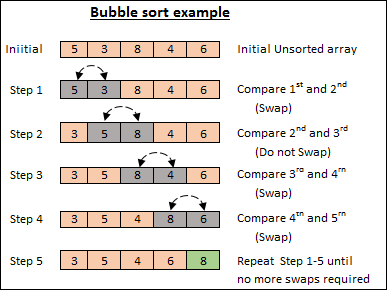
이미지 출처 : Medium
정렬은 데이터 구조와 알고리즘에서 가장 중요한 부분 중 하나입니다. 정렬 알고리즘에는 다양한 유형이 있으며, 가장 쉬운 알고리즘 중 하나인 버블 정렬을 소개합니다.
정렬 알고리즘은 컴퓨터 과학의 기본이며 버블 정렬은 가장 간단하고 직관적인 정렬 알고리즘 중 하나입니다. 이 게시물에서는 버블 정렬의 작동 방식을 살펴보고, 시간 복잡성을 분석하고, JavaScript 구현을 살펴보겠습니다.
이번 시리즈에서는 Javascript를 사용한 완전한 정렬 알고리즘 데이터 구조와 알고리즘을 공유하고 Bubble Sort부터 시작하겠습니다. 당신이 좋아하고 제가 완전한 정렬 알고리즘을 예시와 함께 공유하기를 원하신다면 좋아요와 팔로우를 눌러주세요. 여러분을 위한 콘텐츠를 만들고 준비하는 데 큰 원동력이 됩니다.
버블 정렬은 목록을 반복적으로 살펴보고 인접한 요소(다음 요소)를 비교하고 순서가 잘못된 경우 교체하는 쉬운 정렬 알고리즘입니다. 이 과정은 목록이 정렬될 때까지 반복됩니다. 이 알고리즘이라는 이름은 더 작은 요소가 목록의 맨 위로 올라오면서 "버블링"되기 때문에 붙여진 이름입니다.
JavaScript에서 Bubble Sort가 어떻게 구현되는지 코드를 살펴보겠습니다.
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]

이미 주석을 추가하고 위 코드의 각 줄을 설명했습니다. 하지만 전체 과정과 코드를 이해하는 데 도움이 되도록 자세히 설명하겠습니다.
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]
// optimized version:
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of the array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop run n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
let isSwapped = false;
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
//check if the first element is greater than the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
isSwapped = true;
}
}
//If no element swap by inner loop then break;
if (isSwapped === false) {
break;
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
버블 정렬의 시간 복잡도는 최악의 경우와 평균적인 경우 (O(n²))입니다. 여기서 (n)은 배열의 요소 수입니다. 이는 각 요소가 다른 모든 요소와 비교되기 때문입니다. 최선의 경우, 배열이 이미 정렬되어 있고 스왑이 필요하지 않을 때 알고리즘을 중지하기 위해 최적화를 추가하면 시간 복잡도는 (O(n))이 될 수 있습니다.
최상의 시나리오에서 배열이 이미 정렬된 경우 isSwapped 최적화로 인해 알고리즘이 조기 종료되어 (O(n))의 시간 복잡도가 발생할 수 있습니다.
전반적으로 버블 정렬은 2차 시간 복잡도로 인해 대규모 데이터세트에는 효율적이지 않지만, 작은 배열이나 정렬 알고리즘을 이해하기 위한 교육 도구로 유용할 수 있습니다.
버블 정렬은 단순성으로 인해 교육 목적으로 사용하기에 탁월한 알고리즘입니다. 그러나 2차 시간 복잡도로 인해 대규모 데이터 세트에는 적합하지 않습니다. 비효율성에도 불구하고 버블 정렬을 이해하면 고급 정렬 알고리즘을 학습할 수 있는 기반이 제공됩니다.
위 내용은 버블 정렬 알고리즘 이해: 단계별 가이드의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!