파일 처리란 Java에서 파일을 작업하는 것을 말합니다. 파일을 읽고 Java 파일에 쓰는 것을 Java의 파일 처리라고 합니다. 파일은 다양한 유형의 정보를 담을 수 있는 컨테이너입니다. 파일에는 텍스트, 이미지, 비디오, 표 등이 포함될 수 있습니다.
광고 이 카테고리에서 인기 있는 강좌 JAVA MASTERY - 전문 분야 | 78 코스 시리즈 | 15가지 모의고사무료 소프트웨어 개발 과정 시작
웹 개발, 프로그래밍 언어, 소프트웨어 테스팅 등
Java에서 File 클래스를 사용하면 다양한 유형의 파일로 작업할 수 있습니다. File 클래스는 java.io 패키지의 멤버입니다. Java는 파일을 읽고, 쓰고, 업데이트하고, 삭제할 수 있는 다양한 방법을 제공합니다.
파일에 대해 수행할 수 있는 다양한 작업 유형은 다음과 같습니다.
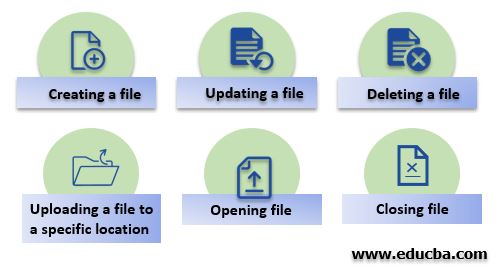
구문:
프로그램에서 파일 작업을 하려면 java.io 패키지를 가져와야 합니다. 이 패키지를 가져오면 File 클래스의 생성자에서 파일을 참조하여 초기화할 수 있는 File 클래스가 제공됩니다.
//importing file class
import java.io.File;
//File name passed to the object
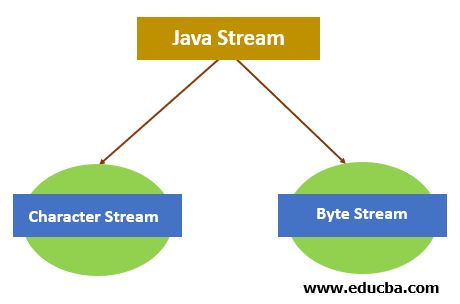
File fileObj = new File("file.txt");Java에서는 스트리밍 개념으로 파일 처리가 이루어집니다. 파일에 대한 입출력 작업은 스트리밍을 통해 수행됩니다. 스트림은 일련의 데이터를 의미합니다.
Java에서 Stream은 두 가지 유형이 있습니다.
Java에서 다양한 작업을 수행하기 위한 몇 가지 방법이 아래에 나와 있습니다.
다음은 Java의 파일 처리 예입니다.
이 예에서 프로그램은 다양한 방법을 사용하여 특정 세부정보를 얻습니다. 이 애플리케이션에서는 파일과 관련된 정보를 가져오기 위해 다음과 같은 다양한 방법이 사용됩니다.
코드:
IO 패키지의 다양한 클래스를 가져옵니다.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileHandlingExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of a file
File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
if (fileObj.exists()) {
//retrieving the path of the specified file
System.out.println("\nSpecified file path: " + fileObj.getAbsolutePath());
//checking whether the file is writable or not
System.out.println("\nIs the file Writable: " + fileObj.canWrite());
//checking whether the file is Readable or not
System.out.println("\nIs the file Readable " + fileObj.canRead());
//retrieving file name
System.out.println("\nFile name: " + fileObj.getName());
//retrieving file size
System.out.println("\nFile size (in bytes) " + fileObj.length());
File fileDirObj = new File("D:/Programs/");
String[] fileList = fileDirObj.list();
//displaying here the list of files available in the directory
for (int i = 0; i < fileList.length; i++) {
System.out.print("\n" + fileList[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
else {
System.out.println("Specified file does not exist.");
}
}
}출력:
위의 예에서는 파일과 관련된 다양한 검사를 수행하는 데 필요한 정보를 제공하는 다양한 방법을 확인할 수 있습니다.
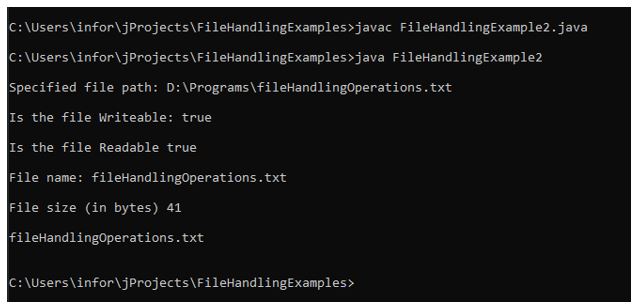
이 예는 다양한 작업 유형에 대해 프로그램에서 다양한 방법이 사용되는 방식을 보여줍니다. 파일이 존재하는지 확인하기 위해 프로그램에서 사용되는 presents() 메소드는 존재하지 않습니다. 그 후 if..else.. 조건이 적용됩니다.
In the If condition, it checks first whether the existing file is writable or not; if the existing file remains writable, then the code block under the if section uses the FileWriter class method to write content into the existing file.
Code:
Importing io package different classes.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileHandlingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
if(fileObj.exists()){
System.out.println("File already exists.");
if(fileObj.canWrite()){
//creating object of FileWriter class to write things on file
FileWriter fwObj = new FileWriter("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
// Writes this content into the specified file
fwObj.write("It is a basic example of writing in file!");
//closing the files once writing completed
fwObj.close();
System.out.println("\nContent has been written to the file.");
}else{
System.out.println("\nFile is not in writable mode.");
}
;
}else{
if (fileObj.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("New File created: " + fileObj.getName());
}
}
}
catch (IOException ioError) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
ioError.printStackTrace();
}
}
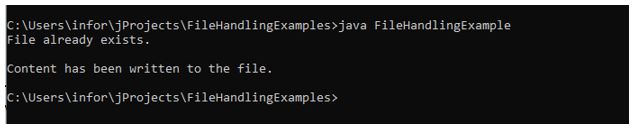
}Output:
In the above-given example, After compilation, running the program the first time will create a file with the specified name in the program.
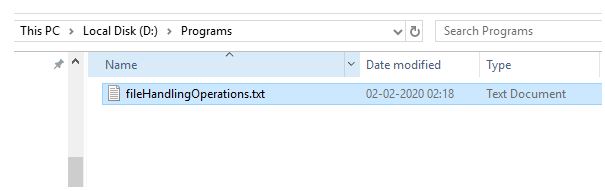
Running the program a second time will write the content in the existing file.
The article above explains what a file is, how to perform operations on it, and how file handling works. It was also demonstrated in the above section about classes & methods that can be used to work with files in java.
위 내용은 Java의 파일 처리의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!