php简略犯错的10个地方
php容易犯错的10个地方
原文地址:
http://www.toptal.com/php/10-most-common-mistakes-php-programmers-make
译文地址:http://codecloud.net/php-2056.html
Common Mistake #1: Leaving dangling array references after foreach loops
Not sure how to use foreach loops in PHP? Using references in foreach loops can be useful if you want to operate on each element in the array that you are iterating over. For example:
<code>$arr = array(1, 2, 3, 4);foreach ($arr as &$value) { $value = $value * 2;}// $arr is now array(2, 4, 6, 8)</code>The problem is that, if you’re not careful, this can also have some undesirable side effects and consequences. Specifically, in the above example, after the code is executed, $value will remain in scope and will hold a reference to the last element in the array. Subsequent operations involving $value could therefore unintentionally end up modifying the last element in the array.
The main thing to remember is that foreach does not create a scope. Thus, $value in the above example is areference within the top scope of the script. On each iteration foreach sets the reference to point to the next element of $array. After the loop completes, therefore, $value still points to the last element of $array and remains in scope.
Here’s an example of the kind of evasive and confusing bugs that this can lead to:
<code>$array = [1, 2, 3];echo implode(',', $array), "\n";foreach ($array as &$value) {} // by referenceecho implode(',', $array), "\n";foreach ($array as $value) {} // by value (i.e., copy)echo implode(',', $array), "\n";</code>The above code will output the following:
<code>1,2,31,2,31,2,2</code>
No, that’s not a typo. The last value on the last line is indeed a 2, not a 3.
Why?
After going through the first foreach loop, $array remains unchanged but, as explained above, $value is left as a dangling reference to the last element in $array (since that foreach loop accessed $value by reference).
As a result, when we go through the second foreach loop, “weird stuff” appears to happen. Specifically, since $value is now being accessed by value (i.e., by copy), foreach copies each sequential $array element into $value in each step of the loop. As a result, here’s what happens during each step of the second foreachloop:
-
Pass 1: Copies
$array[0](i.e., “1”) into$value(which is a reference to$array[2]), so$array[2]now equals 1. So$arraynow contains [1, 2, 1]. -
Pass 2: Copies
$array[1](i.e., “2”) into$value(which is a reference to$array[2]), so$array[2]now equals 2. So$arraynow contains [1, 2, 2]. -
Pass 3: Copies
$array[2](which now equals “2”) into$value(which is a reference to$array[2]), so$array[2]still equals 2. So$arraynow contains [1, 2, 2].
To still get the benefit of using references in foreach loops without running the risk of these kinds of problems, call unset() on the variable, immediately after the foreach loop, to remove the reference; e.g.:
<code>$arr = array(1, 2, 3, 4);foreach ($arr as &$value) { $value = $value * 2;}unset($value); // $value no longer references $arr[3]</code>Common Mistake #2: Misunderstanding isset() behavior
Despite its name, isset() not only returns false if an item does not exist, but also returns false for nullvalues.
This behavior is more problematic than it might appear at first and is a common source of problems.
Consider the following:
<code>$data = fetchRecordFromStorage($storage, $identifier);if (!isset($data['keyShouldBeSet']) { // do something here if 'keyShouldBeSet' is not set}</code>The author of this code presumably wanted to check if keyShouldBeSet was set in $data. But, as discussed, isset($data['keyShouldBeSet']) will also return false if $data['keyShouldBeSet'] was set, but was set to null. So the above logic is flawed.
Here’s another example:
<code>if ($_POST['active']) { $postData = extractSomething($_POST);}// ...if (!isset($postData)) { echo 'post not active';}</code>The above code assumes that if $_POST['active'] returns true, then postData will necessarily be set, and therefore isset($postData) will return true. So conversely, the above code assumes that the only way that isset($postData) will return false is if $_POST['active'] returned false as well.
Not.
As explained, isset($postData) will also return false if $postData was set to null. It therefore is possible for isset($postData) to return false even if $_POST['active'] returned true. So again, the above logic is flawed.
And by the way, as a side point, if the intent in the above code really was to again check if $_POST['active']returned true, relying on isset() for this was a poor coding decision in any case. Instead, it would have been better to just recheck $_POST['active']; i.e.:
<code>if ($_POST['active']) { $postData = extractSomething($_POST);}// ...if ($_POST['active']) { echo 'post not active';}</code>For cases, though, where it is important to check if a variable was really set (i.e., to distinguish between a variable that wasn’t set and a variable that was set to null), the array_key_exists() method is a much more robust solution.
For example, we could rewrite the first of the above two examples as follows:
<code>$data = fetchRecordFromStorage($storage, $identifier);if (! array_key_exists('keyShouldBeSet', $data)) { // do this if 'keyShouldBeSet' isn't set}</code>Moreover, by combining array_key_exists() with get_defined_vars(), we can reliably check whether a variable within the current scope has been set or not:
<code>if (array_key_exists('varShouldBeSet', get_defined_vars())) { // variable $varShouldBeSet exists in current scope}</code>Common Mistake #3: Confusion about returning by reference vs. by value
Consider this code snippet:
<code>class Config{ private $values = []; public function getValues() { return $this->values; }}$config = new Config();$config->getValues()['test'] = 'test';echo $config->getValues()['test'];</code>If you run the above code, you’ll get the following:
<code>PHP Notice: Undefined index: test in /path/to/my/script.php on line 21</code>
What’s wrong?
The issue is that the above code confuses returning arrays by reference with returning arrays by value. Unless you explicitly tell PHP to return an array by reference (i.e., by using&), PHP will by default return the the array “by value”. This means that a copy of the array will be returned and therefore the called function and the caller will not be accessing the same instance of the array.
So the above call to getValues() returns a copy of the $values array rather than a reference to it. With that in mind, let’s revisit the two key lines from the above the example:
<code>// getValues() returns a COPY of the $values array, so this adds a 'test' element// to a COPY of the $values array, but not to the $values array itself.$config->getValues()['test'] = 'test';// getValues() again returns ANOTHER COPY of the $values array, and THIS copy doesn't// contain a 'test' element (which is why we get the "undefined index" message).echo $config->getValues()['test'];</code>
One possible fix would be to save the first copy of the $values array returned by getValues() and then operate on that copy subsequently; e.g.:
<code>$vals = $config->getValues();$vals['test'] = 'test';echo $vals['test'];</code>
That code will work fine (i.e., it will output test without generating any “undefined index” message), but depending on what you’re trying to accomplish, this approach may or may not be adequate. In particular, the above code will not modify the original $values array. So if you do want your modifications (such as adding a ‘test’ element) to affect the original array, you would instead need to modify the getValues() function to return a reference to the $values array itself. This is done by adding a & before the function name, thereby indicating that it should return a reference; i.e.:
<code>class Config{ private $values = []; // return a REFERENCE to the actual $values array public function &getValues() { return $this->values; }}$config = new Config();$config->getValues()['test'] = 'test';echo $config->getValues()['test'];</code>The output of this will be test, as expected.
But to make things more confusing, consider instead the following code snippet:
<code>class Config{ private $values; // using ArrayObject rather than array public function __construct() { $this->values = new ArrayObject(); } public function getValues() { return $this->values; }}$config = new Config();$config->getValues()['test'] = 'test';echo $config->getValues()['test'];</code>If you guessed that this would result in the same “undefined index” error as our earlier array example, you were wrong. In fact, this code will work just fine. The reason is that, unlike arrays, PHP always passes objects by reference. (ArrayObject is an SPL object, which fully mimics arrays usage, but works as an object.)
As these examples demonstrate, it is not always entirely obvious in PHP whether you are dealing with a copy or a reference. It is therefore essential to understand these default behaviors (i.e., variables and arrays are passed by value; objects are passed by reference) and also to carefully check the API documentation for the function you are calling to see if it is returning a value, a copy of an array, a reference to an array, or a reference to an object.
All that said, it is important to note that the practice of returning a reference to an array or an ArrayObject is generally something that should be avoided, as it provides the caller with the ability to modify the instance’s private data. This “flies in the face” of encapsulation. Instead, it’s better to use old style “getters” and “setters”, e.g.:
<code>class Config{ private $values = []; public function setValue($key, $value) { $this->values[$key] = $value; } public function getValue($key) { return $this->values[$key]; }}$config = new Config();$config->setValue('testKey', 'testValue');echo $config->getValue('testKey'); // echos 'testValue'</code>This approach gives the caller the ability to set or get any value in the array without providing public access to the otherwise-private $values array itself.
Common Mistake #4: Performing queries in a loop
It’s not uncommon to come across something like this if your PHP is not working:
<code>$models = [];foreach ($inputValues as $inputValue) { $models[] = $valueRepository->findByValue($inputValue);}</code>While there may be absolutely nothing wrong here, but if you follow the logic in the code, you may find that the innocent looking call above to $valueRepository->findByValue() ultimately results in a query of some sort, such as:
<code>$result = $connection->query("SELECT `x`,`y` FROM `values` WHERE `value`=" . $inputValue);</code>
As a result, each iteration of the above loop would result in a separate query to the database. So if, for example, you supplied an array of 1,000 values to the loop, it would generate 1,000 separate queries to the resource! If such a script is called in multiple threads, it could potentially bring the system to a grinding halt.
It’s therefore crucial to recognize when queries are being made by your code and, whenever possible, gather the values and then run one query to fetch all the results.
One example of a fairly common place to encounter querying being done inefficiently (i.e., in a loop) is when a form is posted with a list of values (IDs, for example). Then, to retrieve the full record data for each of the IDs, the code will loop through the array and do a separate SQL query for each ID. This will often look something like this:
<code>$data = [];foreach ($ids as $id) { $result = $connection->query("SELECT `x`, `y` FROM `values` WHERE `id` = " . $id); $data[] = $result->fetch_row();}</code>But the same thing can be accomplished much more efficiently in a single SQL query as follows:
<code>$data = [];if (count($ids)) { $result = $connection->query("SELECT `x`, `y` FROM `values` WHERE `id` IN (" . implode(',', $ids)); while ($row = $result->fetch_row()) { $data[] = $row; }}</code>It’s therefore crucial to recognize when queries are being made, either directly or indirectly, by your code. Whenever possible, gather the values and then run one query to fetch all the results. Yet caution must be exercised there as well, which leads us to our next common PHP mistake…
Common Mistake #5: Memory usage headfakes and inefficiencies
While fetching many records at once is definitely more efficient than running a single query for each row to fetch, such an approach can potentially lead to an “out of memory” condition in libmysqlclient when using PHP’s mysql extension.
To demonstrate, let’s take a look at a test box with limited resources (512MB RAM), MySQL, and php-cli.
We’ll bootstrap a database table like this:
<code>// connect to mysql$connection = new mysqli('localhost', 'username', 'password', 'database');// create table of 400 columns$query = 'CREATE TABLE `test`(`id` INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT';for ($col = 0; $col query($query);// write 2 million rowsfor ($row = 0; $row query($query);}</code>OK, now let’s check resources usage:
<code>// connect to mysql$connection = new mysqli('localhost', 'username', 'password', 'database');echo "Before: " . memory_get_peak_usage() . "\n";$res = $connection->query('SELECT `x`,`y` FROM `test` LIMIT 1');echo "Limit 1: " . memory_get_peak_usage() . "\n";$res = $connection->query('SELECT `x`,`y` FROM `test` LIMIT 10000');echo "Limit 10000: " . memory_get_peak_usage() . "\n";</code>Output:
<code>Before: 224704Limit 1: 224704Limit 10000: 224704</code>
Cool. Looks like the query is safely managed internally in terms of resources.
Just to be sure, though, let’s boost the limit one more time and set it to 100,000. Uh-oh. When we do that, we get:
<code>PHP Warning: mysqli::query(): (HY000/2013): Lost connection to MySQL server during query in /root/test.php on line 11</code>
What happened?
The issue here is the way PHP’s mysql module works. It’s really just a proxy for libmysqlclient, which does the dirty work. When a portion of data is selected, it goes directly into memory. Since this memory is not managed by PHP’s manager, memory_get_peak_usage() won’t show any increase in resources utilization as we up the limit in our query. This leads to problems like the one demonstrated above where we’re tricked into complacency thinking that our memory management is fine. But in reality, our memory management is seriously flawed and we can experience problems like the one shown above.
You can at least avoid the above headfake (although it won’t itself improve your memory utilization) by instead using the mysqlnd module. mysqlnd is compiled as a native PHP extension and it does use PHP’s memory manager.
Therefore, if we run the above test using mysqlnd rather than mysql, we get a much more realistic picture of our memory utilization:
<code>Before: 232048Limit 1: 324952Limit 10000: 32572912</code>
And it’s even worse than that, by the way. According to PHP documentation, mysql uses twice as many resources as mysqlnd to store data, so the original script using mysql really used even more memory than shown here (roughly twice as much).
To avoid such problems, consider limiting the size of your queries and using a loop with small number of iterations; e.g.:
<code>$totalNumberToFetch = 10000;$portionSize = 100;for ($i = 0; $i query( "SELECT `x`,`y` FROM `test` LIMIT $limitFrom, $portionSize");}</code>
When we consider both this PHP mistake and mistake #4 above, we realize that there is a healthy balance that your code ideally needs to achieve between, on the one hand, having your queries being too granular and repetitive, vs. having each of your individual queries be too large. As is true with most things in life, balance is needed; either extreme is not good and can cause problems with PHP not working properly.
Common Mistake #6: Ignoring Unicode/UTF-8 issues
In some sense, this is really more of an issue in PHP itself than something you would run into while debugging PHP, but it has never been adequately addressed. PHP 6’s core was to be made Unicode-aware, but that was put on hold when development of PHP 6 was suspended back in 2010.
But that by no means absolves the developer from properly handing UTF-8 and avoiding the erroneous assumption that all strings will necessarily be “plain old ASCII”. Code that fails to properly handle non-ASCII strings is notorious for introducing gnarly heisenbugs into your code. Even simple strlen($_POST['name']) calls could cause problems if someone with a last name like “Schrödinger” tried to sign up into your system.
Here’s a small checklist to avoid such problems in your code:
- If you don’t know much about Unicode and UTF-8, you should at least learn the basics. There’s a great primer here.
- Be sure to always use the
mb_*functions instead of the old string functions (make sure the “multibyte” extension is included in your PHP build). - Make sure your database and tables are set to use Unicode (many builds of MySQL still use
latin1by default). - Remember that
json_encode()converts non-ASCII symbols (e.g., “Schrödinger” becomes “Schr\u00f6dinger”) butserialize()does not. - Make sure your PHP code files are also UTF-8 encoded to avoid collisions when concatenating strings with hardcoded or configured string constants.
A particularly valuable resource in this regard is the UTF-8 Primer for PHP and MySQL post by Francisco Claria on this blog.
Common Mistake #7: Assuming $_POST will always contain your POST data
Despite its name, the $_POST array won’t always contain your POST data and can be easily found empty. To understand this, let’s take a look at an example. Assume we make a server request with a jQuery.ajax() call as follows:
<code>// js$.ajax({ url: 'http://my.site/some/path', method: 'post', data: JSON.stringify({a: 'a', b: 'b'}), contentType: 'application/json'});</code>(Incidentally, note the contentType: 'application/json' here. We send data as JSON, which is quite popular for APIs. It’s the default, for example, for posting in the AngularJS $http service.)
On the server side of our example, we simply dump the $_POST array:
<code>// phpvar_dump($_POST);</code>
Surprisingly, the result will be:
<code>array(0) { }</code>Why? What happened to our JSON string {a: 'a', b: 'b'}?
The answer is that PHP only parses a POST payload automatically when it has a content type of application/x-www-form-urlencoded or multipart/form-data. The reasons for this are historical — these two content types were essentially the only ones used years ago when PHP’s $_POST was implemented. So with any other content type (even those that are quite popular today, like application/json), PHP doesn’t automatically load the POST payload.
Since $_POST is a superglobal, if we override it once (preferably early in our script), the modified value (i.e., including the POST payload) will then be referenceable throughout our code. This is important since $_POST is commonly used by PHP frameworks and almost all custom scripts to extract and transform request data.
So, for example, when processing a POST payload with a content type of application/json, we need to manually parse the request contents (i.e., decode the JSON data) and override the $_POST variable, as follows:
<code>// php$_POST = json_decode(file_get_contents('php://input'), true);</code>Then when we dump the $_POST array, we see that it correctly includes the POST payload; e.g.:
<code>array(2) { ["a"]=> string(1) "a" ["b"]=> string(1) "b" }</code>Common Mistake #8: Thinking that PHP supports a character data type
Look at this sample piece of code and try guessing what it will print:
<code>for ($c = 'a'; $c </code>
If you answered ‘a’ through ‘z’, you may be surprised to know that you were wrong.
Yes, it will print ‘a’ through ‘z’, but then it will also print ‘aa’ through ‘yz’. Let’s see why.
In PHP there’s no char datatype; only string is available. With that in mind, incrementing the string z in PHP yields aa:
<code>php> $c = 'z'; echo ++$c . "\n";aa</code>
Yet to further confuse matters, aa is lexicographically less than z:
<code>php> var_export((boolean)('aa' </code>That’s why the sample code presented above prints the letters a through z, but then also prints aa throughyz. It stops when it reachs za, which is the first value it encounters that it “greater than” z:
<code>php> var_export((boolean)('za' </code>That being the case, here’s one way to properly loop through the values ‘a’ through ‘z’ in PHP:
<code>for ($i = ord('a'); $i </code>Or alternatively:
<code>$letters = range('a', 'z');for ($i = 0; $i </code>Common Mistake #9: Ignoring coding standards
Although ignoring coding standards doesn’t directly lead to needing to debug PHP code, it is still probably one of the most important things to discuss here.
Ignoring coding standards can cause a whole slew of problems on a project. At best, it results in code that is inconsistent (since every developer is “doing their own thing”). But at worst, it produces PHP code that does not work or can be difficult (sometimes almost impossible) to navigate, making it extremely difficult to debug, enhance, maintain. And that means reduced productivity for your team, including lots of wasted (or at least unnecessary) effort.
Fortunately for PHP developers, there is the PHP Standards Recommendation (PSR), comprised of the following five standards:
- PSR-0: Autoloading Standard
- PSR-1: Basic Coding Standard
- PSR-2: Coding Style Guide
- PSR-3: Logger Interface
- PSR-4: Autoloader
PSR was originally created based on inputs from maintainers of the most recognized platforms on the market. Zend, Drupal, Symfony, Joomla and others contributed to these standards, and are now following them. Even PEAR, which attempted to be a standard for years before that, participates in PSR now.
In some sense, it almost doesn’t matter what your coding standard is, as long as you agree on a standard and stick to it, but following the PSR is generally a good idea unless you have some compelling reason on your project to do otherwise. More and more teams and projects are conforming with the PSR. Tt’s definitely recognized at this point as “the” standard by the majority of PHP developers, so using it will help ensure that new developers are familiar and comfortable with your coding standard when they join your team.
Common Mistake #10: Misusing empty()
Some PHP developers like using empty() for boolean checks for just about everything. There are case, though, where this can lead to confusion.
First, let’s come back to arrays and ArrayObject instances (which mimic arrays). Given their similarity, it’s easy to assume that arrays and ArrayObject instances will behave identically. This proves, however, to be a dangerous assumption. For example, in PHP 5.0:
<code>// PHP 5.0 or later:$array = [];var_dump(empty($array)); // outputs bool(true) $array = new ArrayObject();var_dump(empty($array)); // outputs bool(false)// why don't these both produce the same output?</code>
And to make matters even worse, the results would have been different prior to PHP 5.0:
<code>// Prior to PHP 5.0:$array = [];var_dump(empty($array)); // outputs bool(false) $array = new ArrayObject();var_dump(empty($array)); // outputs bool(false)</code>
This approach is unfortunately quite popular. For example, this is the way Zend\Db\TableGateway of Zend Framework 2 returns data when calling current() on TableGateway::select() result as the doc suggests. Developer can easily become victim of this mistake with such data.
To avoid these issues, the better approach to checking for empty array structures is to use count():
<code>// Note that this work in ALL versions of PHP (both pre and post 5.0):$array = [];var_dump(count($array)); // outputs int(0)$array = new ArrayObject();var_dump(count($array)); // outputs int(0)</code>
And incidentally, since PHP casts 0 to false, count() can also be used within if () conditions to check for empty arrays. It’s also worth noting that, in PHP, count() is constant complexity (O(1) operation) on arrays, which makes it even clearer that it’s the right choice.
Another example when empty() can be dangerous is when combining it with the magic class function __get(). Let’s define two classes and have a test property in both.
First let’s define a Regular class that includes test as a normal property:
<code>class Regular{ public $test = 'value';}</code>Then let’s define a Magic class that uses the magic __get() operator to access its test property:
<code>class Magic{ private $values = ['test' => 'value']; public function __get($key) { if (isset($this->values[$key])) { return $this->values[$key]; } }}</code>OK, now let’s see what happens when we attempt to access the test property of each of these classes:
<code>$regular = new Regular();var_dump($regular->test); // outputs string(4) "value"$magic = new Magic();var_dump($magic->test); // outputs string(4) "value"</code>
Fine so far.
But now let’s see what happens when we call empty() on each of these:
<code>var_dump(empty($regular->test)); // outputs bool(false)var_dump(empty($magic->test)); // outputs bool(true)</code>
Ugh. So if we rely on empty(), we can be misled into believing that the test property of $magic is empty, whereas in reality it is set to 'value'.
Unfortunately, if a class uses the magic __get() function to retrieve a property’s value, there’s no foolproof way to check if that property value is empty or not. Outside of the class’ scope, you can really only check if a null value will be returned, and that doesn’t necessarily mean that the corresponding key is not set, since it actually could have been set to null.
In contrast, if we attempt to reference a non-existent property of a Regular class instance, we will get a notice similar to the following:
<code>Notice: Undefined property: Regular::$nonExistantTest in /path/to/test.php on line 10Call Stack: 0.0012 234704 1. {main}() /path/to/test.php:0</code>So the main point here is that the empty() method should be used with care as it can lend itself to confusing – or even potentially misleading – results, if one is not careful.
Wrap-up
PHP’s ease of use can lull developers into a false sense of comfort, leaving themselves vulnerable to lengthy PHP debugging due to some of the nuances and idiosyncrasies of the language. This can result in PHP not working and problems such as those described herein.
The PHP language has evolved significantly over the course of its 20 year history. Familiarizing oneself with its subtleties is a worthwhile endeavor, as it will help ensure that the software you produce is more scalable, robust, and maintainable.

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7444
7444
 15
15
 1371
1371
 52
52
 76
76
 11
11
 38
38
 19
19
 9
9
 6
6
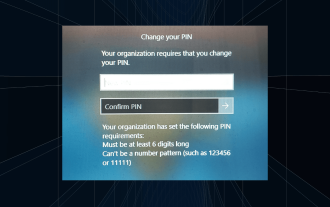 해결 방법: 조직에서 PIN 변경을 요구합니다.
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
해결 방법: 조직에서 PIN 변경을 요구합니다.
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
로그인 화면에 "귀하의 조직에서 PIN 변경을 요구합니다"라는 메시지가 나타납니다. 이는 개인 장치를 제어할 수 있는 조직 기반 계정 설정을 사용하는 컴퓨터에서 PIN 만료 제한에 도달한 경우 발생합니다. 그러나 개인 계정을 사용하여 Windows를 설정하는 경우 이상적으로는 오류 메시지가 나타나지 않습니다. 항상 그런 것은 아니지만. 오류가 발생한 대부분의 사용자는 개인 계정을 사용하여 신고합니다. 조직에서 Windows 11에서 PIN을 변경하도록 요청하는 이유는 무엇입니까? 귀하의 계정이 조직과 연결되어 있을 수 있으므로 이를 확인하는 것이 기본 접근 방식입니다. 도메인 관리자에게 문의하면 도움이 될 수 있습니다! 또한 잘못 구성된 로컬 정책 설정이나 잘못된 레지스트리 키로 인해 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다. 지금 바로
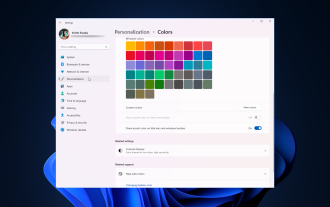 Windows 11에서 창 테두리 설정을 조정하는 방법: 색상 및 크기 변경
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Windows 11에서 창 테두리 설정을 조정하는 방법: 색상 및 크기 변경
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Windows 11은 신선하고 우아한 디자인을 전면에 내세웠습니다. 현대적인 인터페이스를 통해 창 테두리와 같은 미세한 세부 사항을 개인화하고 변경할 수 있습니다. 이 가이드에서는 Windows 운영 체제에서 자신의 스타일을 반영하는 환경을 만드는 데 도움이 되는 단계별 지침을 설명합니다. 창 테두리 설정을 변경하는 방법은 무엇입니까? +를 눌러 설정 앱을 엽니다. Windows개인 설정으로 이동하여 색상 설정을 클릭합니다. 색상 변경 창 테두리 설정 창 11" Width="643" Height="500" > 제목 표시줄 및 창 테두리에 강조 색상 표시 옵션을 찾아 옆에 있는 스위치를 토글합니다. 시작 메뉴 및 작업 표시줄에 강조 색상을 표시하려면 시작 메뉴와 작업 표시줄에 테마 색상을 표시하려면 시작 메뉴와 작업 표시줄에 테마 표시를 켭니다.
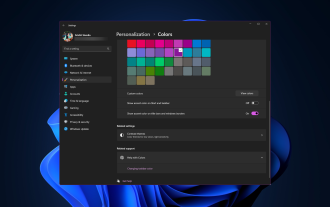 Windows 11에서 제목 표시줄 색상을 변경하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Windows 11에서 제목 표시줄 색상을 변경하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
기본적으로 Windows 11의 제목 표시줄 색상은 선택한 어두운/밝은 테마에 따라 다릅니다. 그러나 원하는 색상으로 변경할 수 있습니다. 이 가이드에서는 이를 변경하고 데스크톱 환경을 개인화하여 시각적으로 매력적으로 만드는 세 가지 방법에 대한 단계별 지침을 논의합니다. 활성 창과 비활성 창의 제목 표시줄 색상을 변경할 수 있습니까? 예, 설정 앱을 사용하여 활성 창의 제목 표시줄 색상을 변경하거나 레지스트리 편집기를 사용하여 비활성 창의 제목 표시줄 색상을 변경할 수 있습니다. 이러한 단계를 알아보려면 다음 섹션으로 이동하세요. Windows 11에서 제목 표시줄 색상을 변경하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 1. 설정 앱을 사용하여 +를 눌러 설정 창을 엽니다. Windows"개인 설정"으로 이동한 다음
 Windows 11/10 복구의 OOBELANGUAGE 오류 문제
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Windows 11/10 복구의 OOBELANGUAGE 오류 문제
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Windows Installer 페이지에 "OOBELANGUAGE" 문과 함께 "문제가 발생했습니다."가 표시됩니까? 이러한 오류로 인해 Windows 설치가 중단되는 경우가 있습니다. OOBE는 즉시 사용 가능한 경험을 의미합니다. 오류 메시지에서 알 수 있듯이 이는 OOBE 언어 선택과 관련된 문제입니다. 걱정할 필요가 없습니다. OOBE 화면 자체에서 레지스트리를 편집하면 이 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다. 빠른 수정 – 1. OOBE 앱 하단에 있는 “다시 시도” 버튼을 클릭하세요. 그러면 더 이상의 문제 없이 프로세스가 계속됩니다. 2. 전원 버튼을 사용하여 시스템을 강제 종료합니다. 시스템이 다시 시작된 후 OOBE가 계속되어야 합니다. 3. 인터넷에서 시스템 연결을 끊습니다. 오프라인 모드에서 OOBE의 모든 측면을 완료하세요.
 Windows 11에서 작업 표시줄 축소판 미리 보기를 활성화 또는 비활성화하는 방법
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Windows 11에서 작업 표시줄 축소판 미리 보기를 활성화 또는 비활성화하는 방법
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
작업 표시줄 축소판은 재미있을 수도 있지만 주의를 산만하게 하거나 짜증나게 할 수도 있습니다. 이 영역 위로 얼마나 자주 마우스를 가져가는지 고려하면 실수로 중요한 창을 몇 번 닫았을 수도 있습니다. 또 다른 단점은 더 많은 시스템 리소스를 사용한다는 것입니다. 따라서 리소스 효율성을 높일 수 있는 방법을 찾고 있다면 비활성화하는 방법을 알려드리겠습니다. 그러나 하드웨어 사양이 이를 처리할 수 있고 미리 보기가 마음에 들면 활성화할 수 있습니다. Windows 11에서 작업 표시줄 축소판 미리 보기를 활성화하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 1. 설정 앱을 사용하여 키를 탭하고 설정을 클릭합니다. Windows에서는 시스템을 클릭하고 정보를 선택합니다. 고급 시스템 설정을 클릭합니다. 고급 탭으로 이동하여 성능 아래에서 설정을 선택합니다. "시각 효과"를 선택하세요.
 Windows 11의 디스플레이 크기 조정 가이드
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Windows 11의 디스플레이 크기 조정 가이드
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Windows 11의 디스플레이 크기 조정과 관련하여 우리 모두는 서로 다른 선호도를 가지고 있습니다. 큰 아이콘을 좋아하는 사람도 있고, 작은 아이콘을 좋아하는 사람도 있습니다. 그러나 올바른 크기 조정이 중요하다는 점에는 모두가 동의합니다. 잘못된 글꼴 크기 조정이나 이미지의 과도한 크기 조정은 작업 시 생산성을 저하시킬 수 있으므로 시스템 기능을 최대한 활용하려면 이를 사용자 정의하는 방법을 알아야 합니다. Custom Zoom의 장점: 화면의 텍스트를 읽기 어려운 사람들에게 유용한 기능입니다. 한 번에 화면에서 더 많은 것을 볼 수 있도록 도와줍니다. 특정 모니터 및 응용 프로그램에만 적용되는 사용자 정의 확장 프로필을 생성할 수 있습니다. 저사양 하드웨어의 성능을 향상시키는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 화면의 내용을 더 효과적으로 제어할 수 있습니다. 윈도우 11을 사용하는 방법
 Windows 11에서 밝기를 조정하는 10가지 방법
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Windows 11에서 밝기를 조정하는 10가지 방법
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
화면 밝기는 최신 컴퓨팅 장치를 사용할 때 필수적인 부분이며, 특히 화면을 장시간 볼 때 더욱 그렇습니다. 눈의 피로를 줄이고, 가독성을 높이며, 콘텐츠를 쉽고 효율적으로 보는 데 도움이 됩니다. 그러나 설정에 따라 밝기 관리가 어려울 수 있으며, 특히 새로운 UI 변경이 적용된 Windows 11에서는 더욱 그렇습니다. 밝기를 조정하는 데 문제가 있는 경우 Windows 11에서 밝기를 관리하는 모든 방법은 다음과 같습니다. Windows 11에서 밝기를 변경하는 방법 [10가지 설명] 단일 모니터 사용자는 다음 방법을 사용하여 Windows 11에서 밝기를 조정할 수 있습니다. 여기에는 단일 모니터를 사용하는 데스크탑 시스템과 노트북이 포함됩니다. 시작하자. 방법 1: 알림 센터 사용 알림 센터에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
 Windows Server에서 활성화 오류 코드 0xc004f069를 수정하는 방법
Jul 22, 2023 am 09:49 AM
Windows Server에서 활성화 오류 코드 0xc004f069를 수정하는 방법
Jul 22, 2023 am 09:49 AM
Windows의 정품 인증 프로세스에서 갑자기 이 오류 코드 0xc004f069가 포함된 오류 메시지가 표시되는 경우가 있습니다. 활성화 프로세스가 온라인으로 진행되더라도 Windows Server를 실행하는 일부 이전 시스템에서 이 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다. 이러한 초기 점검을 수행하고 시스템 활성화에 도움이 되지 않으면 기본 해결 방법으로 이동하여 문제를 해결하십시오. 해결 방법 - 오류 메시지와 활성화 창을 닫습니다. 그런 다음 컴퓨터를 다시 시작하십시오. Windows 정품 인증 프로세스를 처음부터 다시 시도하세요. 수정 1 – 터미널에서 활성화 cmd 터미널에서 Windows Server Edition 시스템을 활성화합니다. 1단계 – Windows Server 버전 확인 현재 사용하고 있는 W 종류를 확인해야 합니다.




