이 기사에서는 주로 Java에서 인터페이스 구현 방법을 동적으로 생성하는 방법에 대한 정보를 소개합니다. 필요한 친구는 이를 참조할 수 있습니다.
다음은 몇 가지 일반적인 응용 프로그램입니다. 1, mybatis/jpa 및 기타 ORM 프레임워크에서는 개발을 위해 인터페이스에 주석을 추가할 수 있으며 구현 클래스를 작성할 필요가 없으며 구현은 런타임에 동적으로 생성됩니다.
2.dubbo와 같은 분산 서비스 프레임워크에서 소비자는 원격 구현을 호출하기 위해 인터페이스를 도입하기만 하면 됩니다. 실제로 소스 코드를 분석한 후 인터페이스의 프록시 구현이 소비자 측에서 생성됩니다. 프록시는 원격 인터페이스를 호출합니다.
3. spring aop 가장 일반적인 동적 프록시입니다.
인터페이스의 동적 구현을 만드는 데 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 두 가지 방법은 JDK 동적 프록시와 CGLIB 동적 프록시입니다.
프록시 패턴은 일반적으로 사용되는 디자인 패턴으로, 그 목적은 실제 객체에 대한 액세스를 제어하기 위해 다른 객체에 대한 프록시를 제공하는 것입니다.
프록시 클래스는 대리자 클래스에 대한 메시지 전처리, 메시지 필터링 및 메시지 전달, 대리자 클래스에서 메시지를 실행한 후 후속 처리 수행을 담당합니다.
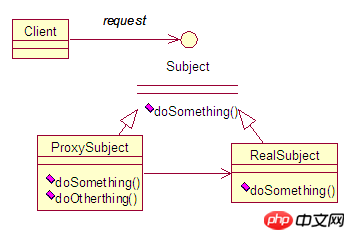 프록시 레이어의 중간 레이어를 통해 실제 대리자 클래스 객체에 대한 직접 액세스를 효과적으로 제어할 수 있으며 맞춤형 제어 전략(스프링의 AOP 메커니즘)을 구현하여 설계 유연성을 높일 수 있습니다.
프록시 레이어의 중간 레이어를 통해 실제 대리자 클래스 객체에 대한 직접 액세스를 효과적으로 제어할 수 있으며 맞춤형 제어 전략(스프링의 AOP 메커니즘)을 구현하여 설계 유연성을 높일 수 있습니다.
다음은 JDK 동적 프록시를 사용하고 이 프로세스를 보여주기 위한 몇 가지 간단한 코드를 추가합니다.
package com.yhouse.modules.daos;
public interface IUserDao {
public String getUserName();
}package com.yhouse.modules.daos;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 创建代理
* @author clonen.cheng
*
*/
public class Invoker {
public Object getInstance(Class<?> cls){
MethodProxy invocationHandler = new MethodProxy();
Object newProxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
cls.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { cls },
invocationHandler);
return (Object)newProxyInstance;
}
}package com.yhouse.modules.daos;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class MethodProxy implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//如果传进来是一个已实现的具体类(本次演示略过此逻辑)
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
//如果传进来的是一个接口(核心)
} else {
return run(method, args);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 实现接口的核心方法
* @param method
* @param args
* @return
*/
public Object run(Method method,Object[] args){
//TODO
//如远程http调用
//如远程方法调用(rmi)
//....
return "method call success!";
}
} 이 원리를 설명하기 위한 간단한 예는 이해를 돕기 위한 원격 인터페이스의 동적 호출의 또 다른 예입니다.
이 원리를 설명하기 위한 간단한 예는 이해를 돕기 위한 원격 인터페이스의 동적 호출의 또 다른 예입니다.
1. 프록시 클래스를 생성하고 대상 클래스는 공통 인터페이스 Service

package com.yhouse.modules.daos;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IUserDao invoker=(IUserDao)new Invoker().getInstance(IUserDao.class);
System.out.println(invoker.getUserName());
}
}2를 구현해야 합니다. 서버 측에서 RemoteService 클래스를 생성하고 서비스 인터페이스를 구현합니다.
package com.markliu.remote.service;
/**
* Service接口。代理类和被代理类抖需要实现该接口
*/
public interface Service {
public String getService(String name, int number);
}
객체 지향 방식으로 클라이언트와 서버 간의 통신을 용이하게 하기 위해 클라이언트가 보내는 정보는 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있습니다. 수업에 전화하세요. Call 객체는 호출 클래스 이름 또는 인터페이스 이름, 메소드 이름, 메소드 매개변수 유형, 메소드 매개변수 값 및 메소드 실행 결과를 포함하는 클라이언트가 시작한 원격 호출을 나타냅니다.
package com.markliu.remote.serviceimpl;
import com.markliu.remote.service.Service;
/**
* 服务器端目标业务类,被代理对象
*/
public class RemoteService implements Service {
@Override
public String getService(String name, int number) {
return name + ":" + number;
}
}package com.markliu.local.bean;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 请求的javabean
*/
public class Call implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5386052199960133937L;
private String className; // 调用的类名或接口名
private String methodName; // 调用的方法名
private Class<?>[] paramTypes; // 方法参数类型
private Object[] params; // 调用方法时传入的参数值
/**
* 表示方法的执行结果 如果方法正常执行,则 result 为方法返回值,
* 如果方法抛出异常,那么 result 为该异常。
*/
private Object result;
public Call() {}
public Call(String className, String methodName, Class<?>[] paramTypes, Object[] params) {
this.className = className;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.paramTypes = paramTypes;
this.params = params;
}
// 省略了get和set方法
}package com.markliu.local.service;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import com.markliu.local.bean.Call;
public class ServiceInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Class<?> classType;
private String host;
private Integer port;
public Class<?> getClassType() {
return classType;
}
public ServiceInvocationHandler(Class<?> classType, String host, Integer port) {
this.classType = classType;
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 封装请求信息
Call call = new Call(classType.getName(), method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes(), args);
// 创建链接
Connector connector = new Connector();
connector.connect(host, port);
// 发送请求
connector.sendCall(call);
// 获取封装远程方法调用结果的对象
connector.close();
Object returnResult = call.getResult();
return returnResult;
}
}package com.markliu.local.service;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 动态创建RemoteService代理类的工厂
*/
public class RemoteServiceProxyFactory {
public static Object getRemoteServiceProxy(InvocationHandler h) {
Class<?> classType = ((ServiceInvocationHandler) h).getClassType();
// 获取动态代理类
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classType.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{classType}, h);
return proxy;
}
}package com.markliu.local.service;
// 省略import
/**
* 负责创建链接
*/
public class Connector {
private Socket linksocket;
private InputStream in;
private ObjectInputStream objIn;
private OutputStream out;
private ObjectOutputStream objOut;
public Connector(){}
/**
* 创建链接
*/
public void connect(String host, Integer port) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
linksocket = new Socket(host, port);
in = linksocket.getInputStream();
out = linksocket.getOutputStream();
objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
objIn = new ObjectInputStream(in);
}
/**
* 发送请求call对象
*/
public void sendCall(Call call) throws IOException {
objOut.writeObject(call);
}
/**
* 获取请求对象
*/
public Call receive() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
return (Call) objIn.readObject();
}
/**
* 简单处理关闭链接
*/
public void close() {
try {
linksocket.close();
objIn.close();
objOut.close();
in.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}package com.markliu.remote.main;
// 省略import
public class RemoteServer {
private Service remoteService;
public RemoteServer() {
remoteService = new RemoteService();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RemoteServer server = new RemoteServer();
System.out.println("远程服务器启动......DONE!");
server.service();
}
public void service() throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8001);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream(in);
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
// 对象输入流读取请求的call对象
Call call = (Call) objIn.readObject();
System.out.println("客户端发送的请求对象:" + call);
call = getCallResult(call);
// 发送处理的结果回客户端
objOut.writeObject(call);
objIn.close();
in.close();
objOut.close();
out.close();
socket.close();
}
}
/**
* 通过反射机制调用call中指定的类的方法,并将返回结果设置到原call对象中
*/
private Call getCallResult(Call call) throws Exception {
String className = call.getClassName();
String methodName = call.getMethodName();
Object[] params = call.getParams();
Class<?>[] paramsTypes = call.getParamTypes();
Class<?> classType = Class.forName(className);
// 获取所要调用的方法
Method method = classType.getMethod(methodName, paramsTypes);
Object result = method.invoke(remoteService, params);
call.setResult(result);
return call;
}
}위 내용은 Java에서 인터페이스를 동적으로 생성하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!