자바의 BinarySearch()
Java에서 BinarySearch()는 이진 검색 알고리즘을 사용하여 여러 요소 중에서 특정 핵심 요소를 검색하는 데 도움을 주는 메서드입니다. 이 작업을 수행하려면 요소를 오름차순으로 정렬해야 합니다. 정렬되지 않은 경우 Arrays.sort(arr) 메서드를 사용하여 정렬할 수 있습니다. 그렇지 않으면 결과가 정의되지 않은 것으로 간주됩니다. 선형 검색에 비해 이진 검색이 더 빠른 것으로 간주됩니다. 이로 인해 이진 검색의 시간 복잡도는 O(log n)이라고 합니다. 또한, BinarySearch() 메소드는 java.util.Arrays 패키지에서 인스턴스화될 수 있습니다. BinarySearch() 메서드에 대한 자세한 내용은 다음 섹션에서 설명합니다.
구문:
무료 소프트웨어 개발 과정 시작
웹 개발, 프로그래밍 언어, 소프트웨어 테스팅 등
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key)
여기서, 매개변수 a와 key는 각각 검색해야 할 배열과 검색해야 할 값입니다.
binarySearch() 메서드는 검색한 핵심 요소의 인덱스를 반환합니다. 키 요소를 찾을 수 없는 경우 삽입되었을 키 요소가 있는 삽입 지점이 반환됩니다. 검색의 핵심 요소가 배열의 다른 요소와 비교할 수 없는 경우 ClassCastException이라는 예외가 발생합니다.
Java에서 BinarySearch() 메서드는 어떻게 작동하나요?
이 메소드가 Java에서 어떻게 작동하는지 살펴보겠습니다.
- k가 검색해야 할 핵심 요소라고 가정해 보겠습니다. k를 배열의 중간 요소와 비교합니다.
- k가 중간 위치에 있는 요소와 일치하는 경우 중간 인덱스를 반환해야 합니다.
- 그렇지 않고 k가 중간 위치의 요소보다 높으면 k는 중간 요소의 오른쪽에서만 찾을 수 있습니다.
- 그렇지 않으면 중간 요소의 왼쪽에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
Java에서 BinarySearch()를 구현하는 예
다음은 BinarySearch() 메서드에 대한 일부 프로그램의 예입니다.
예시 #1
코드:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BinarySearchExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//create a byte array
byte ba[] = {05, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30};
//create a character array
char ca[] = {'a', 'n', 's', 'p', 'v', 'i', 'd'};
//create an integer array
int ia[] = { 10, 20, 15, 22, 35};
//create a double array
double da[] = {10.1 , 15.34 , 22.25, 13.5};
//create a float array
float fa[] = {13.2f, 25.1f , 22.2f , 43.5f };
//sort all the arrays that created above
Arrays.sort(ba);
Arrays.sort(ca);
Arrays.sort(ia);
Arrays.sort(da);
Arrays.sort(fa);
//enter the key elements that has to be searched in the array
byte bKey = 15;
char cKey = 'i';
int iKey = 22;
double dKey = 15.34;
float fKey = 22.2f;
System.out.println("Element "+ bKey + " is found at the position of " + Arrays.binarySearch(ba,bKey) );
System.out.println("Element "+ cKey + " is found at the position of " + Arrays.binarySearch(ca,cKey) );
System.out.println("Element "+ iKey + " is found at the position of " + Arrays.binarySearch(ia,iKey) );
System.out.println("Element "+ dKey + " is found at the position of " + Arrays.binarySearch(da,dKey) );
System.out.println("Element "+ fKey + " is found at the position of " + Arrays.binarySearch(fa,fKey) );
}
}출력:

위의 program.Sort() 메소드에서 Array를 사용하여 배열을 정렬한 후 문자, 정수, 부동 소수점, 더블, 바이트 등 다양한 유형의 특정 배열이 생성되고, 배열에서 검색해야 할 요소가 선언됩니다. 그런 다음 Arrays.binarySearch() 메서드를 사용하여 검색된 요소의 인덱스를 인쇄합니다.
배열에는 없는 핵심 요소가 주어졌다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 출력은 어떻게 될까요??
그것을 찾기 위해 핵심 요소의 코드를 아래와 같이 변경해 보겠습니다.
바이트 bKey = 15;
char cKey = 'i';
int iKey = 89;
이중 dKey = 15.34;
float fKey = 22.2f;
즉, iKey=89가 배열에 없으면 아래와 같이 출력됩니다.

보시다시피 위치는 -6으로 출력됩니다. 요소를 검색했는데 찾을 수 없는 경우 해당 요소가 있으면 인덱스의 음수 값이 반환되기 때문입니다. 즉, int ia[] = { 10, 20, 15, 22, 35} 는 주어진 배열입니다. 89가 존재한다면 배열은 int ia[] = { 10, 20, 15, 22, 35, 89};
인덱스가 6이었음을 분명히 알 수 있습니다. 원래 배열에는 없기 때문에 해당 특정 인덱스의 음수 값이 위 출력에 반환됩니다.
예시 #2
다음과 같이 재귀를 사용하여 이진 검색을 수행할 수도 있습니다.
코드:
//sample class
class BinarySearchExample{
public static int binarySearch(int a[], int f, int l, int k){
//if last element is greater than or equal to first element
if (l>=f)
{
//find the mid
int m = f + (l - f)/2;
//if the key element that is searching is found in middle position, return mid position
if (a[m] == k)
{
return m;
}
//if key element is less than element in middle position, search the left <u>subarray</u>
if (a[m] > k){
return binarySearch(a, f, m-1, k);
}
//if key element is greater than the element in middle position, search the right <u>subarray</u>
else{
return binarySearch(a, m+1, l, k);
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
//initialise the array
int a[] = {34,45,54,68,79};
int k = 68;
int l = a.length-1;
//store the position in variable res
int res = binarySearch(a,0,l,k);
if (res == -1)
System.out.println("Sorry!! Can't find the element....!");
else
System.out.println("Element is found at the position: "+res);
}
}출력:
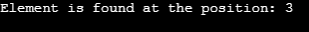
위 프로그램에서는 배열이 먼저 생성되고, 알아낼 요소도 선언됩니다. BinarySearch() 메소드를 사용하면 핵심 요소의 위치를 찾을 수 있습니다. 요소를 찾을 수 없다고 가정하면 "죄송합니다. 요소를 찾을 수 없습니다."라는 메시지가 인쇄됩니다.
결론
binarySearch()는 이진 검색 알고리즘을 사용하여 배열에서 사용 가능한 여러 요소 중에서 특정 핵심 요소를 찾는 데 도움이 되는 Java 메서드입니다. 이 방법의 작업 및 예는 이 문서에 자세히 설명되어 있습니다.
추천기사
Java의 BinarySearch()에 대한 안내입니다. 여기에서는 Java에서 BinarySearch() 메서드가 작동하는 방식과 코드 구현 예제에 대해 설명합니다. 또한 다른 추천 도움말을 통해 자세히 알아볼 수도 있습니다.
- 자바스크립트 수학 함수
- Java의 레이아웃
- 자바 컴파일러
- Java의 병합 정렬
위 내용은 자바의 BinarySearch()의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)
 PHP vs. Python : 차이점 이해
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python : 차이점 이해
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP와 Python은 각각 고유 한 장점이 있으며 선택은 프로젝트 요구 사항을 기반으로해야합니다. 1.PHP는 간단한 구문과 높은 실행 효율로 웹 개발에 적합합니다. 2. Python은 간결한 구문 및 풍부한 라이브러리를 갖춘 데이터 과학 및 기계 학습에 적합합니다.
 PHP : 웹 개발의 핵심 언어
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP : 웹 개발의 핵심 언어
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP는 서버 측에서 널리 사용되는 스크립팅 언어이며 특히 웹 개발에 적합합니다. 1.PHP는 HTML을 포함하고 HTTP 요청 및 응답을 처리 할 수 있으며 다양한 데이터베이스를 지원할 수 있습니다. 2.PHP는 강력한 커뮤니티 지원 및 오픈 소스 리소스를 통해 동적 웹 컨텐츠, 프로세스 양식 데이터, 액세스 데이터베이스 등을 생성하는 데 사용됩니다. 3. PHP는 해석 된 언어이며, 실행 프로세스에는 어휘 분석, 문법 분석, 편집 및 실행이 포함됩니다. 4. PHP는 사용자 등록 시스템과 같은 고급 응용 프로그램을 위해 MySQL과 결합 할 수 있습니다. 5. PHP를 디버깅 할 때 error_reporting () 및 var_dump ()와 같은 함수를 사용할 수 있습니다. 6. 캐싱 메커니즘을 사용하여 PHP 코드를 최적화하고 데이터베이스 쿼리를 최적화하며 내장 기능을 사용하십시오. 7
 Java 8 Stream foreach에서 나누거나 돌아 오시겠습니까?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 Stream foreach에서 나누거나 돌아 오시겠습니까?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8은 스트림 API를 소개하여 데이터 컬렉션을 처리하는 강력하고 표현적인 방법을 제공합니다. 그러나 스트림을 사용할 때 일반적인 질문은 다음과 같은 것입니다. 기존 루프는 조기 중단 또는 반환을 허용하지만 스트림의 Foreach 메소드는이 방법을 직접 지원하지 않습니다. 이 기사는 이유를 설명하고 스트림 처리 시스템에서 조기 종료를 구현하기위한 대체 방법을 탐색합니다. 추가 읽기 : Java Stream API 개선 스트림 foreach를 이해하십시오 Foreach 메소드는 스트림의 각 요소에서 하나의 작업을 수행하는 터미널 작동입니다. 디자인 의도입니다
 PHP 대 기타 언어 : 비교
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP 대 기타 언어 : 비교
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP는 특히 빠른 개발 및 동적 컨텐츠를 처리하는 데 웹 개발에 적합하지만 데이터 과학 및 엔터프라이즈 수준의 애플리케이션에는 적합하지 않습니다. Python과 비교할 때 PHP는 웹 개발에 더 많은 장점이 있지만 데이터 과학 분야에서는 Python만큼 좋지 않습니다. Java와 비교할 때 PHP는 엔터프라이즈 레벨 애플리케이션에서 더 나빠지지만 웹 개발에서는 더 유연합니다. JavaScript와 비교할 때 PHP는 백엔드 개발에서 더 간결하지만 프론트 엔드 개발에서는 JavaScript만큼 좋지 않습니다.
 PHP vs. Python : 핵심 기능 및 기능
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python : 핵심 기능 및 기능
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP와 Python은 각각 고유 한 장점이 있으며 다양한 시나리오에 적합합니다. 1.PHP는 웹 개발에 적합하며 내장 웹 서버 및 풍부한 기능 라이브러리를 제공합니다. 2. Python은 간결한 구문과 강력한 표준 라이브러리가있는 데이터 과학 및 기계 학습에 적합합니다. 선택할 때 프로젝트 요구 사항에 따라 결정해야합니다.
 PHP의 영향 : 웹 개발 및 그 이상
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP의 영향 : 웹 개발 및 그 이상
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
phphassignificallyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit
 PHP : 많은 웹 사이트의 기초
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP : 많은 웹 사이트의 기초
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP가 많은 웹 사이트에서 선호되는 기술 스택 인 이유에는 사용 편의성, 강력한 커뮤니티 지원 및 광범위한 사용이 포함됩니다. 1) 배우고 사용하기 쉽고 초보자에게 적합합니다. 2) 거대한 개발자 커뮤니티와 풍부한 자원이 있습니다. 3) WordPress, Drupal 및 기타 플랫폼에서 널리 사용됩니다. 4) 웹 서버와 밀접하게 통합하여 개발 배포를 단순화합니다.
 PHP vs. Python : 사용 사례 및 응용 프로그램
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP vs. Python : 사용 사례 및 응용 프로그램
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP는 웹 개발 및 컨텐츠 관리 시스템에 적합하며 Python은 데이터 과학, 기계 학습 및 자동화 스크립트에 적합합니다. 1.PHP는 빠르고 확장 가능한 웹 사이트 및 응용 프로그램을 구축하는 데 잘 작동하며 WordPress와 같은 CMS에서 일반적으로 사용됩니다. 2. Python은 Numpy 및 Tensorflow와 같은 풍부한 라이브러리를 통해 데이터 과학 및 기계 학습 분야에서 뛰어난 공연을했습니다.






