MongoDB 출시: 커서 기반 페이지 매김이 항상 오프셋 기반 페이지 매김보다 성능이 뛰어난 이유!
페이지 매김은 대규모 데이터 세트를 처리할 때 데이터베이스 작업에서 중요한 부분입니다. 이를 통해 데이터를 관리 가능한 단위로 분할할 수 있으므로 탐색, 처리 및 표시가 더 쉬워집니다. MongoDB는 오프셋 기반과 커서 기반이라는 두 가지 일반적인 페이지 매김 방법을 제공합니다. 두 가지 방법 모두 동일한 목적을 수행하지만 성능과 유용성 면에서 크게 차이가 있습니다. 특히 데이터세트가 커짐에 따라
두 가지 접근 방식을 살펴보고 커서 기반 페이지 매김이 종종 오프셋 기반 페이지 매김보다 성능이 뛰어난 이유를 살펴보겠습니다.
1. 오프셋 기반 페이지 매김
오프셋 기반 페이지 매김은 간단합니다. 주어진 오프셋에서 시작하여 특정 수의 레코드를 검색합니다. 예를 들어 첫 번째 페이지는 0-9 레코드를 검색하고 두 번째 페이지는 10-19 레코드를 검색하는 식으로 계속됩니다.
그러나 이 방법에는 심각한 단점이 있습니다. 상위 페이지로 이동할수록 쿼리 속도가 느려집니다. 이는 데이터베이스가 이전 페이지의 기록을 건너뛰고 스캔해야 하기 때문입니다.
오프셋 기반 페이지 매김 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
async function offset_based_pagination(params) {
const { page = 5, limit = 100 } = params;
const skip = (page - 1) * limit;
const results = await collection.find({}).skip(skip).limit(limit).toArray();
console.log(`Offset-based pagination (Page ${page}):`, results.length, "page", page, "skip", skip, "limit", limit);
}
2. 커서 기반 페이지 매김
키 세트 페이지 매김이라고도 하는 커서 기반 페이지 매김은 고유 식별자(예: ID 또는 타임스탬프)를 사용하여 레코드를 페이지 매김합니다. 특정 수의 레코드를 건너뛰는 대신 마지막으로 검색된 레코드를 다음 세트를 가져오기 위한 참조 지점으로 사용합니다.
이 접근 방식은 현재 페이지 이전의 기록을 스캔할 필요가 없기 때문에 더 효율적입니다. 결과적으로 데이터세트의 깊이에 관계없이 쿼리 시간이 일정하게 유지됩니다.
커서 기반 페이지 매김 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
async function cursor_based_pagination(params) {
const { lastDocumentId, limit = 100 } = params;
const query = lastDocumentId ? { documentId: { $gt: lastDocumentId } } : {};
const results = await collection
.find(query)
.sort({ documentId: 1 })
.limit(limit)
.toArray();
console.log("Cursor-based pagination:", results.length);
}
이 예에서 lastDocumentId는 이전 페이지의 마지막 문서 ID입니다. 다음 페이지를 쿼리할 때 데이터베이스는 이 값보다 큰 ID를 가진 문서를 가져오므로 다음 레코드 집합으로 원활하게 전환됩니다.
3. 성능비교
이 두 가지 방법이 대규모 데이터세트에서 어떻게 작동하는지 살펴보겠습니다.
async function testMongoDB() {
console.time("MongoDB Insert Time:");
await insertMongoDBRecords();
console.timeEnd("MongoDB Insert Time:");
// Create an index on the documentId field
await collection.createIndex({ documentId: 1 });
console.log("Index created on documentId field");
console.time("Offset-based pagination Time:");
await offset_based_pagination({ page: 2, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Offset-based pagination Time:");
console.time("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await cursor_based_pagination({ lastDocumentId: 170000, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await client.close();
}
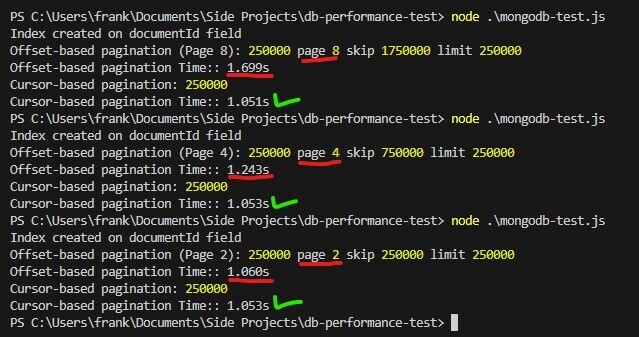
성능 테스트에서 오프셋 기반 페이지 매김은 페이지 번호가 증가할수록 더 길어집니다. 반면 커서 기반 페이지 매기기는 일관성을 유지하여 대규모 데이터 세트에 더 나은 선택입니다. 이 예는 또한 인덱싱의 강력한 기능도 보여줍니다. 인덱스를 제거하고 결과도 확인해보세요!
인덱싱이 중요한 이유
인덱스가 없으면 MongoDB는 컬렉션 스캔을 수행해야 합니다. 즉, 관련 데이터를 찾기 위해 컬렉션의 각 문서를 살펴봐야 합니다. 이는 특히 데이터세트가 커질 때 비효율적입니다. 인덱스를 사용하면 MongoDB가 쿼리 조건과 일치하는 문서를 효율적으로 찾을 수 있어 쿼리 성능이 크게 향상됩니다.
커서 기반 페이지 매김의 맥락에서 인덱스는 문서의 다음 세트(documentId 기반)를 빠르게 가져오는 것을 보장하고 더 많은 문서가 컬렉션에 추가되어도 성능이 저하되지 않도록 합니다.
결론
오프셋 기반 페이지 매김은 구현하기 쉽지만 레코드를 스캔해야 하기 때문에 대규모 데이터 세트에서는 비효율적일 수 있습니다. 반면에 커서 기반 페이지 매김은 더 확장 가능한 솔루션을 제공하여 데이터 세트 크기에 관계없이 성능을 일관되게 유지합니다. MongoDB에서 대규모 컬렉션으로 작업하는 경우 더 부드럽고 빠른 경험을 위해 커서 기반 페이지 매김을 고려해 볼 가치가 있습니다.
로컬에서 실행할 수 있는 전체 index.js는 다음과 같습니다.
const { MongoClient } = require("mongodb");
const uri = "mongodb://localhost:27017";
const client = new MongoClient(uri);
client.connect();
const db = client.db("testdb");
const collection = db.collection("testCollection");
async function insertMongoDBRecords() {
try {
let bulkOps = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 2000000; i++) {
bulkOps.push({
insertOne: {
documentId: i,
name: `Record-${i}`,
value: Math.random() * 1000,
},
});
// Execute every 10000 operations and reinitialize
if (bulkOps.length === 10000) {
await collection.bulkWrite(bulkOps);
bulkOps = [];
}
}
if (bulkOps.length > 0) {
await collection.bulkWrite(bulkOps);
console.log("? Inserted records till now -> ", bulkOps.length);
}
console.log("MongoDB Insertion Completed");
} catch (err) {
console.error("Error in inserting records", err);
}
}
async function offset_based_pagination(params) {
const { page = 5, limit = 100 } = params;
const skip = (page - 1) * limit;
const results = await collection.find({}).skip(skip).limit(limit).toArray();
console.log(`Offset-based pagination (Page ${page}):`, results.length, "page", page, "skip", skip, "limit", limit);
}
async function cursor_based_pagination(params) {
const { lastDocumentId, limit = 100 } = params;
const query = lastDocumentId ? { documentId: { $gt: lastDocumentId } } : {};
const results = await collection
.find(query)
.sort({ documentId: 1 })
.limit(limit)
.toArray();
console.log("Cursor-based pagination:", results.length);
}
async function testMongoDB() {
console.time("MongoDB Insert Time:");
await insertMongoDBRecords();
console.timeEnd("MongoDB Insert Time:");
// Create an index on the documentId field
await collection.createIndex({ documentId: 1 });
console.log("Index created on documentId field");
console.time("Offset-based pagination Time:");
await offset_based_pagination({ page: 2, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Offset-based pagination Time:");
console.time("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await cursor_based_pagination({ lastDocumentId: 170000, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await client.close();
}
testMongoDB();
위 내용은 MongoDB 출시: 커서 기반 페이지 매김이 항상 오프셋 기반 페이지 매김보다 성능이 뛰어난 이유!의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7315
7315
 9
9
 1625
1625
 14
14
 1348
1348
 46
46
 1261
1261
 25
25
 1208
1208
 29
29












