09.Java 기초 - 주석
기본 개념
Annotation(annotation)은 프로그램을 통해 지정된 프로그램 요소의 Annotation 개체를 얻을 수 있는 인터페이스입니다. 그런 다음 Annotation 개체를 통해 주석의 메타데이터를 가져옵니다.
주석의 용도와 목적에 따라 주석을 시스템 주석, 메타 주석, 사용자 정의 주석의 세 가지 범주로 나눌 수 있습니다.
시스템 주석
시스템 주석은 주로 @Override, @Deprecated, @SuppressWarnings를 포함하는 JDK 내장 주석입니다.
1.@Override
메소드 수정이란 해당 메소드가 상위 클래스의 메소드 또는 인터페이스를 구현하는 메소드를 오버라이드한다는 의미입니다
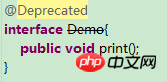
interface Demo{ public void print();
}public class Test implements Demo{
@Override
public void print() {
}
}2.@사용 중단됨
사용되지 않는 메서드 수정
3.@ SuppressWarnnings
컴파일러 경고를 억제합니다. 즉, 경고를 제거합니다.
공통 매개변수 값은 다음과 같습니다.
| 名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| rawtypes | 表示传参时也要传递带泛型的参数 |
| deprecation | 使用了不赞成使用的类或方法时的警告 |
| unchecked | 执行了未检查的转换时的警告,例如当使用集合时没有用泛型 (Generics) 来指定集合保存的类型 |
| fallthrough | 当 Switch 程序块直接通往下一种情况而没有 Break 时的警告; |
| path | 在类路径、源文件路径等中有不存在的路径时的警告; |
| serial | 当在可序列化的类上缺少 serialVersionUID 定义时的警告; |
| finally | 任何 finally 子句不能正常完成时的警告; |
| all | 关于以上所有情况的警告。 |
예시는 다음과 같습니다.
// 抑制单类型@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void print() { @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
}// 抑制多类型@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })public void print() {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
}// 抑制所有类型@SuppressWarnings({ "all" })public void print() {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
}메타 주석
Meta-annotation 다른 주석을 추가하는 기능입니다. Java5.0은 다른 주석 유형에 대한 설명을 제공하는 데 사용되는 4가지 표준 메타 주석 유형을 정의합니다.
정의된 메타 주석은 @Target, @Retention, @Documented, @Inherited입니다.
1.@Target
@Target은 Annotation으로 수정되는 객체의 범위를 정의합니다. 구체적인 수정 범위는 다음과 같습니다.
public enum ElementType { // 用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
TYPE, // 用于描述域(即变量)
FIELD, // 用于描述方法
METHOD, // 用于描述参数
PARAMETER, // 用于描述构造器
CONSTRUCTOR, // 用于描述局部变量
LOCAL_VARIABLE, // 用于描述注解类型
ANNOTATION_TYPE, // 用于描述包
PACKAGE
}2.@Retention
@Retention은 Annotation이 유지되는 기간, 즉 Annotation의 수명 주기를 나타냅니다.
public enum RetentionPolicy { // 在源文件中有效(编译器要丢弃的注解)
SOURCE, // class 文件中有效(默认,编译器将把注解记录在类文件中,但在运行时 VM 不需要保留注解)
CLASS, // 在运行时有效(编译器将把注解记录在类文件中,在运行时 VM 将保留注解,因此可以反射性地读取)
RUNTIME
}3.@Documented
@Documented는 특정 유형의 주석이 javadoc 및 유사한 기본 도구를 통해 문서화됨을 나타내는 Annotation을 정의합니다.
유형 선언에 Documented라는 주석이 달린 경우 해당 주석은 주석이 달린 요소의 공개 API의 일부가 됩니다.
4.@Inherited
@Inherited는 주석 유형이 자동으로 상속됨을 나타내는 Annotation을 정의합니다. 즉, @Inherited로 수정된 주석 유형은 다음과 같습니다. A 클래스를 사용하면 이 주석은 이 클래스의 하위 클래스에 사용됩니다.
클래스 이외의 항목에 주석을 달기 위해 주석 유형을 사용하는 경우 @Inherited가 유효하지 않습니다.
이 메타 주석은 상위 클래스에서 주석 상속을 용이하게 할 뿐입니다. 구현된 인터페이스의 주석은 유효하지 않습니다.
@Inherited 주석 유형으로 주석이 달린 주석의 Retention이 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME인 경우 리플렉션 API는 이 상속을 강화합니다. @Inherited 주석 유형의 주석을 쿼리하기 위해 java.lang.reflect를 사용하면 반사 코드 검사가 작동하기 시작합니다. 지정된 주석 유형을 찾을 때까지 클래스와 해당 상위 클래스를 확인하거나 클래스 상속 구조의 최상위 수준을 확인합니다.
에 도달했습니다. 예는 다음과 같습니다.
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Inherited@interface MyAnotation{
public String name();
}// 作用在类上@MyAnotation(name="parent")
class Parent{
}// 继承 Parent 类public class Test extends Parent{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> cls = Test.class; // 通过 @Inherited 继承父类的注解
Annotation annotation = cls.getAnnotation(MyAnotation.class);
MyAnotation myAnotation = (MyAnotation) annotation;
System.out.println(myAnotation.name());
}
}// 输出结果:parent(若注释掉注解,返回异常)사용자 정의 주석
1.
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@interface MyAnnotation {
public String name(); public String age();
}// 调用注解@MyAnnotation(name="cook",age="100")public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> cls = Test.class; // 1.取得所有注解
Annotation[] annotations =cls.getAnnotations(); // 2.取得指定注解
MyAnnotation annotation =
(MyAnnotation)cls.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
}
}2. 메소드 주석
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 修改作用范围@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@interface MyAnnotation { public String name(); public String age();
}
// 调用注解public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Test.class;
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("print", null); // 1.取得所有注解
Annotation[] annotations = method.getDeclaredAnnotations(); // 2.取得指定注解
MyAnnotation annotation =
(MyAnnotation)method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
}3. 매개변수 주석
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 修改作用范围@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)@interface MyAnnotation { public String name(); public String age();
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Test.class;
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("print", new Class[]{String.class,String.class});
getAllAnnotations(method);
} // 作用在参数上
public void print(@MyAnnotation(name = "cook", age = "100")
String name, String age) { } public static void getAllAnnotations(Method method) {
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotions = method.getParameterAnnotations();
// 通过反射只能取得所有参数类型,不能取得指定参数
Class[] paraemterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
int i = 0;
for (Annotation[] annotations : parameterAnnotions) {
Class paraemterType = paraemterTypes[i++];
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
if (annotation instanceof MyAnnotation) {
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println(paraemterType.getName());
System.out.println(myAnnotation.name());
System.out.println(myAnnotation.age());
}
}
}
}
}4. 변수 주석
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 修改作用范围@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@interface MyAnnotation { public String name(); public String age();
}public class Test {
// 作用在变量上
@MyAnnotation(name = "cook", age = "100")
private String name;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Test.class;
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("name");
Annotation[] fieldAnnotions = field.getDeclaredAnnotations();
MyAnnotation annotation =
(MyAnnotation) field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
}
} 위 내용은 09.Java Basics - Annotations 내용이며, 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 홈페이지(www.php)를 참고하시기 바랍니다. .cn)!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7467
7467
 15
15
 1376
1376
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 48
48
 19
19
 19
19
 22
22
 Java의 난수 생성기
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Java의 난수 생성기
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Java의 난수 생성기 안내. 여기서는 예제를 통해 Java의 함수와 예제를 통해 두 가지 다른 생성기에 대해 설명합니다.
 자바의 웨카
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
자바의 웨카
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Java의 Weka 가이드. 여기에서는 소개, weka java 사용 방법, 플랫폼 유형 및 장점을 예제와 함께 설명합니다.
 Java의 스미스 번호
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Java의 스미스 번호
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Java의 Smith Number 가이드. 여기서는 정의, Java에서 스미스 번호를 확인하는 방법에 대해 논의합니다. 코드 구현의 예.
 Java Spring 인터뷰 질문
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring 인터뷰 질문
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
이 기사에서는 가장 많이 묻는 Java Spring 면접 질문과 자세한 답변을 보관했습니다. 그래야 면접에 합격할 수 있습니다.
 Java 8 Stream foreach에서 나누거나 돌아 오시겠습니까?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 Stream foreach에서 나누거나 돌아 오시겠습니까?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8은 스트림 API를 소개하여 데이터 컬렉션을 처리하는 강력하고 표현적인 방법을 제공합니다. 그러나 스트림을 사용할 때 일반적인 질문은 다음과 같은 것입니다. 기존 루프는 조기 중단 또는 반환을 허용하지만 스트림의 Foreach 메소드는이 방법을 직접 지원하지 않습니다. 이 기사는 이유를 설명하고 스트림 처리 시스템에서 조기 종료를 구현하기위한 대체 방법을 탐색합니다. 추가 읽기 : Java Stream API 개선 스트림 foreach를 이해하십시오 Foreach 메소드는 스트림의 각 요소에서 하나의 작업을 수행하는 터미널 작동입니다. 디자인 의도입니다
 Java의 날짜까지의 타임스탬프
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Java의 날짜까지의 타임스탬프
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Java의 TimeStamp to Date 안내. 여기서는 소개와 예제와 함께 Java에서 타임스탬프를 날짜로 변환하는 방법에 대해서도 설명합니다.






