
글 작성자: Xiaozhuzz 블로그 주소: http://www.php.cn/ 재인쇄할 경우 출처를 명시해 주세요
고성능 소켓 클라이언트 코드를 찾고 있었습니다. 과거에는 Socket 클래스를 사용하여 전통적인 비동기 프로그래밍 모델(BeginSend, BeginReceive 등)을 기반으로 일부 코드를 작성하고 이를 구현하기 위해 Linux에는 poll 및 epoll이 있으며 Windows에서는 많은 블로그 지식을 읽었습니다.
Microsoft MSDN IOCP를 구현하기 위해 SocketAsyncEventArgs 클래스도 제공됩니다. 주소: http://www.php.cn/
NET Framework의 APM은 Begin/End 모드라고도 합니다. 이는 Begin 메서드가 호출되어 비동기 작업을 시작한 다음 IAsyncResult 개체를 반환하기 때문입니다. 선택적으로 비동기 작업이 완료될 때 호출되는 Begin 메서드에 대한 매개 변수로 프록시를 제공할 수 있습니다. 또는 스레드가 IAsyncResult.AsyncWaitHandle을 기다릴 수 있습니다. 콜백이 호출되거나 대기 신호가 발생하면 End 메서드가 호출되어 비동기 작업의 결과를 얻습니다. 이 패턴은 유연하고 비교적 사용이 간단하며 .NET Framework에서 매우 일반적입니다.
그러나 비동기 소켓 작업을 많이 수행하면 지불해야 하는 대가가 있다는 점을 명심해야 합니다. 각 작업에 대해 IAsyncResult 객체를 생성해야 하며 해당 객체는 재사용할 수 없습니다. 이는 객체 할당 및 가비지 수집의 과도한 사용으로 인해 성능에 영향을 미칩니다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 새 버전에서는 소켓을 사용하여 비동기 I/O를 수행하는 또 다른 메서드 패턴을 제공합니다. 이 새로운 모델에서는 각 소켓 작업에 대해 작업 컨텍스트 개체를 할당할 필요가 없습니다.
코드 다운로드: http://www.php.cn/ 여기 코드는
위의 Microsoft에서 제공한 예제는 별로인 것 같습니다. 완료. 특별한 프로세스는 없고 클라이언트 메시지를 받은 후 동일한 내용을 클라이언트에 보냅니다. 완전한 기능을 갖춘 IOCP 서버를 구현하는 데 하루가 걸렸기 때문에 초보자가 프로세스를 이해하기가 쉽지 않습니다.
효과는 다음과 같습니다
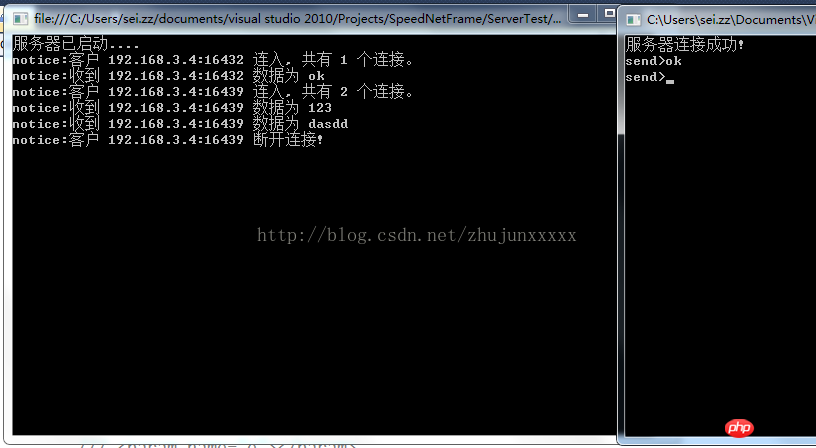
첫번째는 ICOPServer.cs 입니다. 이 클래스는 IOCP 서버의 핵심 클래스입니다. 현재 이 클래스는 인터넷에서 상대적으로 완전한 코드입니다. MSDN의 어떤 예제도 내
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Net;
using System.Threading;
namespace ServerTest
{
/// <summary>
/// IOCP SOCKET服务器
/// </summary>
public class IOCPServer : IDisposable
{
const int opsToPreAlloc = 2;
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// 服务器程序允许的最大客户端连接数
/// </summary>
private int _maxClient;
/// <summary>
/// 监听Socket,用于接受客户端的连接请求
/// </summary>
private Socket _serverSock;
/// <summary>
/// 当前的连接的客户端数
/// </summary>
private int _clientCount;
/// <summary>
/// 用于每个I/O Socket操作的缓冲区大小
/// </summary>
private int _bufferSize = 1024;
/// <summary>
/// 信号量
/// </summary>
Semaphore _maxAcceptedClients;
/// <summary>
/// 缓冲区管理
/// </summary>
BufferManager _bufferManager;
/// <summary>
/// 对象池
/// </summary>
SocketAsyncEventArgsPool _objectPool;
private bool disposed = false;
#endregion
#region Properties
/// <summary>
/// 服务器是否正在运行
/// </summary>
public bool IsRunning { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// 监听的IP地址
/// </summary>
public IPAddress Address { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// 监听的端口
/// </summary>
public int Port { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// 通信使用的编码
/// </summary>
public Encoding Encoding { get; set; }
#endregion
#region Ctors
/// <summary>
/// 异步IOCP SOCKET服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="listenPort">监听的端口</param>
/// <param name="maxClient">最大的客户端数量</param>
public IOCPServer(int listenPort,int maxClient)
: this(IPAddress.Any, listenPort, maxClient)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 异步Socket TCP服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="localEP">监听的终结点</param>
/// <param name="maxClient">最大客户端数量</param>
public IOCPServer(IPEndPoint localEP, int maxClient)
: this(localEP.Address, localEP.Port,maxClient)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 异步Socket TCP服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="localIPAddress">监听的IP地址</param>
/// <param name="listenPort">监听的端口</param>
/// <param name="maxClient">最大客户端数量</param>
public IOCPServer(IPAddress localIPAddress, int listenPort, int maxClient)
{
this.Address = localIPAddress;
this.Port = listenPort;
this.Encoding = Encoding.Default;
_maxClient = maxClient;
_serverSock = new Socket(localIPAddress.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
_bufferManager = new BufferManager(_bufferSize * _maxClient * opsToPreAlloc,_bufferSize);
_objectPool = new SocketAsyncEventArgsPool(_maxClient);
_maxAcceptedClients = new Semaphore(_maxClient, _maxClient);
}
#endregion
#region 初始化
/// <summary>
/// 初始化函数
/// </summary>
public void Init()
{
// Allocates one large byte buffer which all I/O operations use a piece of. This gaurds
// against memory fragmentation
_bufferManager.InitBuffer();
// preallocate pool of SocketAsyncEventArgs objects
SocketAsyncEventArgs readWriteEventArg;
for (int i = 0; i < _maxClient; i++)
{
//Pre-allocate a set of reusable SocketAsyncEventArgs
readWriteEventArg = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
readWriteEventArg.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnIOCompleted);
readWriteEventArg.UserToken = null;
// assign a byte buffer from the buffer pool to the SocketAsyncEventArg object
_bufferManager.SetBuffer(readWriteEventArg);
// add SocketAsyncEventArg to the pool
_objectPool.Push(readWriteEventArg);
}
}
#endregion
#region Start
/// <summary>
/// 启动
/// </summary>
public void Start()
{
if (!IsRunning)
{
Init();
IsRunning = true;
IPEndPoint localEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(Address, Port);
// 创建监听socket
_serverSock = new Socket(localEndPoint.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
//_serverSock.ReceiveBufferSize = _bufferSize;
//_serverSock.SendBufferSize = _bufferSize;
if (localEndPoint.AddressFamily == AddressFamily.InterNetworkV6)
{
// 配置监听socket为 dual-mode (IPv4 & IPv6)
// 27 is equivalent to IPV6_V6ONLY socket option in the winsock snippet below,
_serverSock.SetSocketOption(SocketOptionLevel.IPv6, (SocketOptionName)27, false);
_serverSock.Bind(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.IPv6Any, localEndPoint.Port));
}
else
{
_serverSock.Bind(localEndPoint);
}
// 开始监听
_serverSock.Listen(this._maxClient);
// 在监听Socket上投递一个接受请求。
StartAccept(null);
}
}
#endregion
#region Stop
/// <summary>
/// 停止服务
/// </summary>
public void Stop()
{
if (IsRunning)
{
IsRunning = false;
_serverSock.Close();
//TODO 关闭对所有客户端的连接
}
}
#endregion
#region Accept
/// <summary>
/// 从客户端开始接受一个连接操作
/// </summary>
private void StartAccept(SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar)
{
if (asyniar == null)
{
asyniar = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
asyniar.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnAcceptCompleted);
}
else
{
//socket must be cleared since the context object is being reused
asyniar.AcceptSocket = null;
}
_maxAcceptedClients.WaitOne();
if (!_serverSock.AcceptAsync(asyniar))
{
ProcessAccept(asyniar);
//如果I/O挂起等待异步则触发AcceptAsyn_Asyn_Completed事件
//此时I/O操作同步完成,不会触发Asyn_Completed事件,所以指定BeginAccept()方法
}
}
/// <summary>
/// accept 操作完成时回调函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Object who raised the event.</param>
/// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed accept operation.</param>
private void OnAcceptCompleted(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
ProcessAccept(e);
}
/// <summary>
/// 监听Socket接受处理
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed accept operation.</param>
private void ProcessAccept(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
Socket s = e.AcceptSocket;//和客户端关联的socket
if (s.Connected)
{
try
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref _clientCount);//原子操作加1
SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar = _objectPool.Pop();
asyniar.UserToken = s;
Log4Debug(String.Format("客户 {0} 连入, 共有 {1} 个连接。", s.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), _clientCount));
if (!s.ReceiveAsync(asyniar))//投递接收请求
{
ProcessReceive(asyniar);
}
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
Log4Debug(String.Format("接收客户 {0} 数据出错, 异常信息: {1} 。", s.RemoteEndPoint, ex.ToString()));
//TODO 异常处理
}
//投递下一个接受请求
StartAccept(e);
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 发送数据
/// <summary>
/// 异步的发送数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e"></param>
/// <param name="data"></param>
public void Send(SocketAsyncEventArgs e, byte[] data)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
Socket s = e.AcceptSocket;//和客户端关联的socket
if (s.Connected)
{
Array.Copy(data, 0, e.Buffer, 0, data.Length);//设置发送数据
//e.SetBuffer(data, 0, data.Length); //设置发送数据
if (!s.SendAsync(e))//投递发送请求,这个函数有可能同步发送出去,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件
{
// 同步发送时处理发送完成事件
ProcessSend(e);
}
else
{
CloseClientSocket(e);
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 同步的使用socket发送数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="socket"></param>
/// <param name="buffer"></param>
/// <param name="offset"></param>
/// <param name="size"></param>
/// <param name="timeout"></param>
public void Send(Socket socket, byte[] buffer, int offset, int size, int timeout)
{
socket.SendTimeout = 0;
int startTickCount = Environment.TickCount;
int sent = 0; // how many bytes is already sent
do
{
if (Environment.TickCount > startTickCount + timeout)
{
//throw new Exception("Timeout.");
}
try
{
sent += socket.Send(buffer, offset + sent, size - sent, SocketFlags.None);
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
if (ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.WouldBlock ||
ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.IOPending ||
ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.NoBufferSpaceAvailable)
{
// socket buffer is probably full, wait and try again
Thread.Sleep(30);
}
else
{
throw ex; // any serious error occurr
}
}
} while (sent < size);
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送完成时处理函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">与发送完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void ProcessSend(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken;
//TODO
}
else
{
CloseClientSocket(e);
}
}
#endregion
#region 接收数据
/// <summary>
///接收完成时处理函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">与接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void ProcessReceive(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)//if (e.BytesTransferred > 0 && e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
// 检查远程主机是否关闭连接
if (e.BytesTransferred > 0)
{
Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken;
//判断所有需接收的数据是否已经完成
if (s.Available == 0)
{
//从侦听者获取接收到的消息。
//String received = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(e.Buffer, e.Offset, e.BytesTransferred);
//echo the data received back to the client
//e.SetBuffer(e.Offset, e.BytesTransferred);
byte[] data = new byte[e.BytesTransferred];
Array.Copy(e.Buffer, e.Offset, data, 0, data.Length);//从e.Buffer块中复制数据出来,保证它可重用
string info=Encoding.Default.GetString(data);
Log4Debug(String.Format("收到 {0} 数据为 {1}",s.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(),info));
//TODO 处理数据
//增加服务器接收的总字节数。
}
if (!s.ReceiveAsync(e))//为接收下一段数据,投递接收请求,这个函数有可能同步完成,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件
{
//同步接收时处理接收完成事件
ProcessReceive(e);
}
}
}
else
{
CloseClientSocket(e);
}
}
#endregion
#region 回调函数
/// <summary>
/// 当Socket上的发送或接收请求被完成时,调用此函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">激发事件的对象</param>
/// <param name="e">与发送或接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void OnIOCompleted(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
// Determine which type of operation just completed and call the associated handler.
switch (e.LastOperation)
{
case SocketAsyncOperation.Accept:
ProcessAccept(e);
break;
case SocketAsyncOperation.Receive:
ProcessReceive(e);
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentException("The last operation completed on the socket was not a receive or send");
}
}
#endregion
#region Close
/// <summary>
/// 关闭socket连接
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed send/receive operation.</param>
private void CloseClientSocket(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
Log4Debug(String.Format("客户 {0} 断开连接!",((Socket)e.UserToken).RemoteEndPoint.ToString()));
Socket s = e.UserToken as Socket;
CloseClientSocket(s, e);
}
/// <summary>
/// 关闭socket连接
/// </summary>
/// <param name="s"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void CloseClientSocket(Socket s, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
try
{
s.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Send);
}
catch (Exception)
{
// Throw if client has closed, so it is not necessary to catch.
}
finally
{
s.Close();
}
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _clientCount);
_maxAcceptedClients.Release();
_objectPool.Push(e);//SocketAsyncEventArg 对象被释放,压入可重用队列。
}
#endregion
#region Dispose
/// <summary>
/// Performs application-defined tasks associated with freeing,
/// releasing, or resetting unmanaged resources.
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
/// <summary>
/// Releases unmanaged and - optionally - managed resources
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing"><c>true</c> to release
/// both managed and unmanaged resources; <c>false</c>
/// to release only unmanaged resources.</param>
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!this.disposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
try
{
Stop();
if (_serverSock != null)
{
_serverSock = null;
}
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
//TODO 事件
}
}
disposed = true;
}
}
#endregion
public void Log4Debug(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine("notice:"+msg);
}
}
}
BufferManager.cs만큼 완벽하지 않습니다. 이 클래스는 캐시 관리 클래스입니다. MSDN의 예제와 동일한 주소를 사용합니다: http://www .php.cn/
SocketAsyncEventArgsPool.cs 이 클래스는 MSDN 주소: http://www.php.cn/<에도 있습니다. 🎜>
필요하시면 MSDN 홈페이지에 가서 직접 구하세요. 게시하지 않겠습니다static void Main(string[] args)
{
IOCPServer server = new IOCPServer(8088, 1024);
server.Start();
Console.WriteLine("服务器已启动....");
System.Console.ReadLine();
}static void Main(string[] args)
{
IPAddress remote=IPAddress.Parse("192.168.3.4");
client c = new client(8088,remote);
c.connect();
Console.WriteLine("服务器连接成功!");
while (true)
{
Console.Write("send>");
string msg=Console.ReadLine();
if (msg == "exit")
break;
c.send(msg);
}
c.disconnect();
Console.ReadLine();
}public class client
{
public TcpClient _client;
public int port;
public IPAddress remote;
public client(int port,IPAddress remote)
{
this.port = port;
this.remote = remote;
}
public void connect()
{
this._client=new TcpClient();
_client.Connect(remote, port);
}
public void disconnect()
{
_client.Close();
}
public void send(string msg)
{
byte[] data=Encoding.Default.GetBytes(msg);
_client.GetStream().Write(data, 0, data.Length);
}
}IOCPClient 클래스,
SocketAsyncEventArgs 클래스를 사용하여 소켓 클라이언트를 생성합니다. MSDN에서는 이 클래스가 웹 서버 응용 프로그램용으로 특별히 설계되었다고 말하지만 클라이언트 코드에서 APM을 사용하는 데에는 제한이 없습니다. IOCCPlient 클래스의 샘플 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
public class IOCPClient
{
/// <summary>
/// 连接服务器的socket
/// </summary>
private Socket _clientSock;
/// <summary>
/// 用于服务器执行的互斥同步对象
/// </summary>
private static Mutex mutex = new Mutex();
/// <summary>
/// Socket连接标志
/// </summary>
private Boolean _connected = false;
private const int ReceiveOperation = 1, SendOperation = 0;
private static AutoResetEvent[]
autoSendReceiveEvents = new AutoResetEvent[]
{
new AutoResetEvent(false),
new AutoResetEvent(false)
};
/// <summary>
/// 服务器监听端点
/// </summary>
private IPEndPoint _remoteEndPoint;
public IOCPClient(IPEndPoint local,IPEndPoint remote)
{
_clientSock = new Socket(local.AddressFamily,SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
_remoteEndPoint = remote;
}
#region 连接服务器
/// <summary>
/// 连接远程服务器
/// </summary>
public void Connect()
{
SocketAsyncEventArgs connectArgs = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
connectArgs.UserToken = _clientSock;
connectArgs.RemoteEndPoint = _remoteEndPoint;
connectArgs.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnConnected);
mutex.WaitOne();
if (!_clientSock.ConnectAsync(connectArgs))//异步连接
{
ProcessConnected(connectArgs);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 连接上的事件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
void OnConnected(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
//设置Socket已连接标志。
_connected = (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success);
}
/// <summary>
/// 处理连接服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void ProcessConnected(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
//TODO
}
#endregion
#region 发送消息
/// <summary>
/// 向服务器发送消息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data"></param>
public void Send(byte[] data)
{
SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
asyniar.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnSendComplete);
asyniar.SetBuffer(data, 0, data.Length);
asyniar.UserToken = _clientSock;
asyniar.RemoteEndPoint = _remoteEndPoint;
autoSendReceiveEvents[SendOperation].WaitOne();
if (!_clientSock.SendAsync(asyniar))//投递发送请求,这个函数有可能同步发送出去,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件
{
// 同步发送时处理发送完成事件
ProcessSend(asyniar);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送操作的回调方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void OnSendComplete(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
//发出发送完成信号。
autoSendReceiveEvents[SendOperation].Set();
ProcessSend(e);
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送完成时处理函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">与发送完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void ProcessSend(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
//TODO
}
#endregion
#region 接收消息
/// <summary>
/// 开始监听服务端数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e"></param>
public void StartRecive(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
//准备接收。
Socket s = e.UserToken as Socket;
byte[] receiveBuffer = new byte[255];
e.SetBuffer(receiveBuffer, 0, receiveBuffer.Length);
e.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnReceiveComplete);
autoSendReceiveEvents[ReceiveOperation].WaitOne();
if (!s.ReceiveAsync(e))
{
ProcessReceive(e);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 接收操作的回调方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void OnReceiveComplete(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
//发出接收完成信号。
autoSendReceiveEvents[ReceiveOperation].Set();
ProcessReceive(e);
}
/// <summary>
///接收完成时处理函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e">与接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param>
private void ProcessReceive(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
// 检查远程主机是否关闭连接
if (e.BytesTransferred > 0)
{
Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken;
//判断所有需接收的数据是否已经完成
if (s.Available == 0)
{
byte[] data = new byte[e.BytesTransferred];
Array.Copy(e.Buffer, e.Offset, data, 0, data.Length);//从e.Buffer块中复制数据出来,保证它可重用
//TODO 处理数据
}
if (!s.ReceiveAsync(e))//为接收下一段数据,投递接收请求,这个函数有可能同步完成,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件
{
//同步接收时处理接收完成事件
ProcessReceive(e);
}
}
}
}
#endregion
public void Close()
{
_clientSock.Disconnect(false);
}
/// <summary>
/// 失败时关闭Socket,根据SocketError抛出异常。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void ProcessError(SocketAsyncEventArgs e)
{
Socket s = e.UserToken as Socket;
if (s.Connected)
{
//关闭与客户端关联的Socket
try
{
s.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
}
catch (Exception)
{
//如果客户端处理已经关闭,抛出异常
}
finally
{
if (s.Connected)
{
s.Close();
}
}
}
//抛出SocketException
throw new SocketException((Int32)e.SocketError);
}
/// <summary>
/// 释放SocketClient实例
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
mutex.Close();
autoSendReceiveEvents[SendOperation].Close();
autoSendReceiveEvents[ReceiveOperation].Close();
if (_clientSock.Connected)
{
_clientSock.Close();
}
}
}