비액세스 수정자는 클래스의 동작, 메소드 또는 변수 등에 대해 JVM에 알리기 위해 Java 7에 도입된 키워드입니다. 이는 변수를 두 번 초기화할 수 없음을 나타내는 데 사용되는 final 키워드와 같은 추가 기능을 도입하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 총 7개의 비접근 수식자가 도입되었습니다.
다음은 Java의 비액세스 수정자의 유형입니다.
광고 이 카테고리에서 인기 있는 강좌 JAVA MASTERY - 전문 분야 | 78 코스 시리즈 | 15가지 모의고사이 수정자는 다음과 함께 적용될 수 있습니다.
코드:
final class Honda{
public void myFun1(){
System.out.println("Honda Class");
}
}
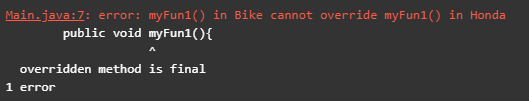
class Bike extends Honda{
public void myFun1(){
System.out.println("Bike Class");
}
}출력:

코드:
class Honda{
public final void myFun1(){
System.out.println("Honda Class");
}
}
class Bike extends Honda{
public void myFun1(){
System.out.println("Bike Class");
}
}출력:

코드:
public abstract class MyActivity{
public MyActivity(){
}
public final String myFun1(){
}
}예: public abstract void fun1();
코드:
abstract class Electronics
{
abstract void display();
abstract void display(String msg);
}
class Computers extends Electronics
{
@Override
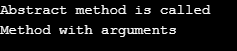
void display() {
System.out.println("Abstract method is called");
}
@Override
void display(String txt) {
System.out.println(txt);
}
}
public class AbstractDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computers obj=new Computers();
obj.display();
obj.display("Method with arguments");
}
}출력:
이 키워드는 여러 스레드가 동시에 하나의 메서드에 액세스하는 것을 방지하여 멀티스레딩 기능을 사용하여 프로그램의 흐름을 동기화하고 원하는 결과를 이끌어내는 데 도움이 됩니다.
코드:
class Person1
{
public synchronized void sendFun(String txt)
{
System.out.println("Sending message\t" + txt );
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Thread interrupted.");
}
System.out.println("\n" + txt + "Sent");
}
}
class DemoThread extends Thread
{
private String txt;
Person1 person;
DemoThread(String m, Person1 obj)
{
txt = m;
person = obj;
}
public void run()
{
synchronized(person)
{
person.sendFun(txt);
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Person1 snd = new Person1();
DemoThread S1 =
new DemoThread( " Hi " , snd );
DemoThread S2 =
new DemoThread( " Bye " , snd );
S1.start();
S2.start();
// wait for threads to end
try
{
S1.join();
S2.join();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
}
}출력:
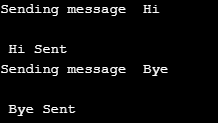
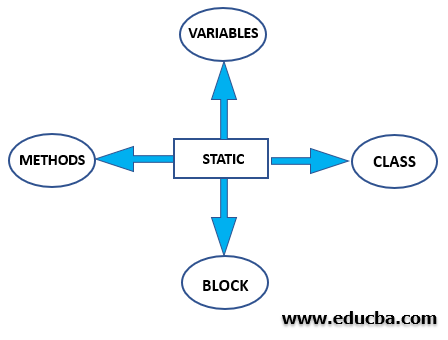
이 변수는 메모리 관리에 사용되며 클래스를 로드할 때 가장 먼저 참조되는 변수입니다. 이러한 구성원은 클래스 수준에서 처리됩니다. 따라서 객체를 사용하여 호출할 수 없습니다. 대신 클래스 이름을 사용하여 이를 참조합니다.
Code:
public class Demo
{
// static variable
static int x = 10;
static int y;
//static class
public static class DemoInnerClass{
static int z=10;
}
// static block
static {
System.out.println("Static block initialized.");
y = x + 4;
}
//static method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("from main");
System.out.println("Value of x : "+x);
System.out.println("Value of y : "+y);
System.out.println("Value of z : "+DemoInnerClass.z);
}
}Output:
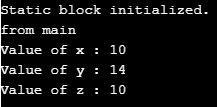
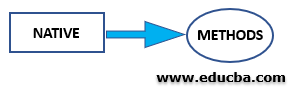
The native keyword is used only with the methods to indicate that the particular method is written in platform -dependent. These are used to improve the system’s performance, and the existing legacy code can be easily reused.
Note: Static, as well as abstract methods, cannot be declared as native.Example: Consider a function myfun1 in class NativeDemo that is written in C++. To use this code, we will create a link library mylib1 and load it using the class’s static block.
public class DateTimeUtils {
public native String getSystemTime();
static {
System.loadLibrary("nativedatetimeutils");
}
}
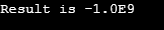
Code:
public class HelloWorld
{
public strictfp double calSum()
{
double n1 = 10e+07;
double n2 = 9e+08;
return (n1+n2);
}
public static strictfp void main(String[] args)
{
HelloWorld t = new HelloWorld ();
System.out.println("Result is -" + t.calSum());
}
}Output:
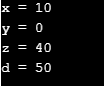
While transferring the data from one end to another over a network, it must be serialised for successful receiving of data, which means convert to byte stream before sending and converting it back at receiving end. To tell JVM about the members who need not undergo serialization instead of being lost during transfer, a transient modifier comes into the picture.
Syntax:
private transient member1;
Code:
import java.io.*;
class Demo implements Serializable
{
int x = 10;
transient int y = 30;
transient static int z = 40;
transient final int d = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Demo input = new Demo();
FileOutputStream tos = new FileOutputStream("abc.txt");
ObjectOutputStream tin = new ObjectOutputStream(tos);
tin.writeObject(input);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("abc.txt"); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
Demo output = (Demo)ois.readObject();
System.out.println("x = " + output.x);
System.out.println("y = " + output.y);
System.out.println("z = " + output.z);
System.out.println("d = " + output.d);
}
}Output:
Non-access modifiers are the type of modifiers that tell JVM about the behavior of classes, methods, or variables defined and prepared accordingly. It also helps in synchronizing the flow as well as displaying similar results from operations being performed irrespective of the platform used for execution.
This is a guide to Non Access Modifiers in Java. Here we discuss the Types of Non Access Modifiersand their methods and code implementation in Java. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
위 내용은 Java의 비 액세스 한정자의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!