
Continue는 C# 프로그래밍 언어의 조건 루프 블록 내에서 사용할 수 있는 여러 조건문 중 하나이며, 반복 조건이 실행된 후 다음 단계로 이동하기 위해 루프 실행을 계속하는 절로 기능할 수 있습니다. 조건부 루프에서 다음 반복 실행. 일반적으로 for-while 루프, do-while 루프 및 for-each 루프와 같은 반복 조건부 루프와 함께 사용됩니다.
아래 다이어그램에서 루프가 시작되고 continue 문이 있으면 현재 반복을 중지하고 루프의 시작 부분으로 돌아가서 제어를 다음 반복으로 전달합니다.
흐름도
다음은 이것이 어떻게 구현되는지 보여주는 continue 문의 흐름도입니다.

다음은 for, while, do-while, foreach 및 내부 루프와 같은 루프 본문에서 작동하는 방식을 보여주는 예입니다.
아. 아래 예시에서는 for 루프를 사용했습니다. 변수 값이 5와 같으면 continue 문은 현재 반복을 건너뛰고 다음 반복으로 점프하여 값을 표시합니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System. Linq;
using System. Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for(int x=1; x<=6; x++ ) // loop runs six times
{
if (x == 5) // value is equal to 5
continue; // skips the iteration
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}출력:

ㄴ. 아래 예시에서는 변수 값이 6보다 작으면 반복을 건너뛰고 값이 6보다 크거나 같은 다음 반복으로 건너뛰어 값을 표시합니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for(int x=1; x<=10; x++ ) // loop runs ten times
{
if (x < 6) // values less than six
continue; // skips the iteration
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}출력:

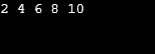
ㄷ. 아래 예에서 루프는 10번 실행되고 변수 x가 홀수일 때마다 반복을 건너뛰고 제어를 다음 반복으로 전달하고 짝수일 때 변수 x의 값을 인쇄합니다. 이것이 continue 문을 사용하여 짝수 시리즈를 인쇄하는 방법입니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int x = 2; x <= 10; x++) // loop runs ten times
{
if (x % 2 == 1) // logic to print even number
{
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.Write("{0} ", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}출력:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 0; // initializing variable
while(x < 7) // loop runs seven times
x++; // incrementing the value of x
if(x==5) // value is equal to 5
continue; // skips the iteration
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}위의 예에서는 while 루프가 사용되었습니다. 변수 x가 초기화되었습니다. x 값이 5인 경우 continue 문을 사용하여 반복을 건너뛰고 다른 값을 표시합니다.
출력:

아. 아래 예에서는 do while looping 문을 사용했습니다. 변수 x가 초기화되고 x의 값이 4가 되면 continue 문은 반복을 중지하고 다음 실행을 제어하고 값을 표시합니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 1; // initializing variable
do
{
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
x++; // incrementing the value of x
if (x == 4)
continue; // skips the iteration
} while(x < 6) ;
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}출력:

ㄴ. 아래 예에서는 while 루프가 사용되었습니다. 변수 x가 초기화되었습니다. x 값이 8이면 continue 문을 사용하여 반복을 건너뛰고 다른 값을 표시합니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 8; // initializing variable
do
{
if (x == 13)
{
x = x + 1;
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.WriteLine("a: {0}", x);
x++; // incrementing the value of x
}
while (x < 15);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}출력:

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int x = 1; x <= 4; x++) // loops run four times
{
for (int y = 1; y <= 4; y++)
{
if (x == 3 && y == 3)
{
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.WriteLine(x + " " + y);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
}위의 예에서는 내부 루프 내에서 continue 문을 사용하여 변수 x 및 y의 값을 기반으로 반복을 건너뜁니다.
출력:

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[]arr = { 2, 4, 25, 34, 28, 57}; // initializing array
foreach (int a in arr) // iteration
{
if (a == 25) //Array element value equal to 25
{
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}위의 예에서는 foreach가 반복에 사용되었습니다. 6개 요소로 구성된 요소 배열이 초기화됩니다. 변수가 25이면 continue 문은 반복을 건너뛰고 제어를 다음 반복으로 전달하고 값을 표시합니다.
출력:

이것은 for, foreach, while, do-while 등과 같은 다양한 루프 본문과 함께 continue 문을 사용하고 조건에 따라 반복을 건너뛸 수 있는 방법입니다. 대부분 continue 문은 for 및 foreach 루프 본문과 함께 사용됩니다.
위 내용은 C#에서 계속의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!