CSS의 z-index에 대한 자세한 설명(2)
CSS의 z-index에 대한 자세한 설명. z-index가 없으면 결과는 어떻게 되나요? 편집자가 여러분을 살펴보도록 안내할 것입니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>z-index</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box1{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
top: 180px;
left: 180px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="box1">box1</p>
<p class="box2">box2</p>
</body>
</html>실행 결과:

box2가 box1 뒤에 있으므로 box2는 z-index를 설정하지 않고 box1을 억제합니다.
다음으로 부모현상이 무엇인지 살펴보겠습니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.p1{
position: relative;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
z-index: 10
}
.p1 .child1{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
top: 240px;
left: 300px;
z-index: 56;
background-color: green;
}
.p2{
position: relative;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color:red;
z-index: 20;
}
.p2 .child2{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
top: 100px;
left: 350px;
z-index: 5;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="p1">
<p class="child1"></p>
</p>
<p class="p2">
<p class="child2"></p>
</p>
</body>
</html>실행 결과:
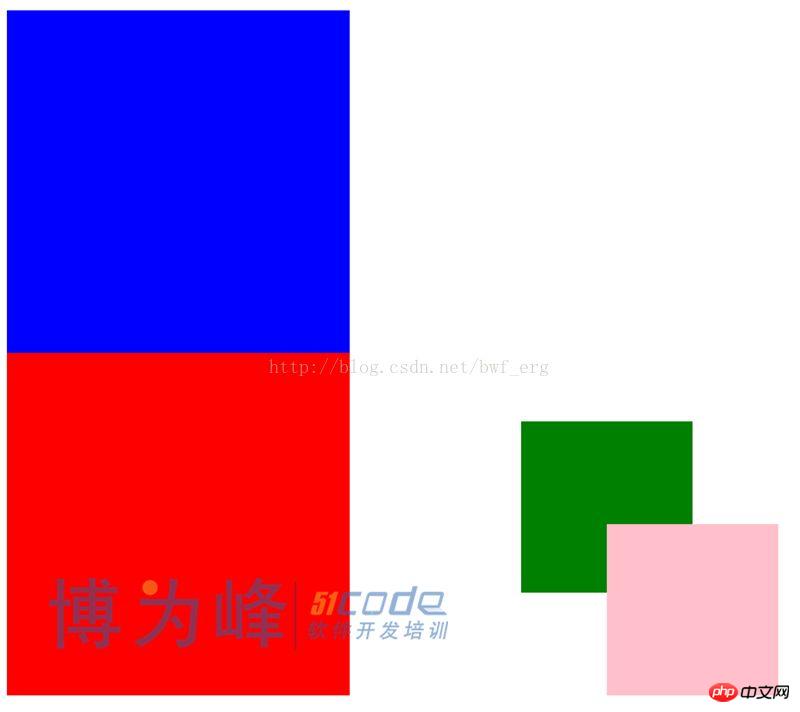
여기서 p2의 z-index를 p1의 z-index보다 작게 설정하고 z-index를 설정합니다. p1의 하위 요소 child1의 인덱스 인덱스는 p2의 하위 요소인 child2의 z-index보다 큽니다. 그러나 작업의 최종 결과는 child2가 child1을 억제한다는 것입니다. 이것이 아버지께 순종하는 현상이다. 이는 상위 요소가 억제된 경우입니다. 하위 요소는 억압되는 운명을 피할 수 없습니다. 하위 요소의 Z-색인 크기에 관계없이.
【관련 추천】
3. php.cn Dugu Jiujian (2) - CSS 비디오 튜토리얼
위 내용은 CSS의 z-index에 대한 자세한 설명(2)의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7345
7345
 15
15
 1627
1627
 14
14
 1352
1352
 52
52
 1265
1265
 25
25
 1214
1214
 29
29
 vue에서 자리 표시자는 무엇을 의미합니까?
May 07, 2024 am 09:57 AM
vue에서 자리 표시자는 무엇을 의미합니까?
May 07, 2024 am 09:57 AM
Vue.js에서 placeholder 속성은 사용자가 콘텐츠를 입력하지 않을 때 표시되는 입력 요소의 자리 표시자 텍스트를 지정하고 입력 팁이나 예제를 제공하며 양식 접근성을 향상시킵니다. 사용법은 입력 요소에 자리 표시자 속성을 설정하고 CSS를 사용하여 모양을 사용자 정의하는 것입니다. 모범 사례에는 입력과 관련성, 짧고 명확함, 기본 텍스트 방지, 접근성 고려 등이 포함됩니다.
 js에서 스팬은 무엇을 의미하나요?
May 06, 2024 am 11:42 AM
js에서 스팬은 무엇을 의미하나요?
May 06, 2024 am 11:42 AM
스팬 태그는 텍스트에 스타일, 속성 또는 동작을 추가할 수 있습니다. 색상 및 글꼴 크기와 같은 스타일을 추가하는 데 사용됩니다. ID, 클래스 등의 속성을 설정합니다. 클릭, 호버 등과 같은 관련 동작 추가 처리 또는 인용을 위해 텍스트를 표시합니다.
 js에서 rem은 무엇을 의미합니까?
May 06, 2024 am 11:30 AM
js에서 rem은 무엇을 의미합니까?
May 06, 2024 am 11:30 AM
CSS의 REM은 루트 요소(html)의 글꼴 크기에 상대적인 단위입니다. 여기에는 다음과 같은 특징이 있습니다. 루트 요소의 글꼴 크기를 기준으로 하며 상위 요소의 영향을 받지 않습니다. 루트 요소의 글꼴 크기가 변경되면 REM을 사용하는 요소가 그에 따라 조정됩니다. 모든 CSS 속성과 함께 사용할 수 있습니다. REM 사용의 장점은 다음과 같습니다. 반응성: 다양한 장치 및 화면 크기에서 텍스트를 읽을 수 있도록 유지합니다. 일관성: 웹사이트 전체에서 글꼴 크기가 일관되게 유지되어야 합니다. 확장성: 루트 요소 글꼴 크기를 조정하여 전역 글꼴 크기를 쉽게 변경할 수 있습니다.
 Vue에 이미지를 삽입하는 방법
May 02, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
Vue에 이미지를 삽입하는 방법
May 02, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
Vue에 이미지를 도입하는 방법에는 URL, 필수 함수, 정적 파일, v-bind 지시어 및 CSS 배경 이미지 등 5가지 방법이 있습니다. 동적 이미지는 Vue의 계산된 속성이나 리스너에서 처리할 수 있으며, 번들 도구를 사용하여 이미지 로딩을 최적화할 수 있습니다. 경로가 올바른지 확인하세요. 그렇지 않으면 로딩 오류가 나타납니다.
 js의 노드 란 무엇입니까?
May 07, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
js의 노드 란 무엇입니까?
May 07, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
노드는 HTML 요소를 나타내는 JavaScript DOM의 엔터티입니다. 이는 페이지의 특정 요소를 나타내며 해당 요소에 액세스하고 조작하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다. 일반적인 노드 유형에는 요소 노드, 텍스트 노드, 주석 노드 및 문서 노드가 포함됩니다. getElementById()와 같은 DOM 메서드를 통해 노드에 액세스하고 속성 수정, 하위 노드 추가/제거, 노드 삽입/교체, 노드 복제 등의 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다. 노드 순회는 DOM 구조 내에서 탐색하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 노드는 페이지 콘텐츠, 이벤트 처리, 애니메이션 및 데이터 바인딩을 동적으로 생성하는 데 유용합니다.
 브라우저 플러그인은 어떤 언어로 작성되어 있나요?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
브라우저 플러그인은 어떤 언어로 작성되어 있나요?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
브라우저 플러그인은 일반적으로 다음 언어로 작성됩니다. 프런트엔드 언어: JavaScript, HTML, CSS 백엔드 언어: C++, Rust, WebAssembly 기타 언어: Python, Java
 vue의 ref와 id는 무엇을 합니까?
May 02, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
vue의 ref와 id는 무엇을 합니까?
May 02, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
Vue.js에서 ref는 JavaScript에서 DOM 요소(하위 구성 요소 및 DOM 요소 자체에 액세스 가능)를 참조하는 데 사용되는 반면 id는 HTML id 속성(CSS 스타일, HTML 마크업 및 JavaScript 조회에 사용할 수 있음)을 설정하는 데 사용됩니다. ).
 알 수 없는 속성을 설정하기 위해 vscode vscode 메소드에서 알 수 없는 속성을 설정하는 방법
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
알 수 없는 속성을 설정하기 위해 vscode vscode 메소드에서 알 수 없는 속성을 설정하는 방법
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
1. 먼저 왼쪽 하단에 있는 설정 아이콘을 열고 설정 옵션을 클릭합니다. 2. 그런 다음 점프된 창에서 CSS 열을 찾습니다. 3. 마지막으로 알 수 없는 속성 메뉴의 드롭다운 옵션을 오류 버튼으로 변경합니다. .




