산자가 있습니다. 여기에는 산술 연산자, 비트 연산자, 비교 연산자, 논리 연산자, 기타가 포함됩니다. 연산자, 할당 연산자 등 이 글에서는 자바의 비교 연산자에 대해 좀 더 자세히 알아보겠습니다.
다음은 Java의 다양한 비교 연산자입니다.
광고 이 카테고리에서 인기 있는 강좌 JAVA MASTERY - 전문 분야 | 78 코스 시리즈 | 15가지 모의고사| Name of the Operator | Operator | Example |
| Equal to | = = | a= =b |
| Not equal to | != | a!=b |
| Less than | < | a |
| Greater than | > | a>b |
| Less than or equal to | <= | a<=b |
| Greater than or equal to | >= | a>=b |
이 연산자는 연산자의 왼쪽 값이 오른쪽 값과 같은지 확인합니다.
예:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are equal; Return true if it is same, else returns false
System.out.println(x == y);
}
}출력:
사례 1: x = 3; 와이 =5; 동일하지 않으므로 false를 반환합니다

사례 2: x = 4; y=4; 동일하므로 true를 반환합니다

이 연산자는 연산자의 왼쪽 값이 오른쪽 값과 같지 않은지 확인합니다.
예:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are not equal; Return true if it is not equal, else returns false
System.out.println(x != y);
}
}출력:
사례 1: x = 3; y=4; 같지 않으므로 true를 반환합니다
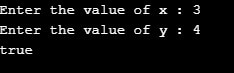
사례 2: x = 3; y=3; 동일하므로 false를 반환합니다

연산자의 왼쪽 값이 오른쪽 값보다 작은지 확인하는 연산자입니다.
예:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is less than y, else false
System.out.println(x < y);
}
}출력:
사례 1: x = 4; 와이=6; x가 y보다 작으므로 true를 반환합니다

사례 2: x = 44; y=32; x가 y보다 작지 않으므로 false를 반환합니다

연산자의 왼쪽 값이 오른쪽 값보다 큰지 확인하는 연산자입니다.
예:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.<em>in</em>);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is greater than y, else false
System.out.println(x > y);
}
}출력:
사례 1: x = 67; y=66; x가 y보다 크면 true를 반환합니다

사례 2: x = 43; 와이 =57; x가 y보다 작으므로 false를 반환합니다

이 연산자는 연산자의 왼쪽 값이 오른쪽 값보다 작거나 같은지 확인합니다.
예:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user and store it in variable y
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is less than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x <= y);
}
}출력:
사례 1: x = 45; y=45; x가 y와 같으므로 true를 반환합니다

사례 2: x = 45; 와이 =54; x가 y보다 작으므로 true를 반환합니다

사례 3: x = 45; y=43; x가 y보다 크면 false를 반환합니다

이 연산자는 연산자의 왼쪽 값이 오른쪽 값보다 크거나 같은지 확인합니다.
예:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is greater than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x >= y);
}
}출력:
사례 1: x = 54; y=67; x가 y보다 작으므로 false를 반환합니다

사례 2: x = 45; 와이=36; x가 y보다 크면 true를 반환합니다

사례 3: x = 55; y=55; x가 y와 같으므로 true를 반환합니다

위 내용은 Java의 비교 연산자의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!