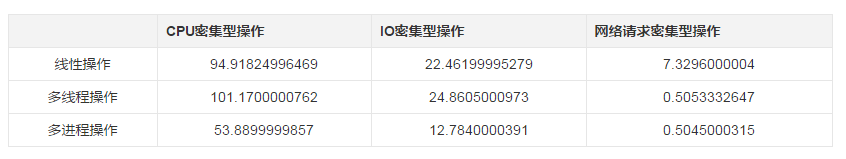
비교 실험
데이터에 따르면 멀티 스레드 프로세스가 CPU 집약적이라면 멀티 스레드는 효율성을 크게 향상시키지 못하고 오히려 스레드를 자주 전환하여 효율성이 저하될 수 있습니다. . IO 집약적인 경우 멀티 프로세스를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다. 멀티 스레드 프로세스는 IO 차단이 다른 스레드를 실행하는 동안 유휴 시간을 사용하여 효율성을 높일 수 있습니다. 그래서 실험을 바탕으로 다양한 시나리오의 효율성을 비교합니다.
|하드 디스크 | -|- ---|---------|
| Windows 10 | 듀얼 코어|8GB|기계식 하드 드라이브|
import requests import time from threading import Thread from multiprocessing import Process
def count(x, y):
# 使程序完成150万计算
c = 0
while c < 500000:
c += 1
x += x
y += ydef write():
f = open("test.txt", "w")
for x in range(5000000):
f.write("testwrite\n")
f.close()
def read():
f = open("test.txt", "r")
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
_head = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/48.0.2564.116 Safari/537.36'}
url = "http://www.tieba.com"
def http_request():
try:
webPage = requests.get(url, headers=_head)
html = webPage.text
return {"context": html}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": e}# CPU密集操作
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
count(1, 1)
print("Line cpu", time.time() - t)
# IO密集操作
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
write()
read()
print("Line IO", time.time() - t)
# 网络请求密集型操作
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
http_request()
print("Line Http Request", time.time() - t)counts = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
thread = Thread(target=count, args=(1,1))
counts.append(thread)
thread.start()
e = counts.__len__()
while True:
for th in counts:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print(time.time() - t)def io():
write()
read()
t = time.time()
ios = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
thread = Thread(target=count, args=(1,1))
ios.append(thread)
thread.start()
e = ios.__len__()
while True:
for th in ios:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print(time.time() - t)t = time.time()
ios = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
thread = Thread(target=http_request)
ios.append(thread)
thread.start()
e = ios.__len__()
while True:
for th in ios:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print("Thread Http Request", time.time() - t)counts = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
process = Process(target=count, args=(1,1))
counts.append(process)
process.start()
e = counts.__len__()
while True:
for th in counts:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print("Multiprocess cpu", time.time() - t)t = time.time()
ios = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
process = Process(target=io)
ios.append(process)
process.start()
e = ios.__len__()
while True:
for th in ios:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print("Multiprocess IO", time.time() - t)t = time.time()
httprs = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
process = Process(target=http_request)
ios.append(process)
process.start()
e = httprs.__len__()
while True:
for th in httprs:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print("Multiprocess Http Request", time.time() - t)실험 결과