ng를 사용할 때 흔히 사용하는 속성에 대해서는 여기서는 소개하지 않겠습니다.
1.multiElement
명령 범위를 지정하는 기능으로, 가장 많이 사용되는 것은 ng-repeat-start와 ng-repeat-end입니다.
2.우선순위
명령 우선순위는 우선순위가 높을수록 명령이 더 빨리 실행됩니다.
3.터미널
우선순위가 낮은 명령어의 작동을 허용할지 여부. true인 경우 현재 명령어와 같거나 높은 명령어만 실행할 수 있습니다. 가장 일반적인 것은 ngIf
4.templateNamespace
선언 템플릿 형식에는 세 가지 옵션이 있습니다: svg, html, math
5.transclude
일부 사람들은 질문을 할 수 있습니다. 포함이 인기 없는 속성으로 간주됩니까? 사실, 모든 사람은 자신이 상상한 것만큼 transclude에 대해 잘 알지 못합니다. 일반적으로 모든 사람이 사용하는 유일한 속성은 true와 false입니다. 여기서는 이 두 가지 속성에 대해 이야기하지 않겠습니다. 여기서 주로 이야기하는 것은 transclude:element입니다. 하루 종일 Google을 검색했지만 이 속성을 올바르게 설명하는 방법을 찾을 수 없었습니다. Google의 답변이 너무 문서화되어 있다고 생각합니다. 마지막으로 $transclude를 공부한 후 이 속성의 기능이 무엇인지 깨달았습니다. 함수에 대해 이야기하기 전에 먼저 $transclude
명령의 컴파일 또는 링크 기간에 상관없이 마지막 매개변수는 $transclude입니다. 여기서는 소스 코드가 실제로 어떻게 정의되는지 살펴보겠습니다. ng1.5.3의
function controllersBoundTransclude(scope, cloneAttachFn, futureParentElement, slotName) {
var transcludeControllers;
// No scope passed in:
if (!isScope(scope)) {
slotName = futureParentElement;
futureParentElement = cloneAttachFn;
cloneAttachFn = scope;
scope = undefined;
}
if (hasElementTranscludeDirective) {
transcludeControllers = elementControllers;
}
if (!futureParentElement) {
futureParentElement = hasElementTranscludeDirective ? $element.parent() : $element;
}
if (slotName) {
// slotTranscludeFn can be one of three things:
// * a transclude function - a filled slot
// * `null` - an optional slot that was not filled
// * `undefined` - a slot that was not declared (i.e. invalid)
var slotTranscludeFn = boundTranscludeFn.$$slots[slotName];
if (slotTranscludeFn) {
return slotTranscludeFn(scope, cloneAttachFn, transcludeControllers, futureParentElement, scopeToChild);
} else if (isUndefined(slotTranscludeFn)) {
throw $compileMinErr('noslot',
'No parent directive that requires a transclusion with slot name "{0}". ' +
'Element: {1}',
slotName, startingTag($element));
}
} else {
return boundTranscludeFn(scope, cloneAttachFn, transcludeControllers, futureParentElement, scopeToChild);
}
}을 살펴보니 특히 짚고 넘어가야 할 함수가 또 있는데, 마지막에 반환되는boundTranscludeFn 메소드는 다음과 같습니다.
function createBoundTranscludeFn(scope, transcludeFn, previousBoundTranscludeFn) {
function boundTranscludeFn(transcludedScope, cloneFn, controllers, futureParentElement, containingScope) {
if (!transcludedScope) {
transcludedScope = scope.$new(false, containingScope);
transcludedScope.$$transcluded = true;
}
return transcludeFn(transcludedScope, cloneFn, {
parentBoundTranscludeFn: previousBoundTranscludeFn,
transcludeControllers: controllers,
futureParentElement: futureParentElement
});
}angular.module('MyApp', [])
.directive('dropPanel', function() {
return {
transclude: 'element',
replace: true,
template: "<div class='drop-panel'>" +
"<span ng-transclude class='111'></span>" +
"</div>",
link: function(scope, el, c, d, $transclude) {
$transclude(function ngRepeatTransclude(clone, scope) {
console.log(clone);
})
}
}
})
.directive('dropPanel2', function() {
return {
transclude: true,
replace: true,
template: "<div class='drop-panel'>" +
"<span ng-transclude class='111'></span>" +
"</div>",
link: function(scope, el, c, d, $transclude) {
$transclude(function ngRepeatTransclude(clone, scope) {
console.log(clone);
})
}
}
})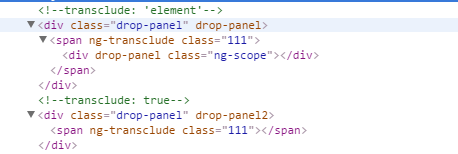 위 그림을 보면 DOM의 두 클론이 다르다는 것을 확실히 알 수 있습니다. 또한, 속성을 'element'로 선언하는 경우 대체를 true로 선언해야 합니다. 렌더링되기 전에. 많은 정보를 확인하고 마침내 중단점을 사용하여 올바른 결론에 도달했습니다. 중단점 추적 결과, 교체가 선언되지 않으면 ngTransclude 명령이 실행되지 않는 것 같습니다. 이는 매우 이상합니다. 이로 인해 렌더링에 실패하게 되었습니다. 둘째, 최종 분석은 두 작업의 DOM 요소가 다르다는 것입니다. transclude를 요소로 선언하면 교체가 true이고, 얻는 DOM 노드는 transclude 속성을 포함하는 노드(자식 노드)이고, 그렇지 않으면 false입니다. , 당신이 얻는 것은 transclude 속성을 포함하는 노드(상위 노드)와 ng 자체가 해당 노드를 순회하지 않아 ngTransclude 명령 실행에 실패하는 결과를 초래한다는 것입니다.
위 그림을 보면 DOM의 두 클론이 다르다는 것을 확실히 알 수 있습니다. 또한, 속성을 'element'로 선언하는 경우 대체를 true로 선언해야 합니다. 렌더링되기 전에. 많은 정보를 확인하고 마침내 중단점을 사용하여 올바른 결론에 도달했습니다. 중단점 추적 결과, 교체가 선언되지 않으면 ngTransclude 명령이 실행되지 않는 것 같습니다. 이는 매우 이상합니다. 이로 인해 렌더링에 실패하게 되었습니다. 둘째, 최종 분석은 두 작업의 DOM 요소가 다르다는 것입니다. transclude를 요소로 선언하면 교체가 true이고, 얻는 DOM 노드는 transclude 속성을 포함하는 노드(자식 노드)이고, 그렇지 않으면 false입니다. , 당신이 얻는 것은 transclude 속성을 포함하는 노드(상위 노드)와 ng 자체가 해당 노드를 순회하지 않아 ngTransclude 명령 실행에 실패하는 결과를 초래한다는 것입니다.
제가 생각했던 점을 봤습니다. 일반적인 의미는 다음과 같습니다. 기능적 고려 사항으로 인해 요소 속성을 사용할 때 일반적으로 복제 기능은 수행해야 하는 작업이 DOM에 추가되는 경우에만 사용됩니다.
이런 관점이 좋다고 생각합니다. ngrepeat에 대한 소개를 많이 읽었는데, ngrepeat 소스 코드가 $scope.$new()를 통해 하위 범위를 생성한다고 합니다. 실제로는 그렇지 않습니다. 완전히 맞습니다. $scope.$new가 하위 범위를 생성하는 데 사용되는 것은 사실이지만 이 생성 기능은 $transclude 함수에 맡겨져 있습니다. 실제로 ngrepeat의 소스 코드는 $transclude를 사용하여 하위 범위를 생성하고 DOM 노드를 추가합니다. 위의 요점과 비슷합니다.