Java에는 값 전달과 주소 전달이라는 두 가지 매개변수 전달 메커니즘이 있습니다.
기본 유형이 매개변수로 전달되면 이 복사본을 어떻게 변경하더라도 원래 값은 변경되지 않습니다. -값별.
객체를 매개변수로 전달하면 메모리에 있는 객체 주소의 복사본이 복사되어 매개변수에 전달됩니다.
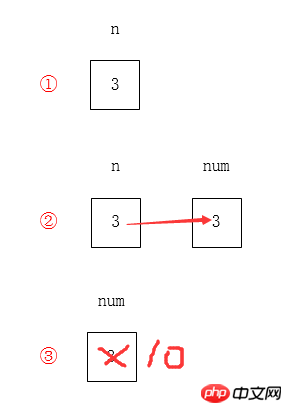
public static void main(String[] args) { int n =3; // ①
System.out.println(n); // 3
chageData(n); // ②
System.out.println(n); // 3}public static void chageData(int num){
num = 10; // ③}관찰 결과를 출력하고 n의 값이 변하지 않았는지 확인합니다.
n, num은 기본형이므로 변수에 값이 직접 저장됩니다.
흐름도는 다음과 같습니다(코드의 ①②③에 해당).
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello"; // ①
System.out.println(str); // hello
chageData(str); //②
System.out.println(str); // hello}public static void chageData(String s){
s ="world"; // ③}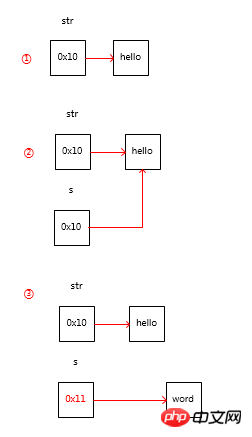
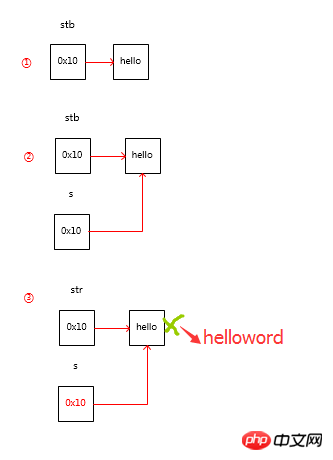
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer stb = new StringBuffer("hello"); // ①
System.out.println(stb); // hello
chageData(stb); // ②
System.out.println(stb); // hello world}public static void chageData(StringBuffer s){
s.append("world"); // ③}
}