이 글에서는 HTML 이벤트 속성에 대해 자세히 설명하겠습니다. 이벤트는 사용자 작업의 결과로 수행되는 작업입니다. 예를 들어, 사용자가 데이터를 읽기 위해 키보드를 누르는 것을 키보드 이벤트라고 합니다. 이러한 활동은 사용자가 웹사이트를 살펴보고 버튼을 클릭할 때 또는 브라우저가 페이지를 조작하는 새로 고침 버튼을 눌러 페이지가 로드될 때 수행됩니다. 이 모든 행동을 하나의 사건이라고 합니다. 여기에서는 이벤트에 대한 기본적인 이해와 이벤트가 브라우저에서 사용자 작업에 따라 어떻게 작동하는지 살펴보겠습니다. 다음 섹션에서 설명하는 전체 브라우저 창에서 발생하는 다양한 유형의 이벤트가 있습니다.
HTML에서 사용할 수 있는 다양한 이벤트 변형이 있습니다. 그리고 이러한 모든 이벤트에는 이벤트 작업이 수행될 때 실행되는 이벤트 핸들러라는 이름의 작은 코드 블록이 있습니다. 이는 HTML 요소에 첨부됩니다. 이벤트 핸들러 또는 이벤트 리스너는 HTML 이벤트 속성에서 중요한 역할을 합니다. 전역적으로 선언되고 HTML 요소에 적용되는 다양한 유형의 이벤트 속성과 해당 작업을 자세히 살펴보겠습니다. 4가지 기본 이벤트 속성이 주로 사용됩니다. 그들은:
예를 들어 이러한 모든 속성을 하나씩 설명하겠습니다. 먼저 같이 가겠습니다.
코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Windows onafterprint Event
</title>
</head>
<body onafterprint="myfun()">
<h1>Windows onafterprint Event </h1>
<p>This attribute works in IE and Mozilla</p>
<body style = "text-align:center">
<script>
function myfun() {
alert("Document is being printed");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>출력:

코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: #9370DB;
background-color: #BC8F8F;
text-align: center;
padding: 20px;
}
p {
font-size: 2rem;
}
</style>
</head>
<body onbeforeprint="get()">
<h1> Attribute Demo</h1>
<p style="color:#0000FF;">trigger to print.</p>
<div class="show"></div>
<script>
function get() {
document.body.style.background = "#00BFFF";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>출력:

코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
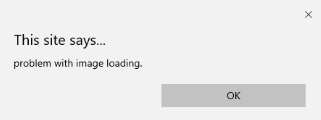
<img src="p.jpg" onerror="myFun()">
<p>hello world.</p>
<script>
function myFun() {
alert("problem with image loading.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>출력:
코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>onload event demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="pic.jpg" onload="ldImg()" width="50" height="92">
<script>
function ldImg() {
alert("image loaded without error");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>출력:
코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<title>onresize event</title>
</head>
<body>
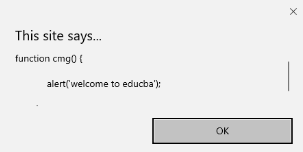
<script type="text/javascript">
function cmg() {
alert('welcome to educba');
}
window.onresize = cmg;
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="Click the button"
onclick="alert(window.onresize);">
</body>
</html>출력:

코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body onunload="onfunc()"><h1>Welcometo educba tutorial</h1>
<p>Leave the page .</p>
<script>
function onfunc() {
alert("Thank you for searching!");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>출력:
양식 컨트롤과 함께 작동합니다. 다음은 사용자가 브라우저와 상호작용할 때 발생하는 속성입니다.
코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> Form onblur </title>
<style>
body {
text-align:center;
}
h1 {
color:pink;
}
</style>
</head>
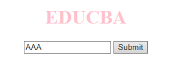
<body>
<h1>EDUCBA</h1>
<input type="text" name="fname" id="aaa"
onblur="myfunc()">
<button type="button">Submit</button>
<script>
function myfunc() {
var a = document.getElementById("aaa");
a.value = a.value.toUpperCase();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>출력:


코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>HTML onchange</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="example" action=""> <input type="text" name="rahul" onchange="alert('input is changed')"><br>
<label>select the dress color</label>
<select onchange="alert('You have changed the selection!');">
<option>pink</option>
<option>Yellow</option>
<option>White</option>
</select>
<p><strong>Note:</strong> Select any option </p>
<label>Describe yourself in short : </label> <br/><textarea cols="15" rows="7" name="details" onchange="alert('description has changed')"> </textarea><br>
<button type="button" name="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>출력:
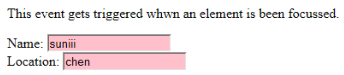
코드:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>This event gets triggered whwn an element is been focussed.</p>
Name: <input type="text" id="name" onfocus="onfoc(this.id)"><br>
Location: <input type="text" id="loc" onfocus="onfoc(this.id)">
<script>
function onfoc(a) {
document.getElementById(a).style.background = "pink";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>출력:
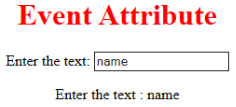
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> HTML oninput </title>
</head>
<style>
body {
text-align:center;
}
h1 {
color:red;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1> Event Attribute </h1>
Enter the text:
<input type="text" id="EDUCBA" oninput="myon()">
<p id= "sid"></p>
<script>
function myon()
{
var x = document.getElementById("EDUCBA").value;
document.getElementById("sid").innerHTML = "Enter the text : " +x;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
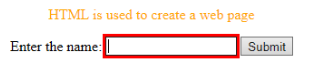

Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> example oninvalid Event </title>
<style>
p {
color:orange;
}
body {
text-align:center;
}
</style> </head>
<body>
<p> HTML is used to create a web page</p>
<form method="get">
Enter the name:
<input type="text" oninvalid="alert('Fill the text form!');" required>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form> </body>
</html>Output:

Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
body {font-family:calibri;}
label {font-variant:small-caps;}
ol {background-color:#610000; margin-top:35px;}
li {margin-top:3px; padding:3px; background-color:rose; font-size:15px;}
div {position:absolute;top:250px;left:70px; font-size:1.5em;
}
</style>
<body>
<ol>
<li>Form with input to reset and submit</li>
</ol>
<form action="" method="get" onreset="onRes()" onsubmit="onSub()">
<label>Enter input:<br /><input type="text" id="iv" oninvalid="onInva()" oninput="onInp()"></label><br /><br />
<input type="submit" value="press"> <input type="reset">
</form>
<div id="a_box"></div>
<script>
function onInva() {
alert("Input field cannot be empty!");
}
function onInp() {
var input_value = document.getElementById("iv").value;
document.getElementById("a_box").innerHTML = "Input value: <br />" + iv;
}
function onRes() {
alert("form is reset!");
}
function onSubmitEvent() {
alert("Form is loading");
location.reload();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Write in the field.</p>
<input type="search" id="value1" onsearch="myF()">
<p id="sample"></p>
<script>
function myF() {
var k = document.getElementById("value1");
document.getElementById("sample").innerHTML = "search element is: " + k.value;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
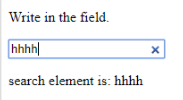
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>onselect demo</title>
<style>
h1 {
color:magenta;
}
body {
text-align:center;
}
</style>
<script>
function eduhtml() {
alert("text highlighted!");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
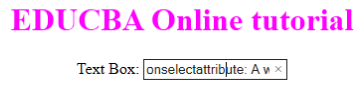
<h1>EDUCBA Online tutorial</h1>
Text Box: <input type="text" value="onselectattribute: A well defined portal" onselect="eduhtml()">
</body>
</html>
</html>Output:
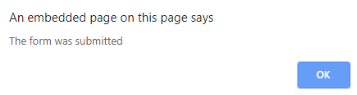
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<head>
<title> Onsubmit Example</title>
</head>
<form action="demo_form.asp" onsubmit="myF()">
Enter name: <input type="text" name="fname">
<label>Email :</label>
<input id="email" name="email" type="text">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<script>
function myF() {
alert("The form was submitted");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Example for Onkeydown.</p>
<input type="text" onkeydown="mykedwn()">
<script>
function mykedwn() {
alert("key press is activated");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p> This example shows when a user type in the text area it triggers an event </p>
<form>
<textarea onkeypress="alert('triggering onkeypress event.')" placeholder="Place the cursor inside the textarea and press a key." " cols="30" rows="4" style="background-color:pink;">> </textarea> </form>
</body>
</html>Output:

Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p> This example transforms the character to lower case.</p>
Fill the name: <input type="text" id="jjj" onkeyup="mykey()">
<script>
function mykey() {
var g = document.getElementById("jjj");
g.value = g.value.toLowerCase();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

This action triggers a mouse event when a mouse is pressed either from a computer or any external devices like a smartphone or tablet. Some of the mouse events are given below:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>HTML onclick Event</h1>
<p> Event plays a vital role in HTML.</p>
<button onclick="oncf()">Click </button>
<p id="sample"></p>
<script>
function oncf() {
document.getElementById("sample").innerHTML = "Hello World";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Code:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head><title> Event onmousemove demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This event is activated when the pointer drags its direction.</p>
<body style="width:200px;height:80px;border:2px solid;" onmousemove="javascript:alert('mouse action');">Sample text</body>
</body>
</html>Output:

Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: "#ff0000";
height: 120vh;
background-color: #610000;
text-align: center;
}
.polygon {
float: right;
shape-inside: polygon(0 0, 0 200px, 100px 200px);
clip-path: polygon(0 0, 0 250px, 100px 300px);
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background: linear-gradient(to bottom left, #7CFC00, #8B008B);
}
p {
margin: 30px auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML onmouseup Demo</h1>
<div class="polygon" onmouseup="mupfn()"></div>
<p> click below object</p>
<script>
function mupFn() {
document.querySelector('.polygon').style.transform = 'scale(2.2)';
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<title>Example demonstrating Onmouseover.</title>
<h1 id="sample" onmouseover="A()" onmouseout="B()">Mouse over </h1>
<script>
function A() {
document.getElementById("sample").style.color = "yellow";}
function B() {
document.getElementById("sample").style.color = "green";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
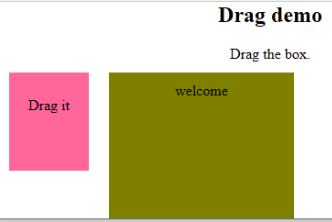
This application helps in the HTML window when the user drags the input element. Below are the different event listeners used in HTML to store dragged data.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style type = "text/css">
#b1, #b2 {
float:left;padding:11px;margin:11px; -moz-user-select:none;
}
#b1 { background-color: #FF6699; width:65px; height:85px; }
#b2 { background-color: #808000; width:180px; height:180px; }
</style>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function dStart(e) {
e.dataTransfer.effectAllowed = 'move';
e.dataTransfer.setData("Text", e.target.getAttribute('id'));
e.dataTransfer.setDragImage(e.target,0,0);
return true;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h2>Drag demo</h2>
<div> Drag the box.</div>
<div id = "b1" draggable = "true"
ondragstart = "return dStart(e)">
<p>Drag it</p>
</div>
<div id = "b2">welcome</div>
</center>
</body>
</html>Output:
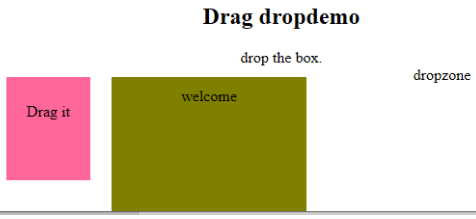
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style type = "text/css">
#b1, #b2 {
float:left;padding:11px;margin:11px; -moz-user-select:none;
}
#b1 { background-color: #FF6699; width:65px; height:85px; }
#b2 { background-color: #808000; width:180px; height:180px; }
</style>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function dStart(e) {
e.dataTransfer.effectAllowed = 'move';
e.dataTransfer.setData("Text", e.target.getAttribute('id'));
e.dataTransfer.setDragImage(e.target,0,0);
return true;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h2>Drag dropdemo</h2>
<div> drop the box.</div>
<div id = "b1" draggable = "true"
ondragstart = "return dStart(e)">
<p>Drag it</p>
</div>
<div class="droptarget"
ondrop="drop(event)"
ondragover="allowDrop(event)">
</div>
<div id = "b2">welcome</div>
<span> dropzone </span>
</center>
</body>
</html>Output:
This event attribute helps to make a web application very easier and attractive. The different occurrence of actions generates various events. Even though this approach is generally avoided, the programmer likes to learn the function assigned for the HTML attributes events. These event handlers are still executed to beautify the web pages.
This is a guide to the HTML Event Attributes. Here we discuss the Introduction to HTML Event Attributes along with Code implementation and Output. you can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –
위 내용은 HTML 이벤트 속성의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!